Penning ports in Linux is an extremely basic skill for those who are given the responsibility of server administration or networked application management. Ports are really merely communication pathways between systems and applications. For example, most web traffic uses port 80 for HTTP and port 443 for HTTPS. Other services and applications work smoothly only if they have to use certain ports. Knowing how to open a port in Linux is very important for the performance of tasks such as hosting websites, enabling remote access, and running database servers.
This is how different distributions of Linux, including Ubuntu, CentOS, and RedHat, provide tools like ufw (Uncomplicated Firewall), firewalld, and iptables for port management. Each tool opens, closes, and monitors ports in a different way, allowing administrators control over network traffic and, above all, security. Also, if you know what a closed port means for your Linux, then you are, certainly, advanced in solving connectivity issues, and will know that such closed ports may “clog” applications working.
The guide will use these tools, opening the port within a Linux system, where each distribution has its specific needs or steps involved for one to pass through. The guide offers temporary and permanent solutions while considering how best to use security, but the system allows network access when necessary. Whether you are new to or advanced in Linux, this guide should give you just enough knowledge to carry out any kind of configuration in network access.
Understanding Ports in Linux
What Are Ports?
Ports are simply numbered channels that organize network traffic to particular processes or services. Each port is assigned a unique number, ranging from 0 to 65535, and applications use these numbers to send and receive data. In the case of Linux, ports are managed at the level of the operating system, with only the intended application able to access its specific port.
Types of Ports
Well-known ports (0–1023): These are used for core services and protocols such as HTTP uses port 80, and HTTPS-443.
Registered ports (1024–49151): Used by user applications and services, like MySQL uses port 3306.
Get exclusive access to all things tech-savvy, and be the first to receive
the latest updates directly in your inbox.
Dynamic/private Ports (49152–65535): Most often used for dynamic connection or ephemeral port
Port Security Implication
Controlling open ports is important in server environments that stop unauthorized access and attacks. Every open port constitutes an entry, and thus it is of great importance to know how to open a port in Linux securely and only when need be. Monitoring open ports can prove to be very effective in keeping things secure.
How To Check If A Port Is Open In Linux
These are the most widely used methods to how to check a port is open in Linux by command-line tools.
Checking if a port is open using netstat
Above, you have been taught how to use the netstat command, which provides statistics pertaining to network files. Sometimes it might be essential to know whether or not a port is open.

- -tuln: Shows only listening TCP and UDP ports in numeric form.
- <port_number>: Replace with the specific port you want to check.
For example, to check if port 22 is open:

Using ss
ss is another command-line tool to view socket information, similar to netstat, but faster.

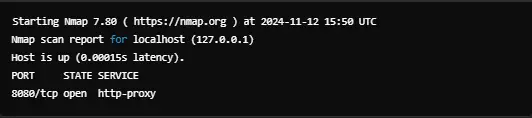
For example, to see if port 8080 is open:


Using nmap
The nmap tool is a powerful network scanning utility. To check if a port is open, install nmap and use the following command:

How to Open a Port in Linux Using ufw
ufw (uncomplicated firewall) is the user interface for the iptables firewall and is preferable in Ubuntu-based systems since it minimizes the steps needed to manage the rules of the firewall.
Opening a port in Linux with ufw
Enable ufw if Not Active:

If ufw is not activated, start it with the following command:

Now, to open a specific port, you can use the following command:

Example: You can use the following command to open port 8080 for TCP traffic::

To allow a range of ports, you can use:

Example: To open ports from 3000 to 4000:

You can also restrict access to a port from a specific IP:

For example, to allow SSH access from IP 192.168.1.10:’’

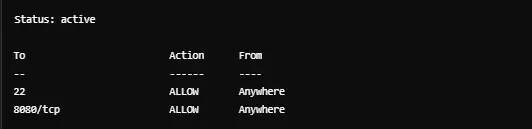
Checking The Status of ufw
You can check which ports are open by using the following command:

Opening Ports in Linux with iptables
iptables is much more complex than ufw and can detail its control over network traffic much further.
How to Open a Port with iptables Step by Step
Allow access to a particular port:
This will open port 8080 for TCP traffic.

