Docker is an open-source tool for creating manageable, lightweight, and portable containers. These containers package your application with all the dependencies, configuration settings, and files into one container to run uniformly across different development environments.
Containerization ensures that a standard practice is followed wherever it is deployed. It helps avoid the issue of “it works on my system.”
What is a Docker registry?
While talking about Dockers, it is essential to understand the concept of the Docker registry. A Docker registry is a storage and management system for Docker images. It ensures reliable and scalable storage and management of shareable container images, making them easily accessible for deployment.
Registries can be public (like Docker Hub) or private, with features such as versioning, secure access, and integration with Docker tools.
How to use a Docker Registry?
- Push an Image: Upload a Docker image to the registry using the command Docker push.
- Pull an Image: Download a Docker image from the registry using the command Docker pull.
- Search for Images: Find images hosted in the registry.
Key features of a Docker registry include image storage, version control, distribution, security, and integration.
What Is A Docker Hub?
While building modern applications, you should take advantage of the containerization process using Docker. After containerization, your application will be pushed and tagged into a public repository, like a Docker Hub.
Get exclusive access to all things tech-savvy, and be the first to receive
the latest updates directly in your inbox.
So, what exactly is a Docker Hub?
Docker Hub is an open-source, scalable, and cloud-hosted version of a Docker registry. It is a service for distributing and locating containers for an image within a team. It is the most comprehensive image repository online with all content sources, including open-source projects and application source code.
Developers can access Dockers publicly and create a private repository to automate applications and build custom functions, work groups, and webhooks.
Key Features Of Docker Hub
Key features of a Docker Hub include:
- Image Repository: Save and share public or private container images
- Automated Builds: Automatically build images from code
- Webhooks: Notify tools and apps for image changes
- Tagging: To organize your images with versions easily
- Security: Image verification to ensure safety
- Integrations: Works smoothly with CI/CD tools like GitHub and Jenkins.
- Team Collaborations: Share with the team effortlessly
- Official images: Ready-to-use images for regularly used software
- Search: Easily look up for millions of images
- Access Tokens: Secure login
- Cross Platform compatibility: Supports various systems across the ecosystem.
How Docker Hub Works
Here is how a Docker Hub works step-wise:
1. Storing Images
You can either use:
- Push images: Developers can build and upload images on their system using the command Docker push to the Docker Hub.
- Public repositories are free and accessible to all.
- Private repositories are on restricted access for secure storage.
2. Searching For Images
Users can search for images using the web interface or the Docker CLI. Or access millions of pictures from trusted software and community-contributed images.
3. Pulling Images
To use an image, use the command Docker pull to download an image in the system. This makes the image available locally to create containers.
4. Automating Build
Docker Hub connects to source code repositories such as GitHub and Bitbucket. When you change the code, the Docker Hub automatically builds and updates the image.
5. Team Collaborations
Docker Hub allows organizations to make developer teams for managing repository access and working on shared images while controlling permissions.

6. Notifications With Webhooks
Docker Hubs trigger webhooks to notify external systems whenever a user uploads or updates an image.
7. Securing Images
DCT ensures image authenticity and security so that users can manage access tokens, passwords, and permissions for repositories.
