What Are Email Headers? An email header is a fragment of code that contains the information needed to verify an email message. Avoiding phishing attempts is as simple as checking the verification results before following a link in a message. Headers always precede the body of an email.
Additionally, understanding email headers aid in the launch of email campaigns. By sending test emails and checking their headers, you may figure out what email security to add to keep communications from ending up in the spam bin.
The processes for viewing an email header are nearly identical across all email services. There are, however, some changes in the first stage.
What is a Header in Email?
An email header is more than just the to, from, date, and subject lines that appear before the body of the email. Because every email message has an email header, headers are also important for tracking an email’s journey.
When sending an email from one address to another, it will pass via mail transfer agents (MTA). As a result, email headers will reveal whether the email was sent to other email addresses before reaching its intended recipient. Users should not open the email if the header information is introduced to be suspicious.
Headers give information about the data transmission by utilizing metadata.
Get exclusive access to all things tech-savvy, and be the first to receive
the latest updates directly in your inbox.
Emails are made up of three primary parts:
- Header: Email headers are unique sets of information that include important information for mail delivery.
- Body: The email’s body comprises the content and attachments of your message.
- Envelope: The email provider and outgoing server employ the envelope, which is invisible to both the sender and the destination, to connect and transmit the intended message email account.
Some email header features (metadata) are reachable from the top of the email, but you must access your custom header separately.
You can see which servers, ISPs, and email services the message passed through by looking at the email headers. You may quickly determine whether the email transfer was secure and whether it arrived at its desired target without faults or modifications.
Why do you Need an Email Header?
Spam is Protected by Email Headers.
The header contains many fields that enable email service providers (ESPs) to distinguish between spam and legitimate emails. The header information is analyzed by ESPs to assess whether the message is legitimate and should be delivered to the intended recipient.
These ESP methods guard your email account and personal information against phishing and spam communications.
The Sender/Receiver Information is Clarified in the Message Header.
The From (message origin) and To fields are seen in every email header. There’s also a Subject box and a Date indicator, which show when a new message was delivered and at what time.
You wouldn’t be able to view origin details or identify the email’s sender or receivers without the info from the message header, and you might not be able to tell if the message body (email body) includes legitimate information without it.
Email Headers Aid in the Tracking of an Email’s Path.
When a user sends an email message, it starts with a sending mail server and travels via many Mail Transfer Agents (MTAs) finally arriving at the intended destination.
The mail server automatically “stamps” this new message with custom header lines like the receiver, date, and time of the letter as it travels through an MTA.
This header information will assist the recipient in tracking the email’s path to its destination by allowing them to examine all of the MTAs the email traveled through on its way there. When trying to check message source details and actually track down the origin of harmful and spam emails, this is helpful.

Metadata of an email header
Metadata is a type of organized reference information that aids in the classification and identification of data attributes. The information about your communications that may be discovered in email headers is referred to as email metadata.
The code is up until the tag is included in an email header. The following is a list of what can be found in any email header.
- From: Contains information about the sender. Keep in mind that phishing scammers and spammers frequently use false email addresses in this section.
- To: Displays the email address and name of the recipient. Email addresses in the “carbon copy” (CC) and “blind carbon copy” (BCC) boxes are also included.
- Date: Indicates when the email was sent. This date is usually displayed in the format day, dd month, yyyy hh:mm:ss in email clients.
- Return-Path: This is a required component that specifies the email address to which the machine will send its message. It will be used as the email address for receivers to respond to if no reply-to address is given.
- Envelope-to: This specifies that an email was sent to the address supplied on this line.
- Subject: The title or subject described by the correspondent in the subject line is included in the subject.
- Message-ID: When you write a message, you establish a unique string of characters and numbers called a message-ID. Although each message has an id Number, be aware that cybercriminals can make minor changes to this field.
- MIME-version: MIME-version is an acronym that stands for Multi-Purpose Internet Mail Extensions. It’s an addition to the online email protocol that allows you to transmit and receive many forms of data files such as photographs, audio, and video via the internet, as the name implies.
- The Content-type: This field indicates whether the email is sent in text or HTML format. If you have an image or video, it will also appear.
