The DNS (Domain Name System) is a vital part of the internet, making it user-friendly. Without DNS, using the internet would be very challenging. It acts like a phone directory, managing website addresses. Sometimes, the need arises to perform a reverse DNS, like finding a domain address from an IP. This process is called reverse DNS lookup. This article will guide you through the process of conducting a reverse DNS lookup.
Reverse DNS requests, including DMARC, are often used to filter email spam. Spammers can manipulate their sending address, even using well-known domains like banks or reputable businesses.
What is reverse DNS (rDNS)?
Reverse DNS (rDNS) is a type of name resolution that looks up IP addresses to get a domain name, rather than the DNS server’s job of converting domain names to IP addresses.
rDNS is a DNS lookup of a domain name from an IP address. rDNS resolves a domain name to an IP address, but regular DNS does the opposite, hence the term reverse. For rDNS lookups, PTR records are used. If no PTR record is specified, a rDNS lookup fails.
Humans, unlike robots, have a difficult time reading and remembering numeric IP addresses. This is why we visit websites using domain names. Reverse DNS converts complex website visit logs into readable domains, making data collection for analytics easier.
Reverse DNS can be used to filter spam. Spammers frequently utilize invalid IP addresses, or addresses that do not match domain names. When a reverse DNS program checks up an incoming message’s IP address and finds no legitimate domain name, the server stops the message. Although rDNS is good at filtering spam, it frequently prevents legitimate emails.
Get exclusive access to all things tech-savvy, and be the first to receive
the latest updates directly in your inbox.
How does reverse DNS (rDNS) work?
The domain name and the IP address assigned to the website’s server can be used to access most websites on the internet. You can get to a website’s homepage by typing the IP address xx.xx.xx.xx into your browser’s address bar. You can access the site by typing its IP address directly into your browser because its domain has a valid rDNS.
PTR records link IPv4 or IPv6 addresses to canonical host names when rDNS lookups are conducted. The lookup, however, fails if the web server does not have a pointer record set up.
PTR records are used to store rDNS entries that have their IP addresses reversed and the suffix.in-addr.arpa appended to each record. The IP address xx.xx.xx.xx.in-addr.arpa, for example, is recorded by PTR as xx.xx.xx.xx.in-addr.arpa, which leads back to the assigned host name.
By typing the IP address of a domain name with a valid rDNS into your browser, you can go to it.
When running an SMTP/mail server, it is critical to set up a proper rDNS record (PTR).
What are the objectives of reverse DNS server?
For folks who run an outgoing mail server, Reverse DNS is quite useful. There are several other reasons to utilise rDNS besides mail servers:
- Spam email filtering: To combat spam, most email servers utilise rDNS to reject messages from IP addresses that do not have rDNS. However, due to the fact that certain legitimate mail servers do not have properly set rDNS records, rDNS is usually utilised as an additional layer of protection.
- A pleasurable network encounter: Reverse DNS has little effect on most corporate administration systems, r-commands, SMTP servers, or network backup solutions. rDNS is also required for the operation of a number of Internet protocols.
- Safeguarding: A reverse IP lookup can be used to find the A records for an IP address, which connect a domain name to the IP address of the device that hosts it. The findings help uncover server faults and determine which virtual hosts are served by a web server.
- Analytics: Reverse DNS assists in giving human-readable data in analytics instead of posting logs of IP addresses.
- Keeping track of website visitors: IP addresses are recorded in visit logs and can help you figure out who is visiting your site. Keeping track of website visitors might help you generate B2B leads.
Reverse DNS and spam filtering
Spam filtering is the most prevalent and important rDNS function. The recipient’s mail server runs a rDNS query to see if the sender’s mail server is valid once a fresh email enters the anti-spam security gateway. The incoming message is automatically discarded if it does not return a valid rDNS record.
That’s why it’s critical to set up PTR records on your mail servers, both to prevent spam and to ensure that messages go to their intended recipients.
Also read: Achieve 10/10 Email score with CyberPanel!
How to reverse look up dns?
Reverse DNS lookup can be done in a variety of ways:

- Use the command prompt in Windows. Using the
nslookupcommand in Windows, perform a manual rDNS lookup. - Use the Linux terminal to get started. You can execute manual rDNS lookups using the
digcommand with the-xparameter. You can also use the host command. - Use lookup tools for rDNS records. rDNS lookup is available through a number of tools.