Allow a Range of Ports:

Allow Port for Specific IP Addresses:
To open port 22 for a specific IP, use:

Save iptables Rules:
To persist iptables changes, save the rules depending on your distribution:
For Ubuntu/Debian:

For CentOS/RHEL:

Check Port Status in iptables:
To check the status of specific ports, use:


How To Open A Port In Linux Using Firewalld
firewalld is a dynamic firewall manager. It is mainly used on CentOS, RHEL, and Fedora.
How to Open a Port using firewalld
Opens a Given Port:
To open port 8080 for TCP traffic:

To apply the changes, reload firewalld:

Allow a Range of Ports:
To allow ports from 3000 to 4000:
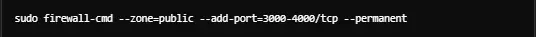
Open Ports Temporarily:
To open a port temporarily without making it permanent:

Confirm Open Ports in firewalld:
To check open ports:


Troubleshooting Open Ports in Linux
If you are unable to open a port, here are some troubleshooting tips below:
Check for Conflicting Services: Make sure no other services will already be using your port.
Verify Firewall Rules: Sometimes there can be conflicting firewall rules with your open port rule. Try checking with ufw status or iptables -L.
Check SELinux (Security-Enhanced Linux): If SELinux is activated, then it might simply prevent the port from opening, even though the firewall rules would otherwise allow its opening. Use the following to disable it temporarily:

Check Running Services: If the service you are trying to allow the incoming communication through a port is not running and/or configured correctly.
Management of Open Ports Using CyberPanel
CyberPanel i.e. an open-source web hosting control panel eases the management of open ports, especially with web hosting and server management needs. It is an advanced web hosting control panel that integrates OpenLiteSpeed, hence not strenuous with the user interface when handling server admin tasks like security issues such as firewall rules and management of ports. The user can easily handle security protocols, change their firewall rule, or even allow or deny entering into ports using CyberPanel.
Key features offered by CyberPanel in port management are as follows:
Firewall Management: Configuration settings of the firewall can be done directly from the control panel without using any manual command-line operations. The beauty of this approach is that it saves time, and the complexity of manual command-line operations is reduced.
Simplified Interface: GUI offered by CyberPanel provides easy visual management of ports, cutting down the need for technical skills.
Security Improvements: This package has security features blocking will prevent access to open ports based on the IP address. This shields against unapproved access.
One who uses CyberPanel finds managing open ports easy and runs a secure environment for hosting services without necessarily treading with whatever Linux knowledge may be needed.
Linux FAQs on Opening Ports
1. How would I check if a certain port is open in Linux?
You can verify an open port using tools like netstat, ss, or even nmap to see the status of specific ports in your system.
2. Can I open several ports in one?
Yes, there are tools like ufw, iptables, and firewalld, which allow you to open several port ranges by specifying start and end ranges, such as 3000-4000.
3. How would I allow a specific IP address to access only one port?
The following commands with an IP, such as sudo ufw allow from <ip_address> to any port <port_number>, limit which accesses your specified IP.
4. Can a port be closed after it is opened?
A port can be closed from the CLI using the deny or delete commands on ufw or by removing the rule from iptables, or firewalld.
5. What is the most accessible way to close ports on Linux for newbies?
For newbies, the easiest method is probably ufw, and another is CyberPanel – a graphical tool for managing ports not requiring the use of the command line.
6. How do I open a port in Linux?
You can use the following command:sudo iptables -A INPUT -p tcp --dport PORT_NUMBER -j ACCEPT
Culmination
To sum up, in securing your Linux environment, managing open ports is one essential feature while providing necessary services with the vulnerabilities at bay. So, covering in this guide, methods of checks, opening, and troubleshooting ports using tools such as ufw, iptables, and firewalld. Besides, CyberPanel has also posed a sleek method of port management that has simply simplified its meaning for people who may not be familiar with the technical aspects of setting up firewall configurations on servers.
Get ready to simplify port management, and increase server security. Learn how to start with CyberPanel today and know how you can have a smooth interface in managing all of your port configurations, firewall settings, as well as your server security. Read on and find out what you need to know about CyberPanel for the kind of performance that’s packed with efficiency and security.