- DomainKeys and DomainKeys Identified Mail (DKIM) Signatures: DomainKeys and DomainKeys Identified Mail (DKIM) signatures let email providers recognize and authenticate messages by associating the domain name with the email.
- X-Spam-Status: This tells you if an email is spam or not. The exact numerical score is also displayed. It will say “no” if it is not spammed.
- X-Spam-Level: SpamAssassin scores are denoted by asterix (*). It is beneficial to receive fewer stars since each star represents a step forward.
- Message Body: The primary content of the email is displayed in this field.
How to read an email header?
Depending on the email service provider, the layout and techniques for reading an email header differ (ESP). Examine it by looking at the email header and looking for the lines that interest you.
Gmail’s Email Headers
Gmail is one of the most popular online email services, with over 1.5 billion active users globally. It’s no surprise that Google constantly adds new features and capabilities to Gmail.
Select the Gmail message that contains the header you would like to view in your client.
Once you see the message body, click on the three dots beside the “Reply” button to access the kebab menu.
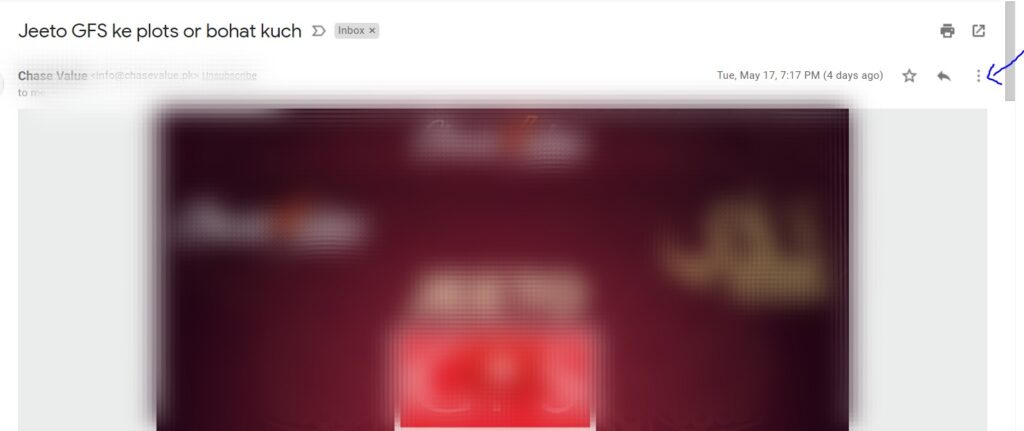
In the dropdown menu, select “Show Original”.
The longer header will appear in its original HTML format in a new window. Details about headers such as authentication statuses, IP addresses, MIME versions, and DKIM signatures can be viewed.
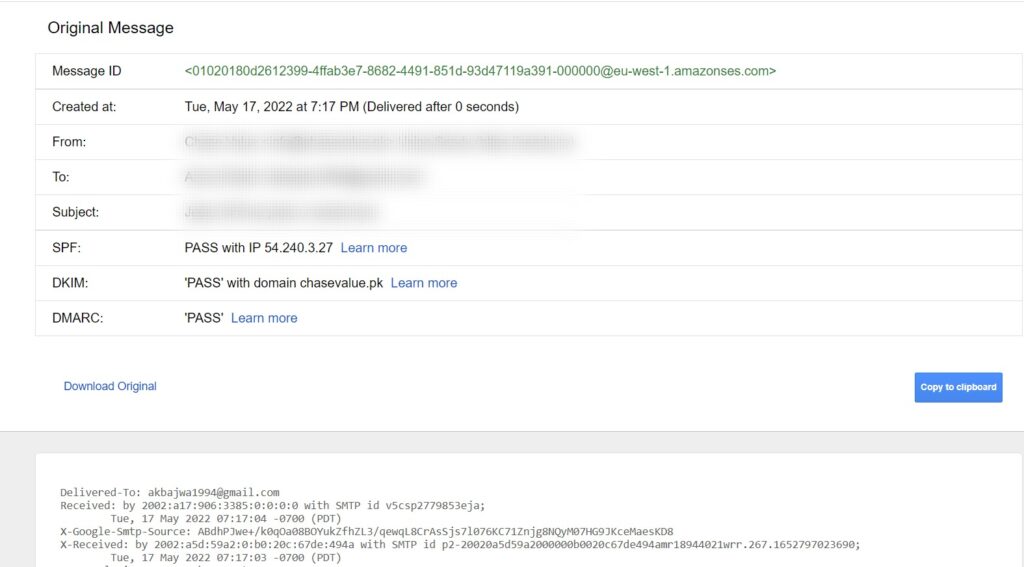
In order to install and view the header data individually, click on “Download Original”. Alternatively, you may email the header data to your tech support team.
