SPF, DKIM, and DMARC control which servers can send emails on your behalf, authenticate messages, and tell recipients what to do if any of these checks fail (DMARC). Similarly you might also receive an error “dmarc policy not enabled cloudflare”.
Which means your DMARC record is not right.
DMARC (Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting, and Conformance) is a system used by mail-receiving businesses to improve mail processing. The ultimate goal of DMARC is to provide a “mechanism by which email operators harness current authenticating and policy enforcement technologies to provide both message-stream feedback and policy enforcement against unauthenticated email.”
In order to specify domain-level transmission regulatory frameworks/policies for message authentication, disposition, and reporting, email originating organizations use DMARC.
Also read: Easily Remove WordPress Malware
What is Cloudflare?
Cloudflare is a web-based application security and performance suite that aims to solve the issues mentioned in the primer. Matthew Prince, Lee Holloway, and Michelle Zatlyn founded Cloudflare in 2007 to provide online security. It serves as a reverse proxy, which is a word for a mechanism on the internet that reduces the burden on internal servers by caching static material in data centers strategically situated across the globe.
Get exclusive access to all things tech-savvy, and be the first to receive
the latest updates directly in your inbox.
Cloudflare, which acts as a reverse proxy, is the barrier that requests must pass through in order to reach your site. Cloudflare works in three areas: security, performance, and reliability, giving you and your visitors the greatest experience possible. Cloudflare protects your online application by analyzing requests for malicious content based on questionable IP addresses, the type of resources sought, the request payload and frequency, and a firewall with rules established by you, the customer.
What is DMARC record?
D omain-based Message Authentication Reporting and Conformance (DMARC) is a free and open technical specification. In a DMARC implementation, the core is a DMARC record that defines the rulesets. If a domain is DMARC-enabled, this record informs email recipients. This means the domain owner can specify which policy he/she wants to use in the DMARC record of the domain. DNS (Domain Name Service) records are in essence DMARC records. A DMARC DNS record can be implemented to use DMARC. Users of email receivers that have adopted DMARC will be able to use this record. As a result, your DMARC policy will allow you to keep track of every message sent to your domain.
Therefore, the organization that publishes the DMARC record will be able to specify how non-compliance will be handled. It is possible to monitor (and deliver) messages, move them to junk folders, or reject them.
What are DMARC policies?
When utilizing DMARC, you may describe how you want recipients to handle emails that fail the DMARC checks by creating a policy. After an email has been checked per SPF and DKIM records, a DMARC policy specifies what happens to it. SPF and DKIM are either passed or failed on an email. The DMARC policy determines whether an email is designated as spam, blocked, or delivered to its addressee if it fails. (Email servers may still identify emails as spam if a DMARC record is missing, but DMARC gives stronger guidelines on when to do so.)
You have three DMARC policies to choose from:
- P=None : Just keep an eye on the numbers and don’t take any action if any messages fail. Use this policy to begin collecting DMARC reports and evaluating the information included in them.
- P=Quarantine : Quarantine any communications that fail the DMARC tests. This usually means that these mails will end up in the garbage folder.
- P=Reject : All messages that fail the DMARC checks are rejected. The receivers should do this ‘at the SMTP level,’ which implies that the messages will bounce right in the middle of the sending process.
How does DMARC works?
Because DMARC is reliant on SPF and/or DKIM results, at least one of these must be in existence for the email domain. You must publish a DMARC entry in the DNS to use DMARC.
After validating SPF and DKIM status, a DMARC record is a text item within the DNS record that tells the world your email domain’s policy. If SPF, DKIM, or both pass, DMARC authenticates. This is known as identifier alignment or DMARC alignment. It’s possible that SPF and DKIM pass, but DMARC fails, based on identifier alignment.
A DMARC record also instructs email servers to submit XML reports to the DMARC record’s reporting email address. These reports show you how your email is traveling around the ecosystem and allow you to see who else is using your email domain.
Making sense of reports written in XML can be difficult, especially when there are a lot of them. The DMARCIAN platform can receive these data and visualize how your email domains are utilized, allowing you to take action and change your DMARC policy to p=reject.
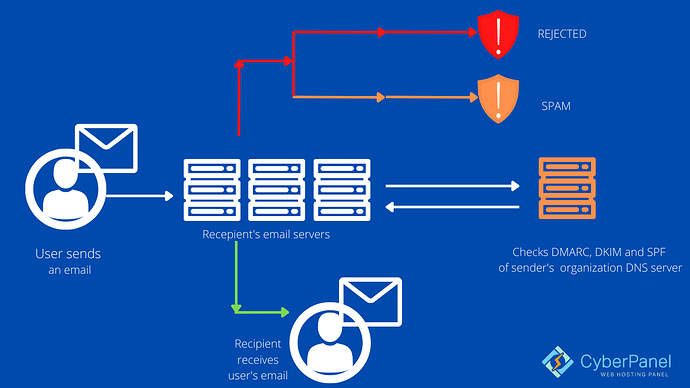
How DMARC works with SPF and DKIM?
To give a more comprehensive validation, DMARC leverages the validation findings from both SPF and DKIM. SPF verifies if an email was sent from an allowed IP address, whereas DKIM verifies whether an email was signed by the same domain as it was sent from or by a domain authorized to send on that domain’s behalf. They both generate authentication identifiers, which are used by DMARC to authenticate emails and specify rules for how recipient servers should handle emails that fail identification checks.

