Samba Linux has become a popular choice for providing file and print services in mixed network environments. It serves as a crucial link between Windows and Unix-like systems, promoting collaboration and resource sharing across different platforms. The adaptability, security, and wide range of features offered by Samba make it a favored option for organizations looking for interoperability and smooth integration among various operating systems.
This is an easy guide to understand what is Samba Linux and how to Install Samba in Linux, and how to restart it in MX Linux. Let’s learn along!
What is Samba in Linux?
Samba is a software suite that enables smooth interaction between Windows, Linux, and Unix operating systems in a network. It allows these systems to share files, printers, and other resources, enabling users on various platforms to work together and access shared resources easily.
The Server Message Block (SMB) Protocol is a communication protocol used by clients and servers to share access to files, printers, serial ports, and other network resources. The Common Internet File System (CIFS) Protocol is a version of the SMB protocol. A dialect refers to a set of message bundles that outlines a specific variant of a protocol.
Main Components and Features
File Sharing: Samba Linux enables file sharing across various operating systems by using the Server Message Block (SMB) protocol. This allows Windows clients to access shared folders and files on Linux and Unix servers as if they were on a Windows server. Likewise, Linux and Unix clients can access shared folders on Windows servers.
Print Services: Samba offers print services, enabling printers connected to Linux or Unix servers to be shared with Windows clients. Windows computers can send print jobs to these shared printers, while Samba manages the necessary protocol conversions and communication with the print server.
Get exclusive access to all things tech-savvy, and be the first to receive
the latest updates directly in your inbox.
Authentication and Authorization: Samba supports various authentication methods, including integration with Windows Active Directory (AD) or acting as a standalone authentication server. Users can authenticate using their Windows domain accounts or local Samba accounts, ensuring secure access to shared resources based on user permissions and access control lists (ACLs).
Name Resolution: Samba works with the Domain Name System (DNS) and NetBIOS Name Service (NBNS) to resolve hostnames and provide name resolution services. This allows systems to discover and connect to each other using their names.
Security: Samba includes security features such as encrypted communication through the Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) and Transport Layer Security (TLS) protocols. It also supports access controls and permissions management to safeguard shared resources from unauthorized access.
Integration with Windows Networking: Samba can integrate into Windows networking environments, allowing it to join Windows domains or workgroups. This integration facilitates smooth collaboration between Windows and non-Windows systems in a mixed network setting.
There Are 5 Main Tasks You Can Do With Samba Linux
- First, you can share a Linux drive with Windows computers.
- Next, we can access an SMB share from Linux machines.
- We can also share a Linux printer with Windows systems.
- Share a Windows printer with Linux devices.
- Finally, we can set up a domain controller on a Unix/Linux server and connect Windows clients to it.
- Samba can work as either a domain controller or a regular domain member, making it essential for mixed networking environments that include both Windows and Linux machines.
How to Install Samba in Linux?
Installing Samba Linux isn’t rocket science, here’s exactly what you need to do!
Installing Samba
To set up Samba, first log into your Linux server using a user that has sudo privileges or as the root user. Start your commands with the “sudo” command. Then, connect a Windows computer to the Linux server.
Update Linux Samba
sudo apt update && sudo apt upgradeTo install Samba, we run:
sudo apt update
sudo apt install samba
We can check if the installation was successful by running:
whereis samba
The following should be its output:

samba: /usr/sbin/samba /usr/lib/samba /etc/samba /usr/share/samba /usr/share/man/man7/samba.7.gz /usr/share/man/man8/samba.8.gzBasic Samba Configuration Steps
After setting up your basic Samba server, you might want to look into advanced configurations that can improve functionality and security. Once Samba is installed, we must configure it to match our setup and standards. Before configuring Samba on our Linux machine, we need to check the workgroup on our Windows computer.
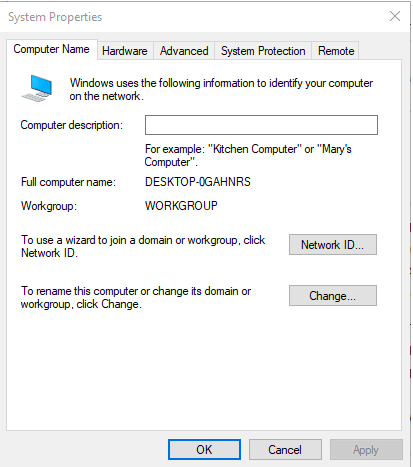
To do this, right-click on “This PC” or “My Computer” → Properties → Advanced System Settings → Computer Name, which will display a window containing the information we need.
These are more detailed steps for further help setting up Samba on a Linux system:
- Use cmd to show information about the workstation domain.
- Make a backup of the original configuration file, named smb.conf_orig.
- Set up Samba for anonymous file-sharing by creating a directory named “anonymous_shared_directory.”
- Set the right permissions on the directory and adjust the SELinux security context for the samba shared directory.
- Open the /etc/samba/smb.conf file using your preferred CLI text editor (like Nano or Vim).
- Set up the anonymous share by adding and modifying directives.
- Run ‘testparm’ to check the configuration.
- Save the changes and exit the text editor.
- Check the current samba settings by executing the following command.
- Load the services file successfully.
- Press enter to view a dump of service definitions.
- Adjust your firewall to work with Samba.
- Open the csf.conf file with your selected text editor.
- Add the necessary ports to the right section.
- Save the changes and refresh the firewall rules.
- Start Samba services and make sure it starts automatically on system boot.
Implementing User Quotas
User quotas let you control how much disk space each user can utilize in your shared directory. This prevents any one user from using all the available storage on your Linux Samba server. You can establish quotas with tools like quota or edquota.
Enabling Encryption
Encrypting data provides an additional layer of security, particularly for sensitive data. You can activate encryption in your Samba configuration by including:
encrypt passwords = yesThis guarantees that passwords are securely stored on your Linux Samba server.
How to Restart Samba in MX Linux
If you are on MX Linux restart Samba, you can restart the Samba service just as you would on any Debian-based distribution:
<br>sudo systemctl restart smbdYou can also verify its status:
<br>sudo systemctl status smbdIf you encounter problems, consider restarting both smbd and nmbd:
<br>sudo systemctl restart smbd nmbdConclusion
Samba Linux is one of the easiest ways to share files between Linux and Windows systems. Setting up a Linux Samba server is a great method for sharing files between various operating systems.
It provides flexibility, saves costs, and allows for centralized file management. Using Zentyal can make this process even easier with its easy-to-use interface and strong features. By following this guide, you can establish a working file-sharing setup that meets your organization’s requirements with a dependable Linux Samba server.
FAQ’s
1: What is Samba in Linux and how does it work?
Samba is a free tool that allows file and printer sharing between Linux/Unix and Windows systems. It uses the SMB/CIFS protocol for smooth communication across different platforms, making it simple to access Linux shares from Windows and the other way around.
2: How do I install Samba on a Linux system?
You can install Samba through your package manager. For instance, on Debian-based systems like Ubuntu or MX Linux, you can run:
sudo apt install sambaAfter installing, configure the smb.conf file to set up your shared folders.
3: How do I mount a Samba share in Linux?
To mount a Samba share, use this command:
sudo mount -t cifs /// /mnt/mountpoint -o username=your_usernameEnsure that the cifs-utils package is installed first for proper mounting.
4: How do I restart Samba in MX Linux?
You can restart Samba in MX Linux with this command:
sudo systemctl restart smbdYou can also check its status with:
sudo systemctl status smbd


