Your organization’s data is a key asset, but when it’s time to pick the best storage solution, how do you decide which type to go for? There are three main methods for storing data in the cloud: block storage, object storage, and cloud file storage. These options allow users and applications to access data remotely through a network connection.
Have you ever found yourself torn between two great options and didn’t know what to pick?
It’s like trying to decide whether you want more storage or faster performance when buying a new smartphone. That’s the kind of dilemma companies face when they have to choose between object storage and block storage in the cloud.
What is Block Storage?
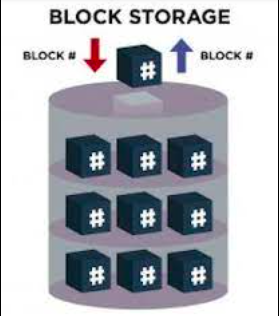
Block storage involves dividing data into fixed-size chunks, each stored separately with its own unique identifier. These chunks can be kept in various environments, like one chunk on Windows and others on Linux. When a user wants to access a chunk, the storage system puts all the pieces back together.
In block storage systems, the storage volume functions similarly to a hard drive and is set up by a storage admin. Each block can be treated like a separate hard drive, and servers connect to them through a fast network. This setup ensures high performance and minimal delays since the server can directly read from or write to a specific block, eliminating the need for a file system to handle the data.
How Block Storage Works!
- Every file or data segment is stored as an “object,” which has a unique name or identification for data retrieval along with metadata. (Consider how a driver may put their space number on paper in a big parking lot to help them remember where their car is.)
- Every item is kept in a “data lake” (also known as a “data pool”). In a manner similar to a big parking lot, which lacks ramps and other levels, data lakes are flat and lack a file hierarchy.
- Block storage is typically used for hard disk drives and data that changes frequently. You can find block storage on Storage Area Networks (SANs) or in cloud storage setups.
Block Storage: Advantages, Disadvantages, and Applications
Pros
- Reliable because of its self-contained nature.
- Offers high performance and quick data access.
- Simple to update without needing to create a new chunk.
Cons
- It can be expensive to add more block storage.
- Lacks metadata, which makes it less suitable for unstructured data.
- Limited search options can make managing large amounts of data tricky.
Applications
- Great for email servers because of their performance and reliability.
- Ideal for transactional databases due to their speed and easy updates.
- Used in virtual machine file system (VMFS) volumes for enterprise deployment.
What is Object Storage?
Object storage is a way of storing data in separate units known as objects, which are kept in isolated containers. This method breaks down data into distinct pieces, each with a unique identifier and metadata that helps describe the data, making it easier to access compared to traditional storage methods.
Get exclusive access to all things tech-savvy, and be the first to receive
the latest updates directly in your inbox.
Object storage vs block storage has become the go-to choice for archiving and backing up data. It provides a level of scalability that traditional file or block storage just can’t match. With this type of storage, you can handle massive amounts of data, ranging from terabytes (TBs) to petabytes (PBs) and beyond.
It operates in a flat data environment or storage pool. While you can store objects on-site, they are more commonly found in the cloud, allowing teams and organizations to access their data from anywhere. When you need to retrieve an object, the system uses its unique identifier and metadata to find it.
This flat structure is perfect for managing large amounts of unstructured data, like social media posts, videos, or sensor data, which can be tricky to organize hierarchically.
Additionally, object vs block storage is much easier to scale since everything is organized within a single global storage pool. You can access and manage your data seamlessly, even if it’s spread across different hardware and locations.
Common uses for object storage include cloud-native applications, the Internet of Things (IoT), big data analytics, rich media storage, and delivery, as well as backups and archiving.
How Object Storage Works!
- Objects are individual data units kept in a flat storage system, simplifying data management compared to traditional hierarchical file systems.
- Each object includes its data, metadata, and a unique identifier.
- Object storage offers limitless scalability and enhances data durability and recovery options.
- Objects can be stored either locally or on cloud servers, making them accessible globally.
- Access to objects is done through Application Programming Interfaces (APIs), primarily using an HTTP-based RESTful API.
- RESTful APIs utilize HTTP commands such as “PUT” or “POST” for uploading, “GET” for retrieving, and “DELETE” for removing objects.
- Object storage can accommodate numerous static files, and new RESTful API standards are developing to handle aspects like containers, accounts, multi-tenancy, security, and billing.
- This storage solution is particularly suited for extensive library systems, as it organizes data and metadata in a flat format, which can complicate search and retrieval.
Pros
- Huge scalability: With object storage, you can scale up almost endlessly by simply adding more devices as needed.
- Designed for big data: It’s great for handling large volumes of unstructured data, making it ideal for big data applications like AI, machine learning, and predictive analytics.
- Easy storage management: The lack of folders or directories simplifies data retrieval since you don’t need to know the exact location.
- Cost-effective on-demand storage: Object storage operates on a consumption basis, meaning you only pay for what you use and can easily scale as needed.
Cons
- No file locking: Everyone can access the objects stored, which can be a downside.
- Slower performance: It takes more processing time compared to file and block storage.
