Cybersecurity professionals are in exceptionally high demand, and their salaries reflect it. The U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics reports a median wage of $124,910 for information security analysts. Even most cyber roles pay mid-six figures on average, and top experts can earn substantially more. In fact, as cyber threats rise and companies prioritize security, the field has become “lucrative”. Those with the right skills, certifications, and experience can expect not only competitive pay but also accelerated career progression and long-term job security.
This blog explores how much you can realistically earn in cybersecurity in 2025, the factors driving pay growth, and how the talent gap creates lasting career opportunities.
Cybersecurity Salaries at a Glance
The World Economic Forum notes that “compensation and financial benefits are often cited as the key reasons why cybersecurity professionals choose to join an organization”. This combination of high pay and near-zero unemployment is driving a new wave of talent into cybersecurity careers.
According to recent industry data by Programs.com the key salary benchmarks for 2025 include:
- Average salary: $128,000 per year
- Salary range (all levels): roughly $101,300 (low) to $154,800 (high)
- High-end roles (security architects): $119k – $180k
- 10+ years’ experience: $143k – $211k
- Regional premium: US jobs tend to pay $40k – $70k more than non-US equivalents
- Top Secret clearance: adds roughly $30k on average
Together, these figures mean a typical entry-level cyber job often starts in the $70k–$90k range, while management roles like CISOs and security directors regularly exceed $150k. As founder of Cybersecurity Ventures Steve Morgan mentioned, cybersecurity is one of the few industries that didn’t experience a downturn in recent years, demand and pay have only grown.
Which Cybersecurity Roles Pay the Most?
There’s a disparity in pay among cyber positions. As a general rule, architects, engineers, and consultants are the highest-paying roles, while analysts and junior positions tend to be among the lowest. Here is a recent breakdown of pay by role (using employer postings and industry data as sources):
Get exclusive access to all things tech-savvy, and be the first to receive
the latest updates directly in your inbox.
- Security Architect: $119,764 – $179,500
- Penetration Tester: $104,582 – $156,427
- Security Consultant: $101,517 – $144,379
- Security Engineer: $96,273 – $154,376
- Cybersecurity Analyst: $88,329 – $143,543
It is worth mentioning that a shortage of skilled talent exists, with significant technology firms such as Palo Alto Networks, McAfee and Cloudflare consistently advertising six-figure salaries for skilled security engineers and architects, according to Business Insider. Non-technical cyber jobs such as project managers and compliance officers in most job markets average around $70k-100k. Meanwhile, organizations seeking higher-level roles, such as CISO or Security Directors, easily average above $200k, depending on organization size and industry.
In practical terms, career-specialty plays a sizable role. Hands-on-function positions, such as pen testing, incident response, and application security typically are viewed as having more value than, say, entry-level roles such as SOC monitoring. Paid compensation for senior level positions typically are valued highest, especially when the position requires extensive experience or secret/TS clearance. Cloud and AI-security roles also offer high salaries because organizations are generally quickly moving to secure new technology platforms.
Essentially, the higher level of professional and experience you attain in all jobs, the greater the salary. After mid-career, jobs with six-figure salaries are common.
Why do Cybersecurity Professionals Demand so Highly?
The skill shortage in cybersecurity is one of the most acute talent gaps in tech today. There are about 4 million unoccupied cyber jobs in the world. In fact, according to Business Insider, hiring for a cyber position takes 21 percent longer than any other IT position, and there are currently more than 700,000 vacancies in the United States.
This imbalance of demand and supply is pushing salaries higher. All types of firms, across finance, healthcare, government, and even retail, are actively pursuing skilled defenders. For example, high-profile breaches and larger regulations that require mandatory breach reporting have led to massive hiring booms.
The major drivers of demand are:
- Escalating threats:
Cyber-attacks like ransomware and supply-chain hacks have surged year-over-year, pushing organizations to beef up their security teams. - Digital transformation:
Rapid cloud adoption and remote work have expanded attack surfaces, creating an urgent need for cloud- and network-security experts. - Regulations and compliance:
Laws like GDPR, CCPA, and industry mandates force companies to invest in security staff or face penalties. - Legacy talent gap:
The workforce itself is aging out, and schools/bootcamps aren’t producing enough entrants fast enough.
In short, supply simply can’t keep up with demand. The outcome is strong bargaining power for cyber professionals: bonuses when hiring, accelerated pay raises and sign-on bonuses are the order of the day. This is the reason why salaries are so competitive even at the early stages of a career.
What is the Relationship between Location and Cybersecurity Salaries?