View Email Header in Outlook
Method 1: Using the Ribbon
- Open Outlook: Launch Microsoft Outlook on your computer.
- Select the Email: Go to the Inbox or any other folder where you received the email whose header you want to view.
- Double-Click the Email: Open the email by double-clicking on it.
- Navigate to the Message Options: Once the email is open, go to the “Message” tab in the ribbon at the top of the window.
- Find the “More Options” Group: Within the “Message” tab, you’ll find a group called “Tags,” and within that group, there’s a “More Options” button. Click on it.
- View the Internet Headers: In the “Message Options” dialog box, you’ll see a section called “Internet Headers.” This section contains the technical details of the email. You can copy and paste this information if needed.
Method 2: Using Right-Click
- Open Outlook: Launch Microsoft Outlook.
- Select the Email: Locate the email you want to check the headers for in your inbox or another folder.
- Right-Click on the Email: Right-click on the email to bring up a context menu.
- Choose “Message Options”: From the context menu, select “Message Options.” This will open a dialog box with the email’s headers.
- View the Internet Headers: In the “Message Options” dialog box, you’ll see the “Internet Headers” section containing the technical information about the email.
Remember that the headers might look a bit cryptic if you’re not familiar with email protocols, but they can be useful for diagnosing issues, verifying the origin of an email, and checking for signs of spam or phishing attempts.
It’s important to note that the steps may vary slightly depending on the version of Outlook you’re using, but generally, these methods should work for most versions of Outlook. Viewing email headers can be particularly useful for advanced users or when troubleshooting email-related problems.
View Apple iCloud Email Headers
Of course, I’d be glad to explain how you can view email headers in Apple iCloud mail!
Method: Using Apple Mail on Mac
- Open Apple Mail: Launch the Apple Mail application on your Mac computer.
- Select the Email: Find the email for which you want to see the headers and click on it to open it.
- Access the Menu: From the top menu, click on “View.”
- Show Headers: In the “View” menu, hover over “Message” to reveal a submenu, and then click on “All Headers.” This will display the extended headers for the email.
Method: Using iCloud Mail on Web
- Open Web Browser: Open any web browser on your computer.
- Sign in to iCloud: Go to the iCloud website (icloud.com) and log in with your Apple ID credentials.
- Open Email: Navigate to the “Mail” app within iCloud.
- Select Email: Click on the email you want to examine to open it.
- View Headers: In the open email, click on the small arrow next to the sender’s name. This should expand the header information, providing you with the technical details of the email.
Email Header Analyzers
Instead of manually searching through email headers, you can use a handy tool like MxToolbox or Mailheader.org. Just copy and paste the email header into the tool, then click “analyze.” These tools don’t just find key details for you; they might even show if the message was verified.
This way, you save time and effort while understanding important info about the email. It’s like having a detective help you without any complicated steps. Give it a try to make things simpler!
FAQS
1. What are email headers in Outlook?
Email headers in Outlook are hidden technical details within an email. They contain information about the sender, recipient, date, subject, and the path the email took through servers. These details can help verify the authenticity of the email and prevent phishing attacks.
How do I view email headers in Gmail?
To view email headers in Gmail, open the email, click on the three dots (More options), and choose “Show original.” This will display the email’s headers, revealing vital information about its source and route.
Why are email headers important for cybersecurity?
Email headers provide insights into an email’s origin, route, and authenticity. By analyzing these headers, users can identify potentially harmful emails, avoid phishing scams, and enhance their overall cybersecurity.
