Introduction
If you own a WordPress website, you must ensure that it is well-protected and you remove WordPress malware. Cyber criminals will find it easy to target a vulnerable site. They have the ability to harm your website in a variety of ways, including infecting it with malware.
Malware is not to be treated lightly, as it evolves and grows each year. You may prevent this problem by upgrading your website on a frequent basis, for example.
Aside from that, you should arm yourself with WordPress and web-related knowledge to help you figure out what’s best for your website.
What is Malware?
Software that exploits a website’s security flaws in order to carry out unwanted operations is commonly referred to as malware. In the context of WordPress sites, malware can negatively impact a site’s performance on every level, including the web server, user experience, and even SEO. In other words, if you ignore what’s going on with your website now, you might find out too late to save it.
In order to create a secure WordPress site, you must monitor the performance of your site and detect changes as they occur.
What are different types of malware?
It comes in a variety of shapes and sizes, each of which can cause its own set of problems. Here are some of the most frequent types of malware to be aware of:
Get exclusive access to all things tech-savvy, and be the first to receive
the latest updates directly in your inbox.
- Adware – displays unwanted advertising items on your website automatically.
- Spyware – collects data invisibly to steal sensitive information.
- Trojans— malicious software that masquerades as legitimate software in order to deceive people into running a deadly programme. It may change the appearance and content of your site on its own in some situations.
- Virus– contain malicious code that corrupts files and spreads throughout a website. It’s generally accompanied by a spike in server usage.
- Ransomware– encrypts a website until a certain amount of money is paid.
You may be suffering from a malware infection if you notice any of the above symptoms on your website.
Furthermore, it can affect the search engine optimization (SEO) ranking of your website. If Google finds a site infested with malware or deemed hazardous, it will display a warning.
This is why protecting your WordPress site from malware should be your first priority.
What can a malware do to your site?
Despite the fact that WordPress is well-maintained and secure, it does contain a number of flaws that might expose your site and its visitors to malware threats. As a result, paying close attention to the security of your website is critical.
The following are some of the dangers posed by malware:
- Unwanted alterations to your content or website, such as items being added or removed without your consent.
- Sensitive data, such as users’ personal information, has been compromised.
- Spam can take the shape of emails or questionable links propagated through your website.
- Your URL is being diverted to shady websites that promote scams, improper content, or dangerous advertisements.
- A sudden increase in server resource usage.
- Your site has been flagged as dangerous by Google in both the browser and search results.
- SEO’s negative impact.
How to detect malware in WordPress site?
There are various methods for determining whether or not your WordPress website has been hacked or infected with dangerous code or malware.
The most crucial aspect of being protected against any danger is prevention, which means we must take specific steps to remove malware from our WordPress site and safeguard it.
The most important thing for WordPress users to do is to keep their sites updated to the most recent stable version available; a new version usually fixes common WordPress Vulnerabilities discovered in earlier versions. Furthermore, it is critical to do the same with the plugins we use, as well as to remove any that we do not utilize.
Run An Antivirus Scan
Because most new WordPress website owners don’t immediately install a security scanner, malware or malicious code injection can be undetected for a long time. A comprehensive virus removal tool can help identify hidden malware and safeguard your site effectively.
As a result, the optimum time to search your website for malicious code and malware is right now. Many users will not detect that their website is malfunctioning until it is too late.

Even if your site hasn’t been hacked or isn’t infected, you should learn to scan it for harmful code. It will aid in the prevention of future attacks on your website.
Furthermore, knowing the correct tools and methods to utilize will help you strengthen your WordPress security and lock down your site like a pro.
Wordfence is a popular WordPress security plugin that lets you quickly scan your WordPress site for suspicious code, backdoors, malicious code and URLs, and known patterns of infections.
It will automatically scan your website for common online threats, but you can also launch your own in depth website scan at any time.
Scan with Wordfence (If you have WordPress admin access)
Click on Plugins → Add new from the left hand side menu
Search for Wordfence, and install and activate.
Now, you can easily Go to Dashboard → Wordfence from the left hand side menu to scan your WordPress site.
List Files By Modification Date
Accessing files via FTP and sorting them by modification date is one of the quickest ways to find possibly harmful files. As a result, people who have recently experienced some form of change will display first.
If we haven’t made any changes to them, it could be a sign that there is some kind of code inside that is creating the issue.