For windows:
In Windows, the reverse DNS lookup command is:
nslookup [ip address]
For, example:
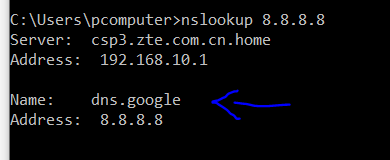
As we can see, dns.google is the reverse DNS of the IP we had given.
Reverse DNS Lookup Command Linux
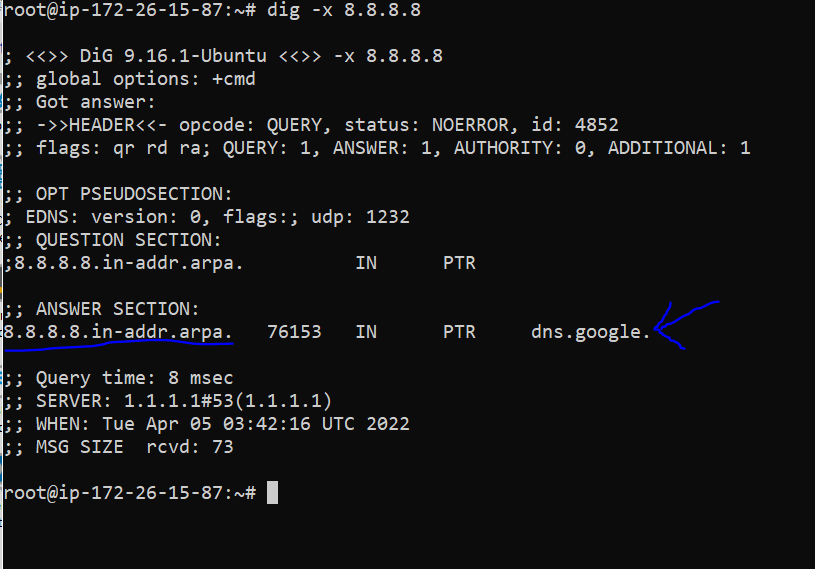
The “dig” command is used to search for information. Use the dig command in Linux to perform a manual reverse DNS lookup. The following is the syntax:
dig -x [ip_address]
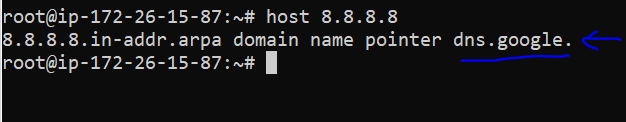
“host” is a command. You may also run a reverse DNS query in Linux with the following command:
host [ip_address]
Lookup tools
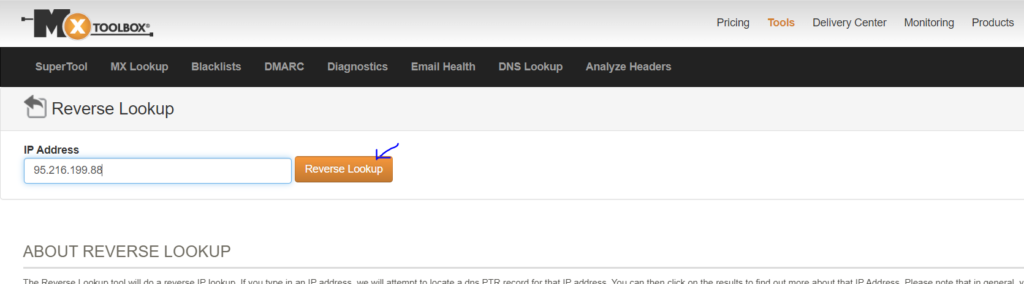
You can lookup a limited number of IP addresses using online reverse DNS tools. Some may also offer an API for business applications.
mxToolBox is one of these tools. Simply enter your IP in there to find the rDNS.