What information is included in an email header?
Email headers include sender and recipient addresses, timestamps, subject, server information, and routing details. They give a comprehensive view of an email’s journey from sender to recipient.
How can email header analysis prevent phishing attacks?
Analyzing email headers allows users to spot inconsistencies and irregularities in the email’s path and source. This can help identify forged emails, malicious links, and potentially harmful attachments commonly associated with phishing attacks.
Are email headers visible to recipients?
By default, email headers are usually hidden from recipients. They contain technical information that is not relevant to most users. However, users can access and view email headers if needed, often through the email client’s settings or options.
Can email headers be manipulated?
Yes, email headers can be manipulated by skilled individuals to falsify information about the sender or the email’s route. This is why it’s important to understand the structure of email headers and use reliable tools to verify their authenticity.
How do I analyze email headers for suspicious activity?
To analyze email headers, look for inconsistencies in the routing path, unexpected server names, or discrepancies in sender addresses. Using online email header analyzers or consulting IT professionals can aid in detecting suspicious activity.
Do email headers contain personal information?
Email headers typically do not contain personal content but rather technical information about the email’s transmission. Personal information is usually found within the email’s body and attachments.
How can I protect myself from email-based threats using email headers?
By learning how to interpret email headers, you can recognize potentially harmful emails and avoid falling victim to phishing attempts. Regularly check email headers before clicking on links or downloading attachments to ensure your online safety.
What information is in an Email Header Example?
An email header example holds essential details like the sender’s email address, recipient’s address, subject, and date. It also reveals the route the email took through different servers, which helps verify its authenticity. You’ll find technical info about the servers involved, like IP addresses and domain names. This hidden section provides a snapshot of the email’s journey and origin, aiding in identifying potential spam or phishing attempts.
Familiarizing yourself with these details can enhance your email security and protect you from cyber threats. Always remember to check the email header before taking any actions within the email.
What is Email Header for reply?
An email header example holds essential details like the sender’s email address, recipient’s address, subject, and date. It also reveals the route the email took through different servers, which helps verify its authenticity. You’ll find technical info about the servers involved, like IP addresses and domain names. This hidden section provides a snapshot of the email’s journey and origin, aiding in identifying potential spam or phishing attempts.
Familiarizing yourself with these details can enhance your email security and protect you from cyber threats. Always remember to check the email header before taking any actions within the email.
What is an email Header Value?
An email header value is a specific piece of information within an email header. It holds important details such as the sender’s email address, recipient’s email address, subject, date and time, and other technical information. These values provide essential context and information about the email’s origin, route, and content.
They are like pieces of a puzzle that help email clients and servers understand how to handle and display the email correctly. Interpreting these values can offer insights into the authenticity of the email and aid in identifying potential issues or security threats.
Email Header Size
Email header size refers to the amount of data that the header of an email message occupies. The header contains technical information about the email, including sender and recipient details, subject, timestamps, and routing information.
While the header itself is generally small compared to the overall email size, its length can vary based on factors like the number of recipients, the complexity of the routing path, and any additional metadata. The header size is a critical consideration for email efficiency, as larger headers can impact email delivery and storage, especially in cases of mass or automated sending.
Conclusion
Emails hold more than just the words you read – they also contain information about the sender and the person who should receive it. Additionally, like a trail of breadcrumbs, email headers reveal the path the message traveled through different servers. By following this trail, you can figure out if the email is genuine and secure or if something fishy might be going on. These little details tucked away in email headers play a big role in keeping you safe from cyber threats.
Always remember, before you decide to click on any links within an email, take a moment to examine the email header. It’s like checking the ID of someone before opening your door to them.
Understanding the benefits of email headers and knowing how to make sense of them is like having a secret weapon against phishing attacks. Being able to decode these headers can be your armor in the digital world, protecting you from scams and tricks that cybercriminals might try to pull off.
Related Content
Benefits of Dedicated IP Addresses in Web Hosting and Email Marketing
How to Set Apache Request Headers
Why Your Business Should use Multiple Cloud Service Providers