The drawback with this technique is that you must go through all of the site’s folders to find each of the infected files, which can be a time-consuming task if the code has been inserted in a big number of files.
You can use below command to find out recently modified files
find /home/domain.com/public_html -mtime -2 -ls
You will have to replace /home/domain.com/public_html with actual path of your site.
You can also find modified files in last 5 days using
find /home/domain.com/public_html -mtime -5 -ls
You can also use grep command to find refrences of base64 encoding which is most commonly used by hackers.
grep --include=*.php -rn . -e "base64_decode"
In the following command, all directories and subdirectories are searched for files that end in .php, and any files that contain the text string “base64_decode” are printed along with the line number, so you can see where it appears in each file.
Backup your WordPress Site First
The first thing to do before moving forward is to backup your WordPress site.
It is crucial to be able to backup files on your WordPress website. You have a fail-safe in place if your website is hacked or if you need to restore your site to a prior version by periodically backing up your website.
You run the danger of losing all of your hard work if you don’t have a backup mechanism in place. This is something you wouldn’t want to happen to your worst enemy.
Before trying to recover your site, lets backup files and database so that we can revert to point A when things go south. The following items must be saved:
- Your MySQL database
- Your website data
To do so, follow the steps below
- Go to your CyberPanel dashboard account and click on list website
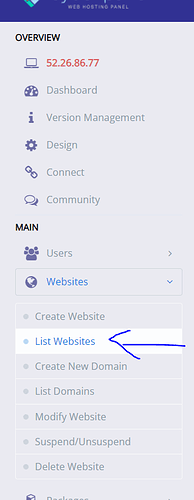
- Click on your site’s file manager
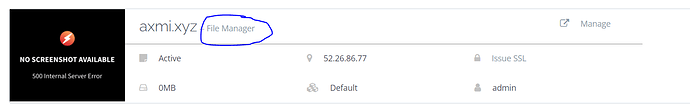
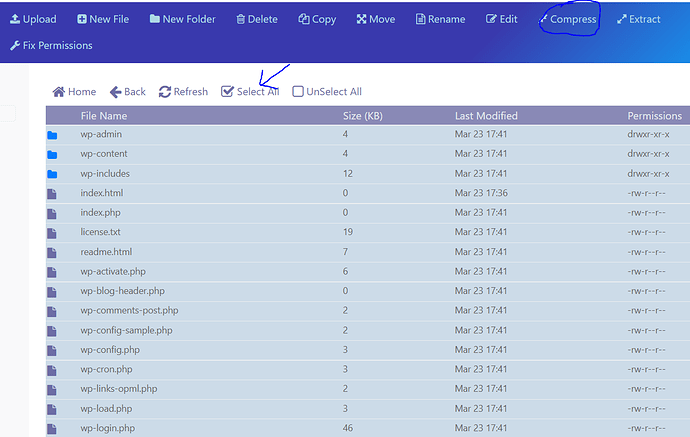
- Open
public_htmland select all files and click on Compress
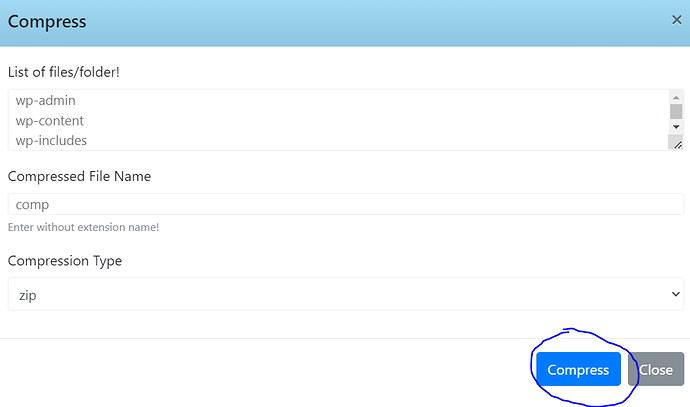
- Name the file and Select Compression Type and click on Compress
- Right click on your zip file and click download
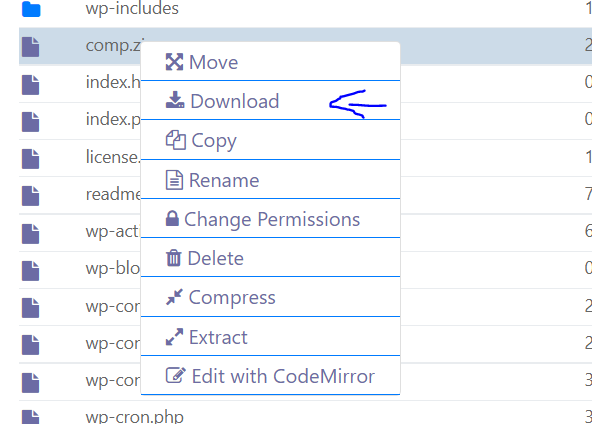
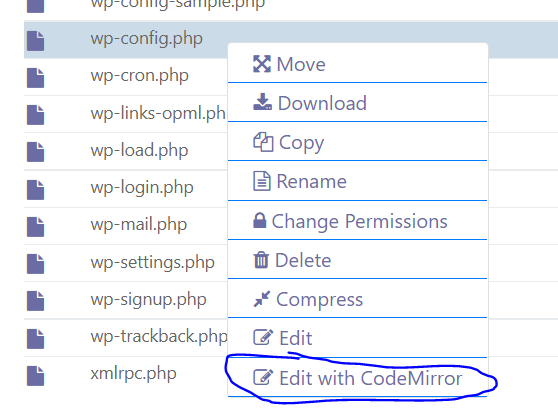
- Right click on
wp-config.phpand click on Edit with Code Mirror
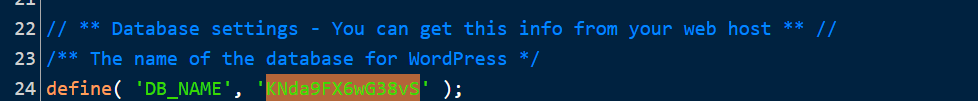
- Note your database’s name
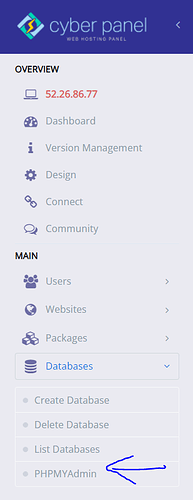
8.Go to Dashboard → Database → PHPMyAdmin from the left hand side menu
- Find your database from the left hand side menu and click Export
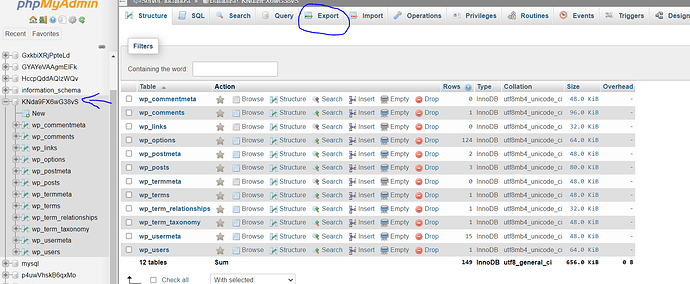
- Fix your format and click on Go
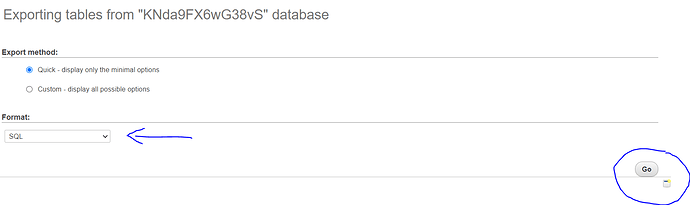
Method 1: Remove WordPress Malware by Replacing files from Original WordPress Files
Open your file manager → public_html. Select all files except for wp-content and wp-config.php and click Delete
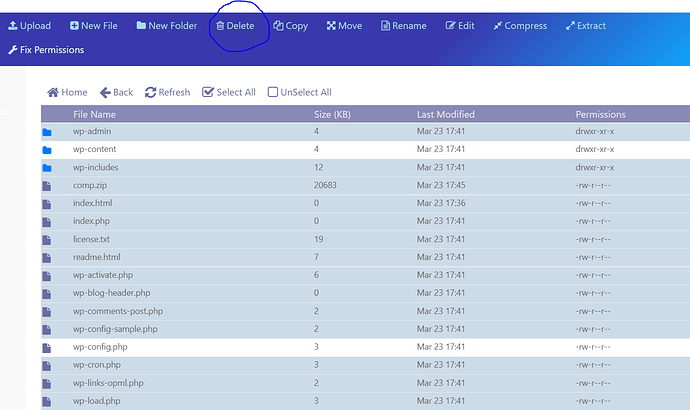
- Click on Upload and upload your default wordpress zip folder, you can download that from here.