What is a DMARC report?
Instructions for sending reports regarding emails that pass or fail DKIM or SPF can be found in DMARC policies. Generally, admins set up reports to be forwarded to a third-party provider that diffuses them into a more readable format, so they aren’t overburdened with data. DMARC reports are critical because they provide administrators with the information they need to alter their DMARC policies, such as if valid emails fail SPF and DKIM or if a spammer is attempting to send fraudulent emails.
For email, why use DMARC?
Email is used in more than 90% of all network assaults, and without DMARC, it might be difficult to determine if an email is legitimate or a forgery. By combating fraud, counterfeiting, and Business Email Compromise, DMARC allows domain owners to secure their domain(s) from unlawful use.
The operator of an Internet domain can inform the world that “everything I transmit is easy to identify using DMARC—feel free to dump counterfeit email that purports to be me” by always sending DMARC compliant emails.
In order to be effective as an anti-spoofing solution, DMARC has developed a significant innovation: instead of trying to filter out malicious mail, why not make it easier for operators to recognize valid mail? As part of DMARC, email security will be replaced by a policy that filters in good instead of filtering out the bad.
Advantages when you use or enable DMARC policy?
There are a few important reasons why you should use DMARC:
- Reputation : Publication of a DMARC record safeguards your brand by blocking unauthorized parties from sending email from your domain. Merely publishing a DMARC record might sometimes result in a good reputation boost.
- Visibility : DMARC reports improve your email program’s visibility by informing you of who is sending email from your domain.
- Security : DMARC assists the email community in establishing a uniform policy for dealing with failed authentication messages. This contributes to the overall security and trustworthiness of the email ecosystem.
How to fix “dmarc policy not enabled cloudflare”
Make sure your SFP and DKIM records are also set using this guide: Achieve 10/10 Email score with CyberPanel!
You don’t have to enter DMARC records if DNS is managed by CyberPanel. CyberPanel enters them for you. However, if its DNS is managed by Cloudflare, they would need to enter DMARC records in Cloudflare manully.
- Go to your CyberPanel’s Dashboard
- Click on DNS → Add/delete records from the left hand side menu
- Select your domain
- Click on TXT records tab
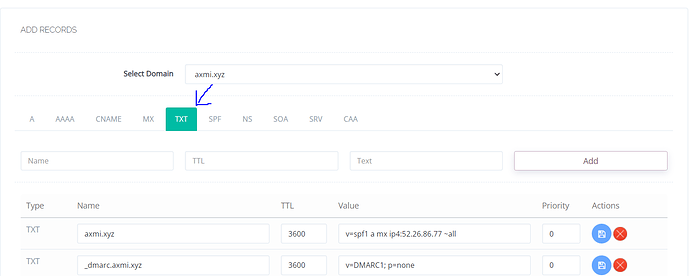
- 2nd record is your DMARC record. Save this name and value.
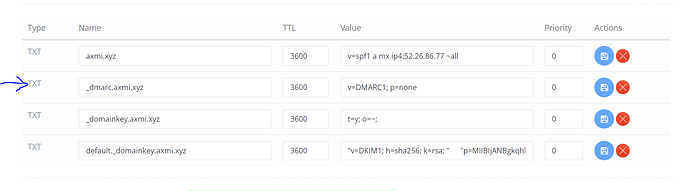
- Go to Cloudflare’s Dashboard and select your site
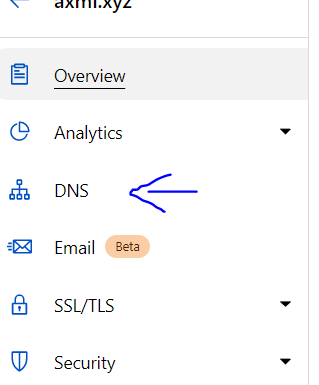
- Click on DNS from the left hand side menu
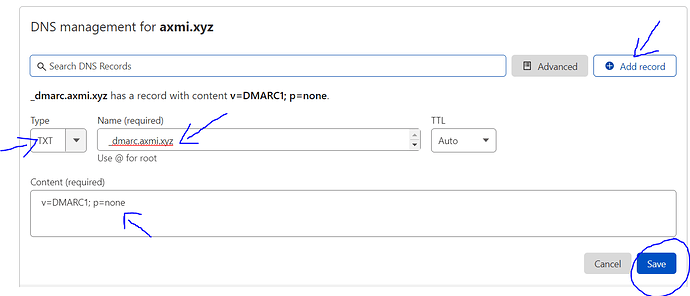
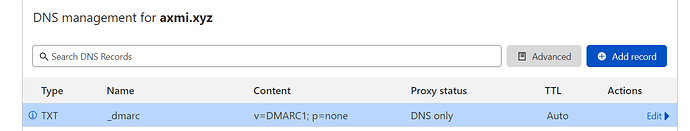
- Your record is added.
Conclusion
The ultimate purpose of DMARC is to give email operators a way to use current authentication and policy enforcement technology to offer message-stream feedback and enforce policies against unauthenticated email. Email originating businesses use DMARC to provide domain-level transmission regulatory frameworks/policies for message authentication, disposition, and reporting.