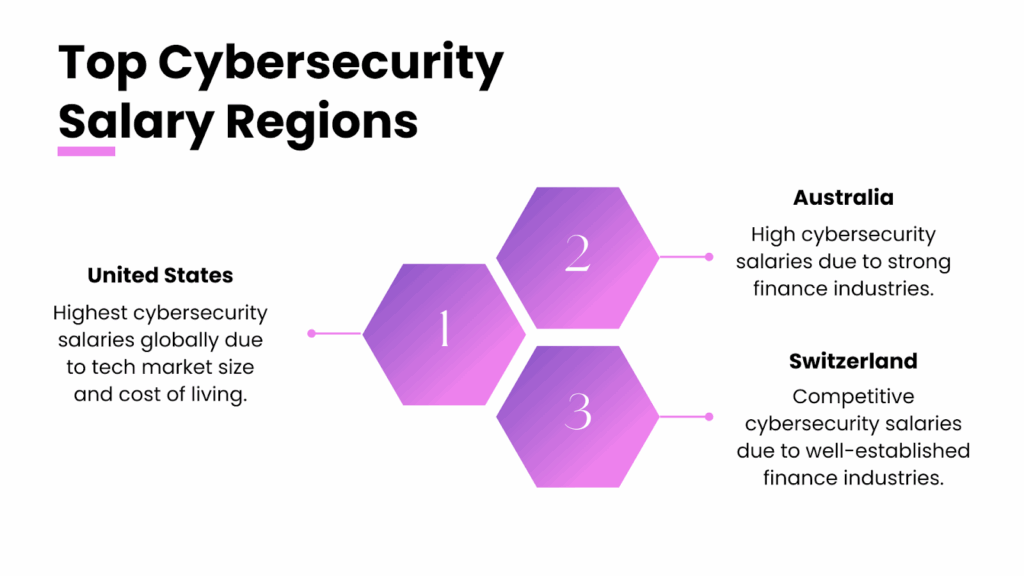
The location is an important factor in salary. Cybersecurity salaries in the U.S. are among the highest in the world. In fact, as referenced earlier in the blog, statistics suggest that a U.S. listing experiences about $40,000-70,000 more annually than the same listing in another location outside the U.S. So, employees in the U.S. are paid a significant amount more than their counterparts in other countries, even for the same employer.
The reasons for this are the size of the tech market in the U.S., the high cost of living in hotbeds like Silicon Valley or New York City, and multinational companies that are paying U.S. rates for U.S. offices. In the U.S., job salaries vary greatly depending on the region. California, Washington D.C./Virginia and New York are likely to be the highest paying markets based on local demand and standard-of-living costs. This disparity at the regional level is also evidenced by international surveys of countries with the highest salaries expected for cyber experts who migrate abroad, which include the U.S., Australia, Switzerland and the U.K., and often revolve around the established finance scenes there. On the outside, Asian, Eastern European or Latin American countries typically pay less.
In addition, a job in the U.S. has not only a higher pay baseline, but greater access to bonuses or stock options. For a non-U.S. citizen, the baseline will typically be lower but the experience of non-U.S. residents at a top company such as Google, Microsoft, Amazon, etc. could get a higher offer to return to their country. In any case, the bottom line is that cybersecurity salary is the highest in North America and select European areas, which shows that the field is globally competitive.

What Are the Factors of Cybersecurity Compensation?
Here are a few points that cause a variability in cybersecurity pay:
Role/Seniority:
Managers and architects usually earn more than junior analysts. For example, a CISO or top-level security architect may earn over $200,000 in total compensation, while entry-level analysts may be starting at $70,000 -$90,000.
Experience:
Cybersecurity compensation increases exponentially with experience. As mentioned above, professionals with more than ten years of experience can earn anywhere from $143,000 – $211,000. Each step in your career (i.e. mid-level to senior or senior to lead) can ultimately add $10,000 – $30,000 to your total compensation.
Certifications:
Vendor-neutral certifications such as CISSP & CISM or cloud security certifications can help boosted your pay. Having top certifications is often associated with being paid more and hired quicker. Employers know certifications signal competency and skill level to some degree, which is particularly useful in a crowded space.
Industry:
Some industries simply pay more. In general, the defense, finance, and tech industries generally pay higher cybersecurity salaries than other industries such as nonprofit or education. For example, a security analyst in a bank may start at around $90,000 or so, while the same position in a small charity might start around $60,000.
Education vs. Skills:
It’s no secret that cyber hiring managers give primacy to work experience and certifications over degrees. Therefore, bootcamps and independent study can still result in six-figure salaries next to degrees, as long as they lead to verifiable skills.
Thus, pay reflects the convergence of role, experience, and qualifications. Companies are in acute competition for proven talent, which is why roles with skills they can’t find, such as cloud security, AI security, and forensic analysis, will offer an easily attainable six-figure salary (like a hundred grand, not a hundred and twenty).