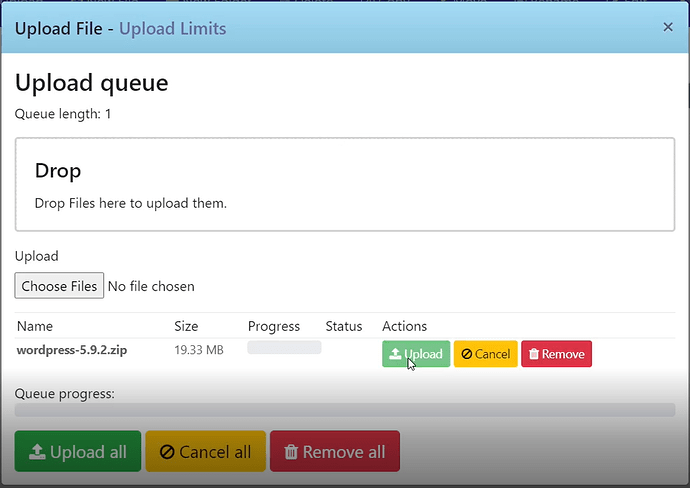
- Open your zip file by selecting your file and clicking Extract
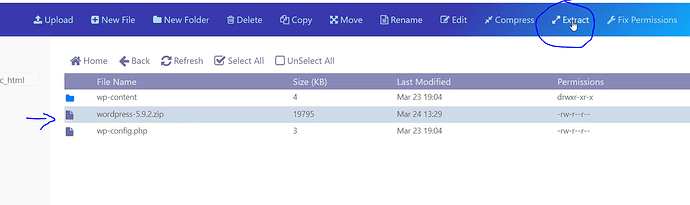
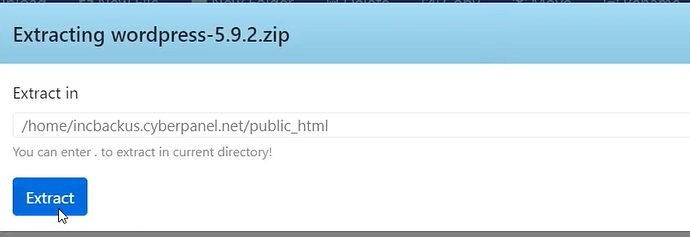
- Open your extracted folder and select all files except for “wp-content” and click copy
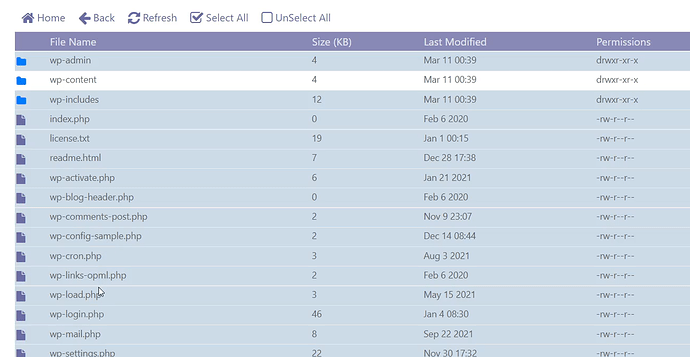
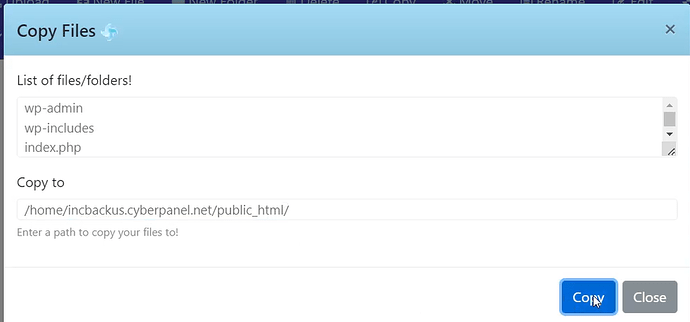
- Set the right path and click Copy
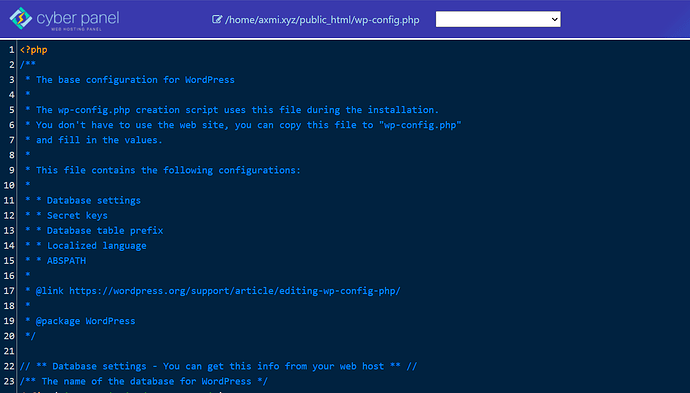
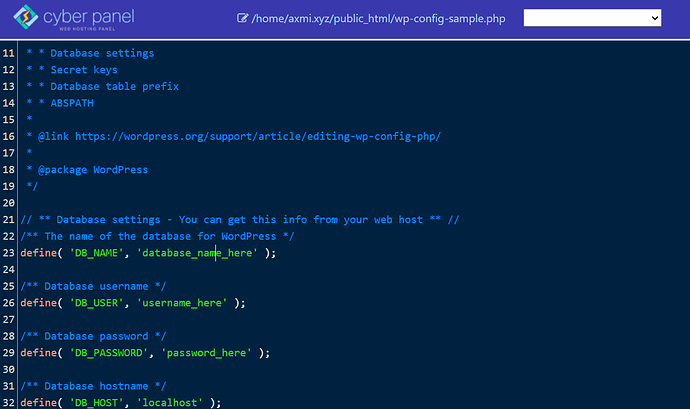
- Open
wp-config-sample.phpandwp-config.phpand compare the two files for malicious code and remove if you find any.
Method 2: How to remove malware from a WordPress site If you have WordPress Access?
Go to your WordPress Dashboard
Click on Plugins → Add new from the left hand side menu
Search for Wordfence, and install and activate.
Now, you can easily Go to Dashboard → Wordfence from the left hand side menu to scan your WordPress site.
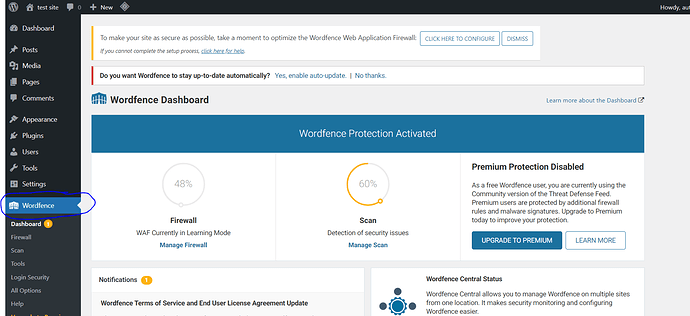