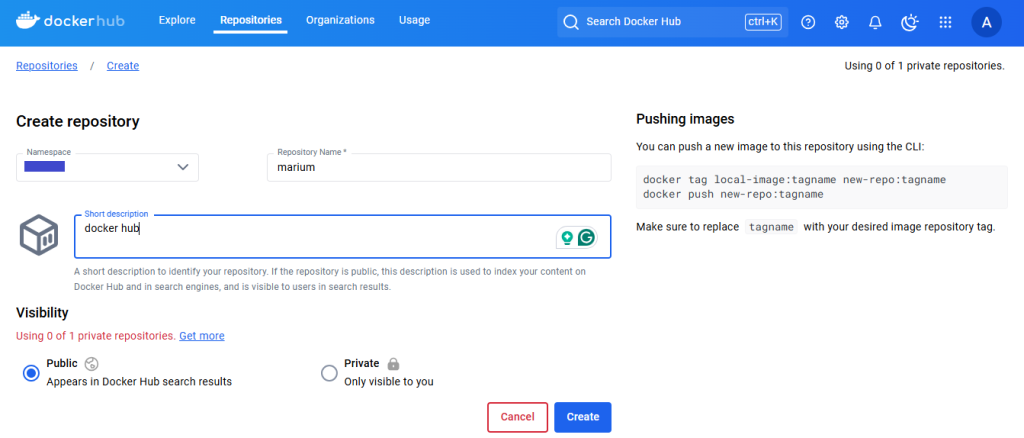
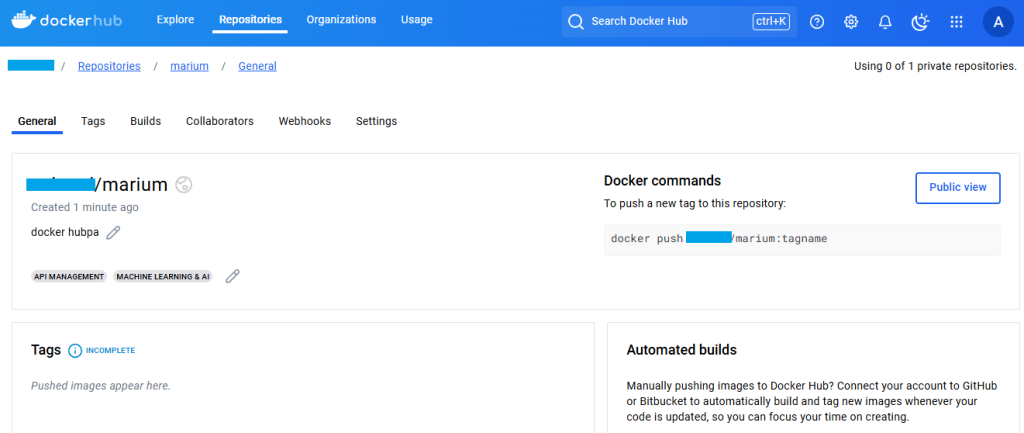
Example: Pushing And Pulling Docker Images
This example shows how you can push a Docker image to the Docker Hub and then pull it from the coding environment when needed.
Step 1:
Build a Docker image using a simple Dockerfile for a Python application.
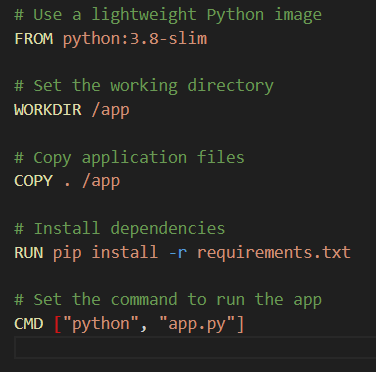
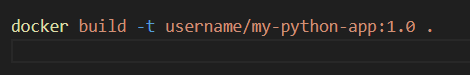
Then build the image:
Step 2:
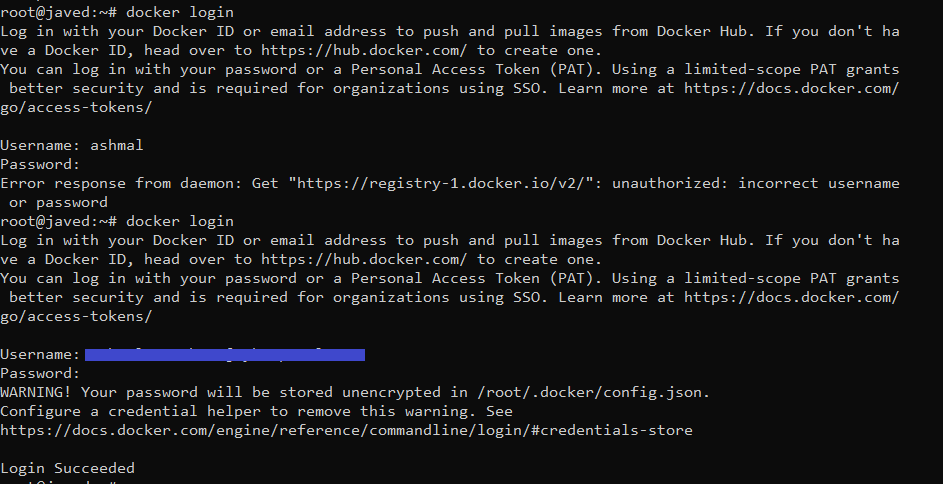
Push the image to the Docker Hub. Login to the Docker Hub using your admin name and password.