- Can’t modify parts of a file: Once an object is created, you can only create a new one instead of changing the existing one.
Applications
- IoT data management: It scales quickly and allows for easy data retrieval, making it perfect for industries like manufacturing and healthcare.
- Email storage: Great for managing large volumes of emails for historical records and compliance.
- Backup and recovery: Less focused on performance, making it suitable for backup and recovery tasks.
- Video surveillance: A cost-effective solution for long-term storage of video recordings.
Block Storage vs Object Storage: Key Differences
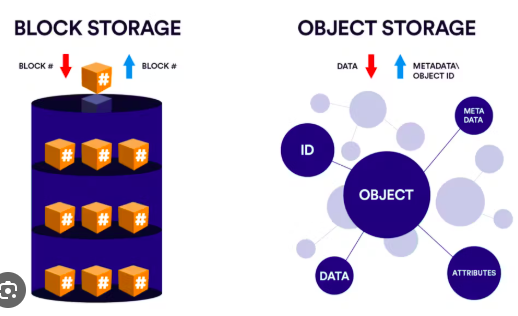
Let’s see how the Block storage vs object storage differ in terms of their features:
1. Performance
Block storage vs object storage provides excellent performance with minimal delay, making it ideal for applications that need quick access to data blocks, such as databases and high-performance computing tasks.
Object storage vs Block storage, on the other hand, is usually slower for some functions but is highly efficient for data retrieval in specific scenarios like content delivery networks and big data analytics.
2. Scalability
Scaling block storage vs object can be more difficult, as increasing capacity often requires manual setup. There may also be restrictions on the maximum volume size and the number of blocks that can be handled.
In contrast, object storage is built for easy scalability. Adding more storage nodes is simple, and its flat data structure allows for nearly unlimited growth.

3. Data organization
In block storage, data is divided into fixed-size blocks, each identified by a unique ID. This allows for quick, random access, but it also means that metadata and data organization are usually managed externally by a file system.
But in object storage vs block storage, each object contains the data, metadata, and a unique identifier, which enhances data management capabilities. This built-in intelligence makes object storage more suitable for unstructured data.
4. Cost
Although block storage vs object storage provides performance advantages, it often comes with a higher price tag, especially for large datasets. Additional expenses may arise from management overhead and the need for specialized hardware or software.
Object vs block storage is typically more affordable, especially for large-scale, unstructured data. Its design reduces the need for manual management, leading to lower operational costs.
5. File management
Object vs block storage solutions allow files to be stored as objects. Accessing these files with existing applications requires new coding, use of APIs, and an understanding of naming conventions.
Similarly, block storage vs object storage can serve as the foundational storage for a self-managed file storage solution.
Block Storage vs Object Storage: Comparison At A Glance!
| Feature | Block Storage | Object Storage |
| Data Structure | Breaks files into chunks | Stores data as whole objects |
| Performance | Quick response time, high data transfer rate | Built for growth |
| Scalability | Constrained | Highly scalable |
| Use Cases | Databases, virtual machines, transactional info | Backups, media files, big data |
| Storage Capacity | Capped by volume size | Practically limitless |
| Storage Method | Uniform blocks with identifiers | Objects accompanied by metadata and unique identifiers |
Key Takeaways- How To Choose The Right Storage For Your Cloud!
Choosing between Block Storage vs Object Storage entirely depends on your specific cloud needs.
Block vs Object storage is perfect for handling large amounts of unstructured data. It provides durability, endless storage capacity, scalability, and advanced metadata management. On the other hand, block storage excels in delivering fast processing speeds, low latency, and high performance, making it great for real-time analytics and quick transactions.
Organizations need to grasp the different types of storage options out there and assess their data requirements to choose the best fit. As new data types come into play, it’s important for storage strategies and choices to adapt in order to keep up with business demands and technological advancements.
FAQ’s
1. Which one is quicker, block storage vs object storage?
Block storage vs Object storage is quicker because it provides low-latency data access, making it perfect for apps that need fast read/write operations.
2. Is object storage more affordable than block storage?
Definitely! Object storage is usually more budget-friendly for keeping large volumes of unstructured data since it doesn’t require complicated file systems.
3. Can I combine block storage and object storage?
For sure! Many companies use block storage for applications that need high-performance and object storage for scalable, long-term data storage.
4. What are the security differences between block and object storage?
Object vs block storage comes with enhanced security features like encryption and immutability, making it a great fit for industries that need to meet strict compliance standards.
5. Does object storage utilize a file system?
Nope, object storage doesn’t use a traditional file system. It manages and retrieves data through metadata and unique identifiers instead.
6. How does object storage manage large-scale data better than block storage?
Object storage vs block storage is built for massive scalability and can hold endless amounts of data without being limited by fixed-size volumes, unlike block storage.
7. Which storage type is best for AI and Machine Learning?
Object storage is the go-to option for AI and ML applications because of its scalability, metadata features, and capacity to handle large datasets.
8. How does network performance influence storage selection?
Block storage needs low-latency network performance, object storage vs block storage can work well even on networks with higher latency, making it ideal for distributed access.