It’s possible that you’ll get a lot of results that you’ll have to sort through. Each result will explain what Wordfence discovered and walk you through the process of fixing it.
You can go much further with your investigation. On the left, go to the “All Options” menu.
Scroll down to the “Basic Scan Type Options” header and click the option for “High Sensitivity.”
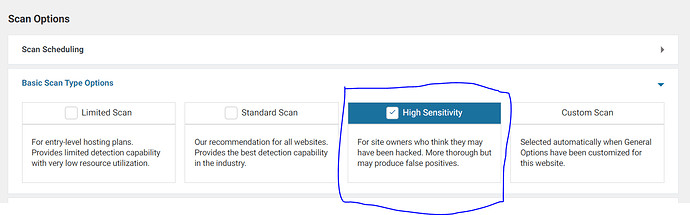
On the left, click on scan and start another scan. This will perform a far more thorough scan that will take a little longer, but it will uncover highly obstinate malware that is difficult to detect and remove.
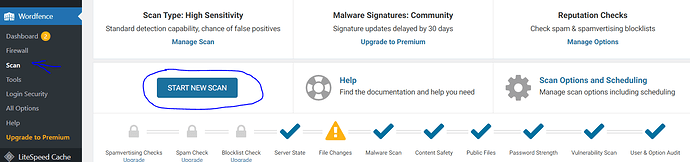
If you want to run more scans, go to the “All Options” page and tailor your Wordfence scan to your specific needs. Make as many scans as you want.
When the findings are displayed, you may notice a lengthy list of infected files. Take your time and go over the list one by one.