Apart from the external conditions at play, organizations also need to develop effective systems for structuring and managing compensation. In an environment where cybersecurity experts have significant bargaining power, and salary expectations are volatile, relying on manual methods becomes impractical and uncompetitive. That’s part of the reason why many HR departments use HR tools to benchmark salary against industry data, track individual performance, and provide visibility into internal pay equity. In particular for cybersecurity teams where there is limited talent and retention is critical, having a tool supports employers to offer an attractive and repeatable compensation package that maintains a global benchmarking approach while understanding the evolving requirements of the role.
What Skills and Certifications Boost Cybersecurity Salaries?
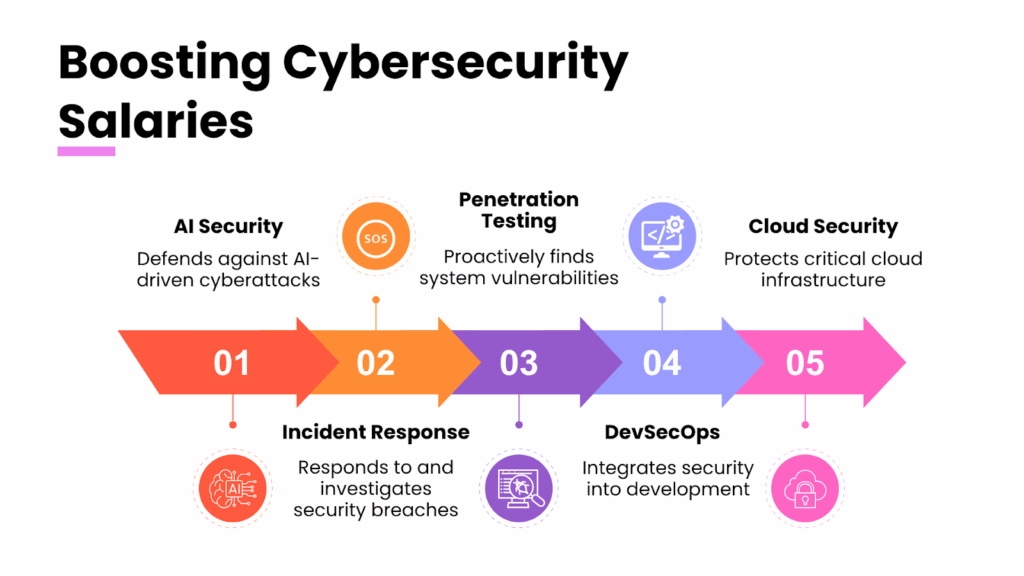
Some expertise and certifications can substantially increase cybersecurity salary level. Employers often want to hire candidates with verified credentials and hands-on experience. These are the key areas that enhance salary level.
In-Demand Skills
- Cloud Security: Safeguarding AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud environments is a lucrative specialization.
- AI & Automation Security: More assets and applications are being automated and/or driven through AI, and are creating demand for professionals who can defend against these threats and secure automated systems.
- Penetration Testing: Ethical hacking and vulnerability assessments remain very valuable to organizations in relation to weakness response.
- Incident Response & Forensics: The ability to detect, contain, and investigate breaches is highly compensated. That’s why cybersecurity experts try to find out and use solutions like iClear that validates data and provides fraud prevention.
- DevSecOps: Organizations are embedding security into their software development pipeline, increasing demand for these hybrid roles, so there’s a higher demand for MLOps and automation in cybersecurity.
Certifications That Pay Off
- CISSP (Certified Information Systems Security Professional): This certification is often a must-have for those aiming for senior or leadership positions in the field.
- CISM (Certified Information Security Manager): A globally recognized credential that’s perfect for management and governance roles.
- CEH (Certified Ethical Hacker): This one really enhances credibility for penetration testers and ethical hackers alike.
- CompTIA Security+: A fantastic entry-level certification that can help kickstart your career in cybersecurity
- Cloud Certifications: Earning credentials like AWS Certified Security or Microsoft Azure Security Engineer can significantly boost your earning potential.
Conclusion
Cybersecurity has emerged as one of the most rewarding and robust career paths available today, offering professionals both stability and a significant impact. Unlike many other sectors that can be swayed by market changes, the importance of cybersecurity is only growing as organizations face increasing threats in the digital landscape. Beyond attractive salaries, this field allows individuals to be on the front lines of digital protection, tackling challenges that affect businesses, governments, and people around the globe. For those entering the field, it’s a chance to build a fulfilling career with skills that will always be in demand. For companies, it underscores the necessity of attracting and keeping top talent to safeguard their operations.