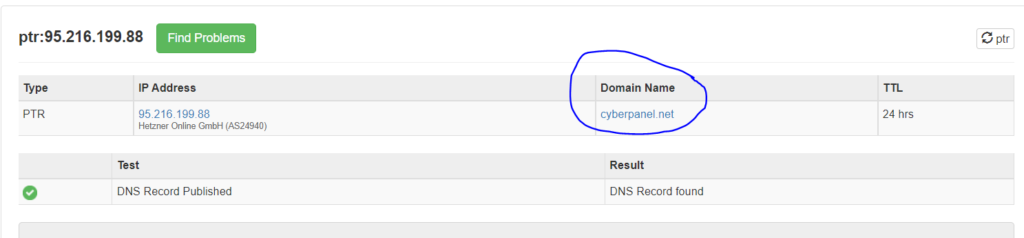
How to set rDNS in Vultr
- Login and select the VPS for which you want to set rDNS for
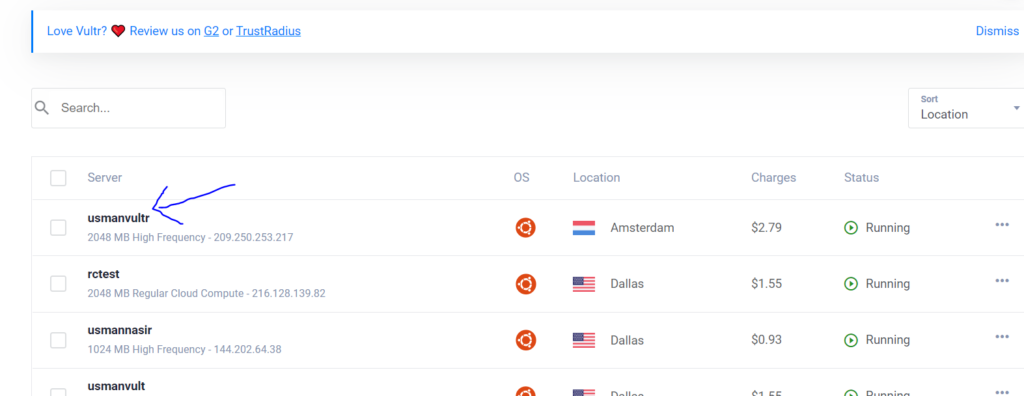
- Click on settings
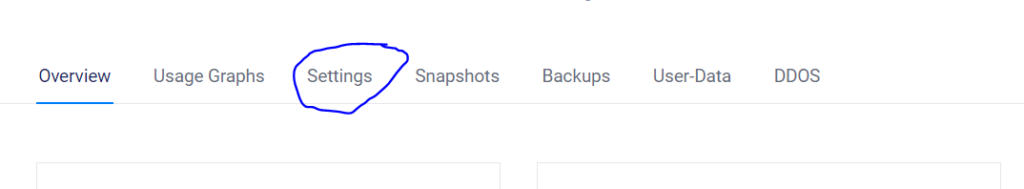
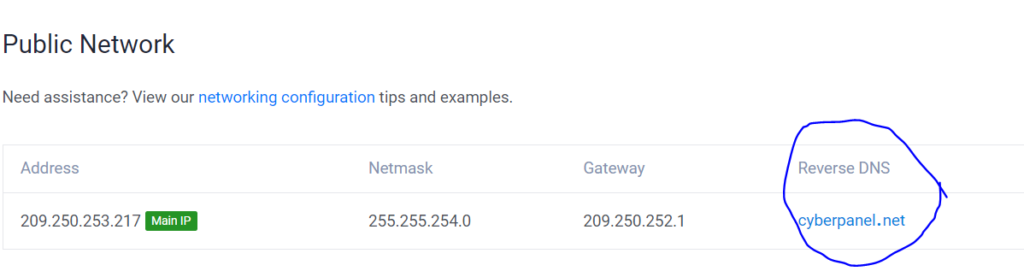
- Click on rDNS
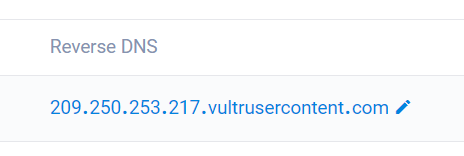
- Edit rDNS and click the tick mark to save
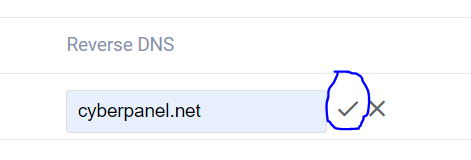
- Your DNS has been set
How to set rDNS in Hetzner
- Login to your Hetzner account