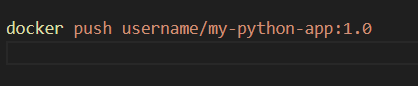
Push the image to be saved into your private or public repository.
Step 3:
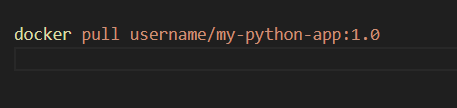
Pull the image on another development environment.
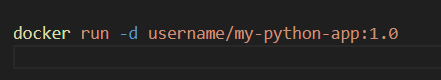
Using the pulled image, run the container.
How To Find And Use Docker Hub Token
Docker Hub tokens are a perfectly secure way to authenticate API requests without using private credentials. Here is how you can find and use them easily.
1. Locating Your Docker Hub Access Token
- Login to your Docker Hub with your username and password.
- Go to your profile icon and tap on account settings.
- From the left-hand menu, tap security and then access tokens.
- Click on Create Access Token and name it accordingly before tapping on Generate.
- Copy the access token and keep it safe for later again.
- You won’t be able to see the token once you have copied it.
2. Using The Token For Authentication
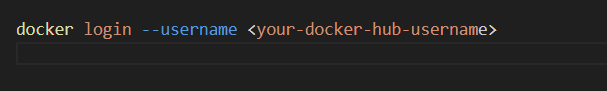
- For Docker CLI
Log in using your username and token in place of your password.
- For automation
Use the saved token as an access bearer token while calling the API.

Using access tokens keeps your private information secure and is perfect for automation.
Public Vs. Private Repositories
Learning their proper use cases and differences is essential to use private and public repositories appropriately.
| Feature | Public Repository | Private Repository |
| Access | Open to all | Restricted to authorized users |
| Cost | Free | Free (limited) or paid plans |
| Use Case | Open-source/community projects | Proprietary/sensitive projects |
| Security | Less secure | Highly secure with access control |
Here are some more details to differentiate between the two.
Features
Public repositories:
- Anyone can pull images without any authentication.
- Increases visibility, use, and reach of the images.
- Ideal for open-source projects.
Public repositories:
- Restricted access; therefore, only people with appropriate permissions can pull images.
- Keep images secure and only available to use within the project.
- Only selected collaborators can be invited.
Advantages
Public repositories:
- Unlimited pulls and free
- Good for the ecosystem
Public repositories:
- Ideal for teams working on private systems
- Enhanced security for product-based images
Disadvantages
Public repositories:
- No control over images
- Not suitable for sensitive images
Public repositories:
- Limited repositories in the free version.
Best Practices For Using Docker Hub
Keeping the best practices in mind is extremely important; here are a few to follow:
- Use a small image size to fill the space smartly and remove unnecessary files.
- Use proper and meaningful tags with the version.
- Enable Docker Content Trust.
- Scan images for vulnerabilities.
- Use access tokens for security.
- Name and organize repositories clearly for ease of use.
- Use smart collaborations to manage permissions.
- Connect to GitHub.
- Track API usage and scale on demand.
Wrapping Up
Docker Hubs are crucial to organizing, managing, and storing container images. Docker Hubs can organize your project in more ways than one by keeping it easily scalable and secure. It provides the proper flexibility that you need for a comfortable coding environment.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Is the Docker Hub free?
Docker Hub offers free and paid plans with different numbers of public and private repositories and features.
2. How do I push an image to Docker Hub?
Use the command Docker push after you tag your repository name, build an image locally, and log in to your account.
3. What are Docker Hub rate limits?
The free plan offers 100 pulls per six hours. Paid plans provide a different limit and unlimited pulls for specific features.
4. How do I automate builds on Docker Hub?
Connect your Docker Hub to an open-source repository like GitHub or BitBucket. It would automatically update builds for new images.
5. How do I scan Docker images for vulnerabilities?
Docker Hub offers a native feature for scanning vulnerabilities. This helps identify malicious images.



