We are going to learn data center types. Today, businesses, governments, and individuals heavily rely on data more than ever before. Due to digitization, its management, processing, and storage have become of utmost importance. Data centers today have become the backbone of modern IT infrastructure.
Data centers have experienced much change over the years and can be tailored to fit different industries that utilize them. Cloud services and edge computing, it guarantee that organizations have an easy way to store, process, and retrieve information over a network. This guide explores what data centers are, the benefits, use cases, and types of data centers. At a time when everyone needs to understand the functionality in these data centers, explaining this concept as an IT professional or business owner will take you quite far in the tech world.
What Are Data Centers?
A data center refers to an industrial facility that houses critical IT infrastructure. Data centers provide space to park, power, and cool servers, networking equipment, and other storage devices where businesses use digital services continuously without interruption.
How Data Centers Work
Data centers are designed to process, store, and securely share data. They allow businesses to:
- Run applications such as e-commerce platforms.
- Host websites and manage databases.
- Enable cloud computing and remote work setups.
Key Characteristics of Data Centers
Redundancy: There is always a backup in case of power, networking, and cooling to ensure not even a single disturbance to the operations.
Scalability: As business needs scale up, data centers increase their capacity to meet increased workload requirements.
Get exclusive access to all things tech-savvy, and be the first to receive
the latest updates directly in your inbox.
Security: Highly advanced systems protect the data by minimizing breaks and physical damage. For example, many facilities now deploy Coram’s best NVR camera system to ensure 24/7 surveillance, secure access control, and real-time monitoring of critical zones in the data center.
For instance, Google’s humongous global network of data centers ensures that its 2 billion active users worldwide deal with minimal latency and guarantee high availability.
Benefits of Data Centers
1. Security
Data breaches can be avoided through some basic tools such as firewalls, intrusion detection, and encryption that come with data centers and form part of the prime benefits.
2. Performance
These data centers optimize IT operations, thus giving low latency connectivity and robust infrastructure for application performance to run perfectly.
3. Scalability and Flexibility
Data centers, especially the cloud-based, make it possible to up-size or down-size infrastructure as business demand shifts and thereby save unnecessary costs.
4. Disaster Recovery and Business Continuity
Data centers ensure the continued operation of critical systems during a disaster with alternative power supplies and redundant storage.
5. Cost Optimization
A business can either opt for colocation and cloud data centers. Both options provide world-class facilities without capital expenditures on infrastructure.
6. Innovation Enablement
Modern data centers supply the computation power for AI, machine learning, and IoT applications to bring innovation.
For example, Netflix relies on these centers to stream video without interruption in several locations while warehousing stacks of user information.
Use Cases of Data Centers
1. E-commerce and Retail
Data centers facilitate e-commerce companies like Amazon by processing millions of orders, inventory management, and user information. These centers allow customers to shop 24/7 through safe payment gateways.

2. Cloud Computing Platforms
Data centers are the backbone of services for firms such as AWS and Microsoft Azure, providing virtualized resources for remote work and scalable computing.
3. Healthcare Systems
Data centers in hospitals and clinics hold electronic medical records; and provide capabilities to deploy AI diagnostics and power telemedicine portals for uninterrupted patient care.
4. Government and Public Sector
Data centers host national databases e-governance platforms and critical public services in secure computing environments.
5. Media Streaming
Data centers provide networks offering high-definition content for use on streaming media services such as Netflix and YouTube, providing low-latency access to some of the world’s largest audiences, with billions of users at any given time.
The rise of OTT platforms has significantly accelerated demand for these services, driving the need for faster and more reliable streaming infrastructure.
Data Center Types
1. Enterprise Data Centers
Enterprise data centers are one type of data center. These are private facilities owned and managed by a single organization. These can be built to manage the specific IT workloads of that company. Enterprise data centers are usually on-site or close to the organization’s headquarters for direct access and management.
In-depth Example
For instance, Facebook constructed proprietary enterprise data centers designed to specifically support their social networking site’s massive data needs. They come with some of the latest technologies such as AI-powered cooling systems that work to ensure maximal efficiency.
Advantages
- Customization: These centers can be designed and run, and enterprises can customize the hardware and software exactly to serve their purposes.
- Security: Since the infrastructure is owned privately, there is high security achieved because tight security procedures can be implemented to protect sensitive data.
- Control: Organizations are in complete control of their activities and, therefore, ensure that they are up to the regulators’ and performance standards.
Best Fit
Corporate institutions such as banking institutions, healthcare providers, and multi-national corporations require robust security and controls over their information
2. Colocation Data Centers
A colocation data center, more commonly referred to simply as a “colo,” is basically a shared facility that renting space, power, and cooling so that businesses can host their servers there. It’s mostly operated by a third-party provider; thus, it ensures the site operates 24/7 without the businesses directly managing its maintenance.
Detailed Example
A company that does not have the wherewithal for a data center of its own may opt to take up space in a colocation facility at Digital Realty. There, they may install their servers and get power backups, cooling, and physical security from the provider.
Benefits
- Lease: No upfront capital expense on a data center.