- Enter your project
- Click on the VPS for which you want to create rDNS for and click on “Networking” from the left hand side menu
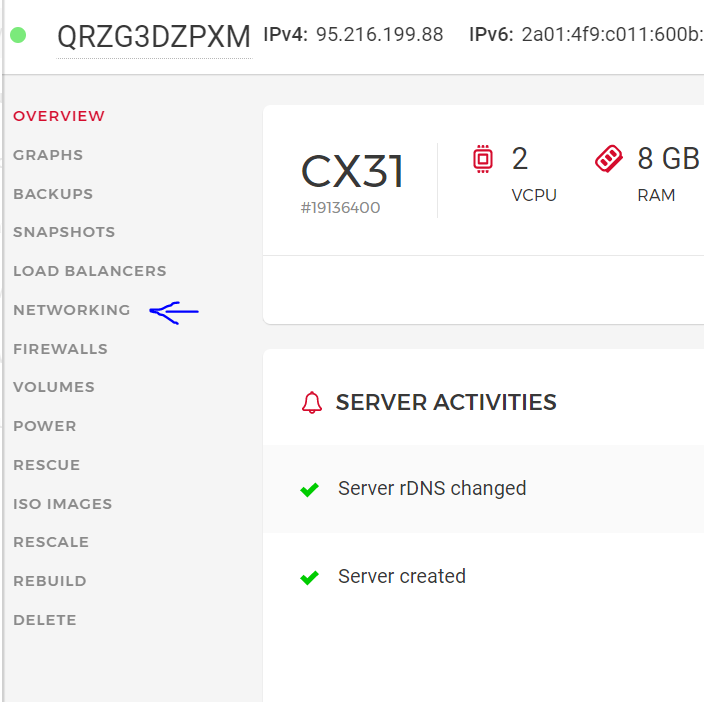
- Click on options and select “Edit Reverse DNS”
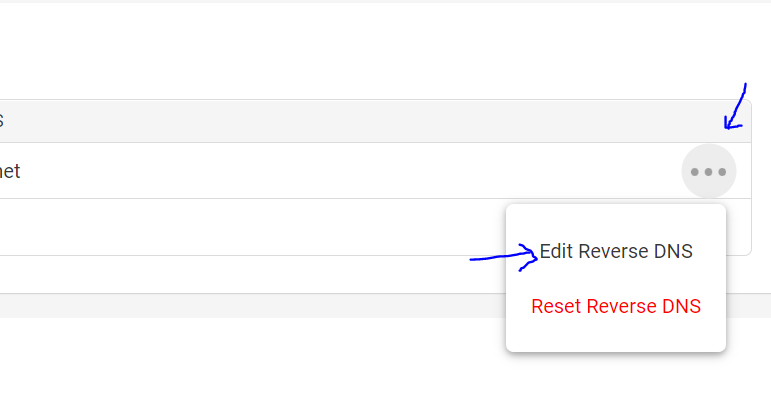
- Edit your rDNS and click “Edit Reverse DNS”
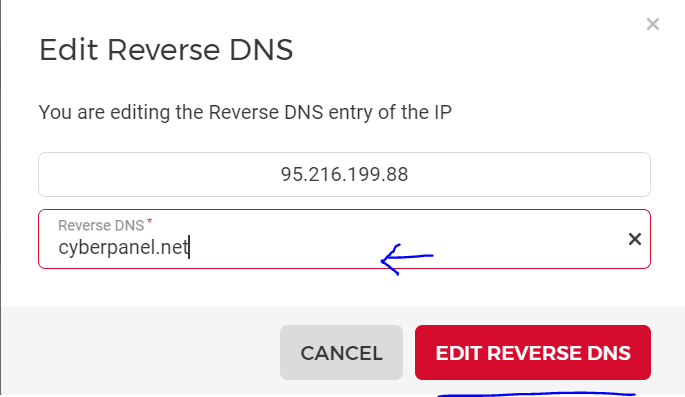
you have succefully set rDNS in Hetzner
How to issue mail server SSL against the domain for which you want to create rDNS for in CyberPanel?