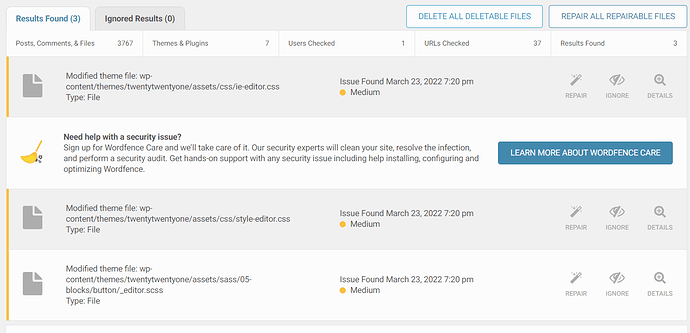
Examine any questionable files and either clean them up by hand or delete them entirely. Remember that deletions are irreversible. You can always restore the file if you remove the wrong thing if you took the backup we mentioned above. Examine any modified core, theme, or plugin files. To view what has changed between the original and your file, use the Wordfence option. If the modifications appear to be malicious, fix the file with Wordfence. Work your way down the list until it’s completely empty. Confirm that your site is clean by running another scan.
Deactivate Plugins/Clean Up WP-Themes
The most likely way that WordPress has been hacked is through a vulnerability in a plugin or theme. Alternatively, you may have obtained the software for free from untrustworthy sources.
- Deactivate all plugins and run a WordFence scan on the site.
- Then, one by one, activate the plugins and scan the site to see which one is creating issues.
- Make adjustments to the required plugin or remove it and reinstall it.
- Scan and detect malware in WordPress themes, ensuring that we download themes from the original source and replacing the files in the folder with the name of the template in
/wp-content/themes/with the freshly downloaded. - You will lose any modifications you made to these files without using a child theme if you did not use a child theme.
- The next step is to replicate the previous steps, but this time with the plugin folders. We’ll have to download and replace the clean plugins from their respective repositories.
- That is, delete the plugins’ folders from
/wp-content/plugins/and replace them with the new files.
Change Passwords
One critical step you should do is to update all of the passwords associated with your website.
- All users with administrator privileges should change their passwords.
- Change the password to your hosting panel’s access.
- Change the password even if you don’t use FTP often.
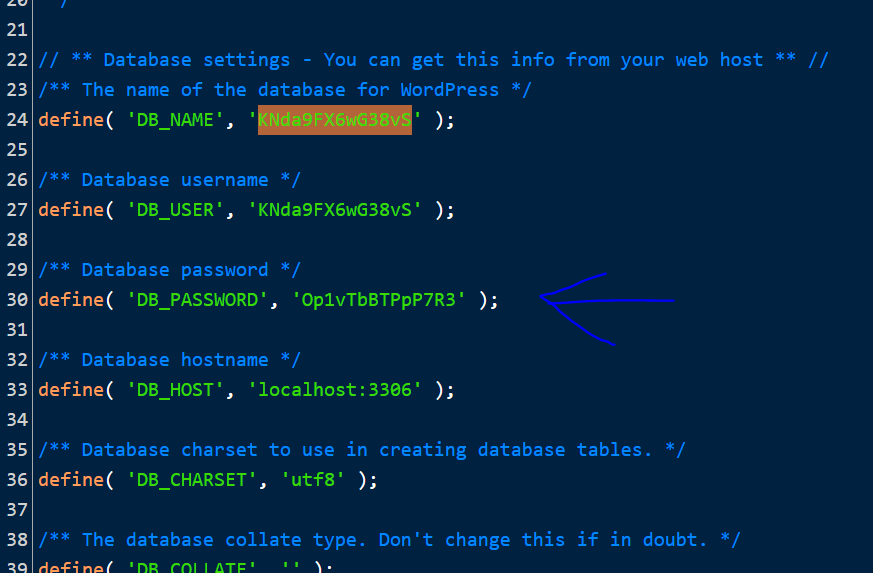
- Finally, the database user’s password should be changed.