- Reliability: The providers maintain high uptimes through redundancy on power, cooling, and connectivity.
- Scalability: As the requirement goes up, server space can easily be expanded.
Ideal For
SMEs and start-ups looking for inexpensive, scalable, and secure hosting of data.
3. Cloud Data Centers
Cloud data centers are virtual buildings providing computing resources such as servers, storage, and databases across the web. These units are based on the pay-as-you-go model and allow companies to access infrastructure without owning any hardware at all.
Example
Netflix relies heavily on AWS’s cloud data centers to stream crystal-clear content for millions of subscribers around the world. It is possible with cloud computing, so Netflix scales up immediately as soon as a series premiere, and that happens in seconds.
Benefits
- Flexibility: Scale up or down at real-time needs.
- Global Reach: Using multiple data centers by the cloud providers guarantees low latency in every location.
- Cost Efficiency: Businesses only pay for the resources utilized.
Best Fit
Companies with dynamic loads, for instance, media streaming, e-commerce, AI-driven apps.
4. Hyperscale Data Centers
Hyperscale Data Center is a massive facility constructed to house the humongous IT operations of some of the largest technology companies such as Google, Amazon, and Microsoft. It’s especially designed to scale, be efficient, and be automated according to the needs of cloud computing and Big Data.
Example
They are Azure, Xbox Cloud Gaming, and LinkedIn with Microsoft hyperscale data centers. It makes use of AI to get maximum energy efficiency and lower expenses on cooling.
Advantages
- Energy Efficiency: Powerful cooling technologies and renewable sources minimize expenses.
- Automation: AI technologies monitor and optimize real-time operations.
- Scalability: Built to handle exponential growth in IT workloads.
Best Suited For
- Tech companies
- Global cloud providers
- AI-focused firms
5. Edge Data Centers
Edge data centers are small-sized facilities that are strategically located closer to the end users so that latency is minimized and hence the performance of real-time applications is maximized. These edge data centers are highly important for IoT-based industries, 5G, and AR-based applications.
Illustrative Explanation
Telecom companies establish their edge data centers near urban areas in order to underpin their 5G networks to ensure Internet connectivity with high-definition video streaming or online gaming without any delays.
Benefits
- Low Latency: The edge center’s closeness to the users facilitates faster handling of data.
- Real-Time Applications: IoT, AR, and autonomous vehicles running applications
- Cost Savings: Less expensive for data communications not to be transported over long distances
Best Fit
Gaming, Telecommunications, Healthcare (telemedicine), and Retail (smart stores).
Types of Data Center Cooling Systems
Effective cooling is important to the performance and lifetime of the servers. When the servers get heated up, this can be bad to the hardware with resultant downtime as well as increased operational costs. The following are cooling systems used in data centers, explained in greater detail:
1. Air Cooling
Cooling methods that use the flow of cool air through server racks by means of fans or cooling air-conditioning systems.
Detailed Example
Older enterprise data centers, for instance, rely on raised floors to supply cool air under server racks in traditional air-cooled systems.
Pros
- Easy and inexpensive.
- Applicable for facilities with low density of servers.
Cons
- Not ideal for high-density workloads.
- Energy-consuming.
2. Liquid Cooling
Liquid cooling systems circulate water or coolant throughout pipe network near servers, absorbing heat far more effectively compared with air.
Detailed Example
Google’s AI-driven data centers cool their high-performance computing systems with liquid cooling.
Advantages
- More efficient compared to air cooling, especially with high-density setups.
- Less energy required to maintain optimal temperatures.
Disadvantages
- Higher upfront costs for the infrastructure.
- Maintenance must be constantly scheduled to prevent leaks.
3. Immersion Cooling
Immersion cooling immerses servers in a dielectric fluid that absorbs the heat directly from the components.
Example Details
Cryptocurrency mining facilities utilize immersion cooling because the heat generated by mining rigs is insurmountable.
Advantages
- Ultra-efficient cooling of high-performance workloads
- It completely obliterates the need for traditional HVAC systems
Disadvantages
- Capital intensive to deploy
- Requires specialized hardware
4. Free Cooling
Free cooling is a system that utilizes natural air and water sources to cool servers as much as possible and reduce dependency on energy-intensive systems.
Example in Detail
Data centers in colder climates, such as those in Scandinavia, also use free cooling by drawing in cold air from outside to regulate internal temperatures.
Advantages
- Environment friendly and cost-saving.
- Carbon footprint reduces.
Disadvantages
- Location and weather dependency.