- Login to your CyberPanel account and select SSL -> Mail Server SSL from the left hand side menu
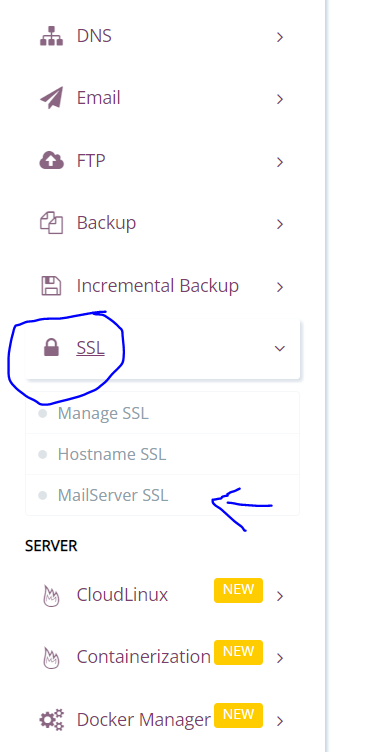
- Select your domain. If your issuing SSL for mail sever against that domain, then your rDNS should also be same as the domain
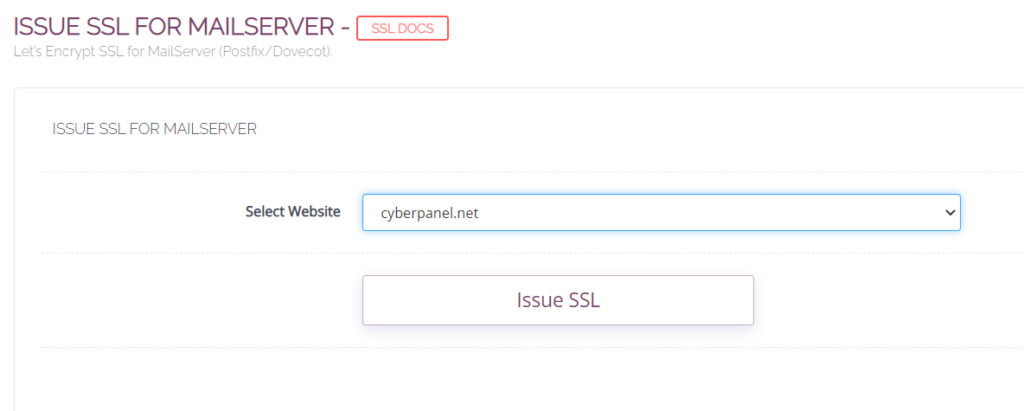
Now mail server’s host name will be this domain name. So when ever you send an email, this domain name will appear.
What does reverse DNS lookup do?
Reverse DNS lookup is like finding a person’s name from their phone number. Instead of searching for a website’s IP address, it takes an IP address and finds the associated domain name. This process helps identify the origin of an IP, making it useful for security, spam filtering, and troubleshooting.
Just as a phone number might lead to a name and location, reverse DNS lookup helps computers figure out the name of the server that’s connected to an IP address. It’s an essential tool to better understand the online world and manage network activities effectively.
What is an example of reverse DNS lookup?
Certainly! Imagine you’re an online detective investigating an IP address, like “192.168.1.1”. You’re curious to know which website or server is connected to it. So, you use a reverse DNS lookup tool. This tool checks its databases and finds out that the IP “192.168.1.1” belongs to the domain “router.example.com”. This is like finding the name of a person when given their phone number.
Reverse DNS lookup helps you unveil the online identity of an IP address, which is crucial for tasks like identifying spammers, ensuring security, and troubleshooting network issues.
What type of record is a DNS reverse lookup?
A DNS reverse lookup involves what’s called a “PTR record” or “Pointer record.” Just like in a regular phone directory where you match names with phone numbers, a PTR record associates an IP address with a domain name. When you perform a reverse DNS lookup, it’s like looking up the name of a person using their phone number.
In this case, the IP address is the “phone number,” and the PTR record reveals the corresponding domain name. This helps computers understand the human-readable names behind IP addresses, making it useful for security, network management, and understanding online connections.
What is forward lookup and reverse lookup in DNS?
Certainly! DNS uses forward and reverse lookups to translate between human-friendly names and computer-friendly numbers.
Forward lookup: When you type a website name like “www.example.com” in your browser, DNS does a forward lookup. It finds the corresponding IP address (like a phone number) so your browser can reach the right server.
Reverse lookup: In reverse lookup, you start with an IP address (like “203.0.113.45”) and want to know its associated name. It’s like identifying a person by their phone number. Reverse lookup helps computers understand which domain is linked to an IP, useful for security and system troubleshooting.
Conclusion
Utilizing reverse DNS lookup is the most effective way to connect an individual IP address to its corresponding domain name. However, this process requires the ISP provider to direct the zone to the IP’s DNS server system. This action then enables the creation of PTR records, which are essential for reverse DNS entries. These records can associate IPv4 or IPv6 addresses with the canonical names of hosts.
Reverse DNS lookup is commonly employed to sift through spam emails and identify the domains of website visitors, crucial for obtaining vital information and generating B2B leads. You can manually unveil the domain linked to any IP address by performing a reverse lookup. Nonetheless, if numerous reverse DNS lookups are necessary, the procedure can become quite labor-intensive.
Related Content:
Improve Speed By Reducing DNS Lookups in WordPress