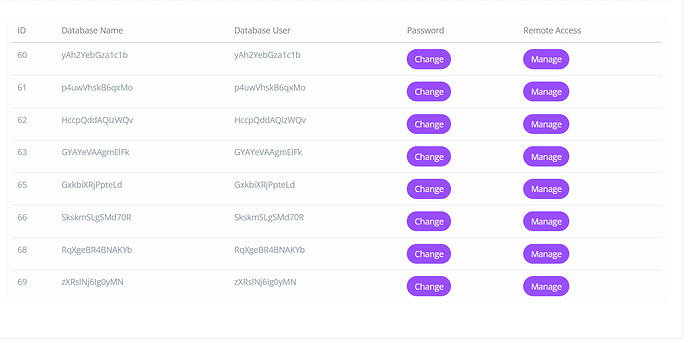
To change database’s passwords, Go to Dashboard → Database → List databases, from the left hand side menu
Select your site
Change your passwords here
Make sure you update it in the wp-config.php or else the web will not work properly and will not connect to the database.
Remove Default ‘admin’ Account
Some hackers register on your WordPress site and use malicious scripts that take advantage of any flaw in their theme or plugin.
Go to Dashboard → Users → Add new
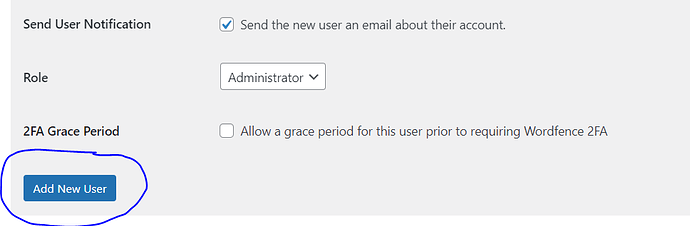
Fill in the information and select role “Administrator” and click “Add new”
Login using the new info and delete the previous user.
Lock WP Login
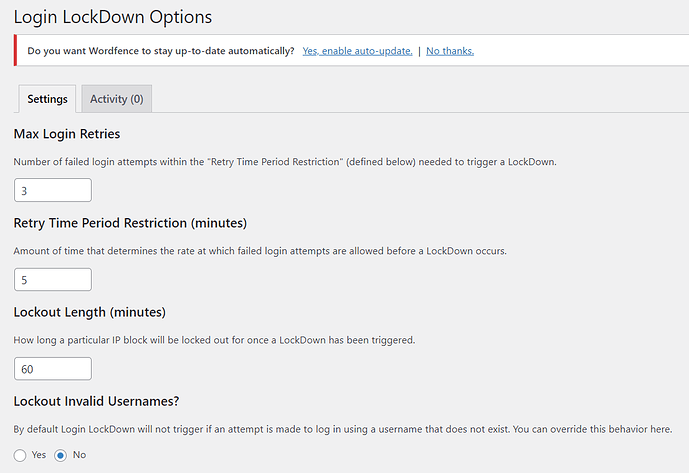
By default, you can access to your WordPress administration with as many login/password pairs as you wish. Every failed WordPress login attempt is recorded by Login LockDown, which saves the IP address and timestamp. When a particular number of login attempts from the same IP range are discovered in a short period of time, the login function is disabled. This protects your WordPress site from brute force attacks by preventing brute force password finding.
Go to Dashboard → Plugin → Add new from the left hand side menu
Search for “Login LockDown” . Install and activate
Click on Settings → Login LockDown
This is the page to configure the plugin settings to lock the WP login
Install Security Plugins
WordPress security, despite being pretty good, is not perfect, as you have discovered in your own flesh. That is why it is critical that you take the time to install multiple points of security reinforcement.
Change Hosting Provider
Perhaps, after all of this WordPress cleaning, it’s time to consider switching hosting providers. Contact your hosting provider first; if they are unable to assist you further, get a new, more dependable hosting company with superior customer care.
Indeed, the infection of your website was not caused by the security of your hosting, far from it. But it all adds up, and having a solid server with well-established security procedures is critical.
Request Google Security Review
We can use the “Request a Review” tool in the same prior menu next to the warning that your website includes hazardous software to ask Google to rethink the website once you’ve cleared up all traces of malware.
You should write a brief report outlining the steps you took and how you resolved the hack and send it. Wait for the outcome to be emailed to you once you check your website.
It should be simple to remove “Google Blacklist Warnings” if everything has been done correctly.
Conclusion
You’ll need to be patient and cautious while following all of the WordPress virus removal techniques outlined until your website is clean and functional once more.
True, the infection could have gone a step farther and infiltrated the code database. In this situation, recovery is more difficult since all of the tables must be searched for specific patterns that are employed as harmful code.
It’s also true that these techniques may not always result in a comprehensive cleaning, necessitating the use of more artillery and a magnifying glass to locate the source of the problem.
However, following cleaning procedures frequently solve the most common WordPress hacks.