Role of CyberPanel in Data Centers
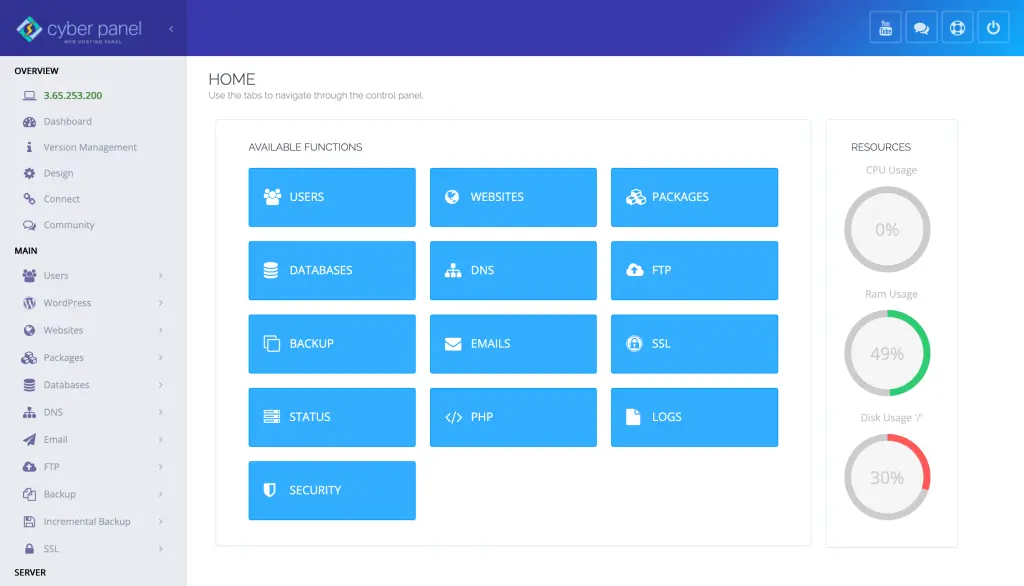
CyberPanel is the next-generation web hosting control panel that makes the management process, related to the servers and the data center, very convenient. Integrate CyberPanel into your workflow at a data center, and you could automate most of the critical tasks that add value to performance and decrease the overhead of operational levels.
1. Server Management
With the help of CyberPanel, administrators can manage their servers with ease, especially without requiring much technical knowledge.
With CyberPanel, one can configure, monitor, and manage the server resources within a matter of just a few minutes. Valuable time is saved.
2. Automated Backups
CyberPanel ensures business continuity in case of hardware failure or cyberattacks by having data backups automated.
CyberPanel can be used for the daily data backup of e-commerce platforms to protect all such critical customer information.
3. Enhanced Security
CyberPanel provides robust security features in the form of firewalls, malware scanning, and SSL certificate management, which ensures that data remains safe.
A healthcare organization can use CyberPanel to safeguard patient information deemed confidential and, in this regard, meet HIPAA standards.
4. Effective Resource Allocation
CyberPanel enables administrators to monitor the current usage of resources and re-allocate them in a distribution manner to prevent those servers from becoming overwhelmed.
Hosting providers monitor and optimize CPU, memory, and bandwidth usage on a multiple server configuration using CyberPanel.
5. Compatibility with OpenLiteSpeed
CyberPanel is on OpenLiteSpeed: a high-performance web server intended to increase the speed and reliability of hosted applications.
CyberPanel does operations in simpler ways, saves costs; ensures business efficiency through well-optimized data centers. Running this business requires a need to have modern IT infrastructure.
FAQs for Data Center Types
1. What is the role of a data center?
The central role of a data center is to act as a central facility that holds, manages, and processes all critical data associated with an organization. It houses servers, storage systems, networking equipment, and cooling systems needed to run a data center efficiently. Data centers aid modern business operations by hosting websites, managing cloud computing, and processing large-scale applications.
2. How do data centers ensure security?
Data centers are built with layers of security that impact their underlying infrastructure, which may include:
Physical Security; Biometric authentication, security personnel, and CCTV surveillance
Network Security; Firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and DDoS protection
Backup Protocols: Scheduled backups and disaster recovery planning that will avoid losing data.
3. What is the main difference between the cloud and traditional data centers?
Traditional Data Centers: They belong to an organization and is managed by the same organization. This gives total control but requires very heavy investments in hardware and maintenance.
Cloud Data Centers: Third-party hosted, virtual infrastructures, scalable and flexible, using a pay-for-as-used model. Even the smallest business can utilize cloud data centers, not invest in physical structures.
4. Why is cooling so important in a data center?
Cooling systems are used to prevent servers from overheating, thus hardware failures, downtime, and data loss. Highly efficient cooling technologies, such as liquid cooling and immersion cooling, ensure optimal performance while reducing energy consumption.
5. How do organizations select the correct data center types?
Selection depends on organizational needs:
Enterprise Data Center: Complete control and security for large organizations
Colocation Data Center: Low-cost hosting for start-ups and SMEs
Cloud Data Center: Dynamic workloads from businesses
Edge Data Center: IoT 5G and other low-latency applications
Final Remarks On Data Center Types
To sum up, data centers are considered the backbone of a modern structure of IT support for businesses to store, process, and deliver data with efficiency. Right from the enterprise to the edge facilities, each of the data center types is suited to the specific needs and is supported with the latest cooling systems that ensure its performance and reliability. CyberPanel plays a pivotal role in the simplification of data center management ensures security, and optimization of resource utilization, and delivers high-speed performance by making seamless integration with OpenLiteSpeed.
Want to improve your data center operation for your business’s digital presence? Then integrating CyberPanel is what you need.
Unlock all the functionalities of your data center with CyberPanel. Visit CyberPanel’s official website now!