Ifconfig commands are one of the basic commands in Linux networking. Basically, it is used to configure and manage various network interfaces. However, with newer commands such as ip in modern distributions these days, ifconfig is still popular among network administrators and enthusiasts of Linux. It enables users to manage IP addresses, troubleshoot network connectivity, and configure network interface settings important for maintaining a Linux system’s network stability and operation.
Here we’ll discuss the common uses, syntax, and examples of using the ifconfig command effectively. We’ll also show how the most advanced web hosting control panel, CyberPanel, can make the management of your network much easier while also improving the control over your server.
What is the ifconfig Command?
It stands for “interface configuration”. This command is a powerful command-line utility established to control and administer network interfaces on Unix-like systems. Traditionally, the ifconfig command is used to let you view the IP addresses assigned and to modify such addresses on network interfaces. This command enables network administrators to connect a specific interface, Ethernet or Wi-Fi, and troubleshoot some interfaces as well.
For example, if the servers fail to connect, the running of ifconfig provides a snapshot immediately regarding which IP addresses, subnet masks, and broadcast addresses are being used by every network interface. This makes the networks in the servers and other appliances connected run better since the configuration settings are accomplished through the use of the command ifconfig.
Linux ifconfig Command Options
| Option | Description |
| -a | Shows configurations for all network interfaces, even inactive ones. |
| -s | Displays a summary of network interfaces. |
| -v | Provides an expanded configuration view for network interfaces. |
| interface_name | Specifies the interface name and displays its configuration details. |
| down | Deactivates the specified network interface. |
| up | Activates the specified network interface. |
| [IP_address] | Assigns an IP address to a network interface. |
| Netmask [address] | Sets a custom subnet mask for the interface. |
| Broadcast [address] | Defines a broadcast address for the network interface. |
| mtu [number] | Sets the Maximum Transfer Unit (MTU) for the interface. |
| promisc | Enables promiscuous mode, allowing the interface to capture all packets. |
| -[promisc] | Disables promiscuous mode. |
| arp | Enables the Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) for the interface. |
| -[arp] | Disables ARP for the interface. |
| allmulti | Turns on all-multicast mode to receive all multicast packets. |
| -[allmulti] | Turns off all-multicast mode for the network interface. |
Syntax and Basic Usage of ifconfig Command
The syntax of the ifconfig command is very simple. Just type the following command and you will get all the status of the network interfaces:

The command will display all the available network interfaces and their respective IP addresses, subnet masks, and MAC addresses. Here’s the basic syntax:
Get exclusive access to all things tech-savvy, and be the first to receive
the latest updates directly in your inbox.

interface: This is the network interface, like eth0 or wlan0.
options: Other options define more configurations like the possibility of specifying an IP address or enabling/disabling interfaces.
address: assigns an IP address to an interface.
Basic Example of ifconfig Command and Its Output

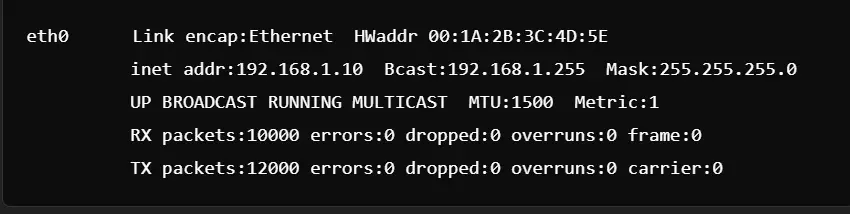
This command displays the configuration of the eth0 interface, showing details such as the IP address, subnet mask, and hardware address (MAC address).
ifconfig Advanced Options and Configurations
Static IP Address
To assign a static IP address to an interface, you would use:

This sets the IP address to be 192.168.1.100 and assigns the subnet mask 255.255.255.0 to the eth0 interface.
Enable/Disable Network Interfaces
To enable or disable network interfaces, you would use the ifconfig command as shown below:
Enable Interface: ifconfig eth0 up
Disable Interface: ifconfig eth0 down
One feature explains this because disabling and re-enabling an interface solves the connectivity issues.

Setting A Broadcast Address
The ifconfig command helps you set a broadcast address for an interface

This command assigns the broadcast address 192.168.1.255 to eth0, which is useful for network-wide communication.
Examples of ifconfig Command in Action
Viewing All Network Interfaces

Changing the MAC Address of an Interface
To set a custom MAC address:

This is helpful for privacy or security reasons, as some network services rely on MAC addresses for identification.
Comprehensive Guide to the ifconfig Command in Linux
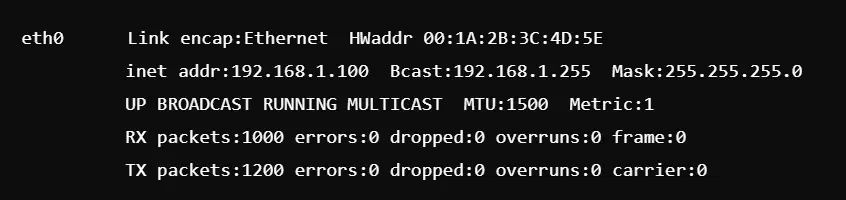
1. ifconfig Command For Linux
The ifconfig command in Linux is the most powerful tool for configuration, management, and troubleshooting of network interfaces based on Linux systems. Here’s how it works:
Basic Command Example:

This command displays all active network interfaces, showing details like IP addresses, MAC addresses, and packet statistics.
2. ifconfig command in Ubuntu
You probably won’t find the command ifconfig pre-installed under Ubuntu. In this case, you can install the net-tools package to enable the installation of the command ifconfig:

After you install it, you are able to run ifconfig to view network configurations, which is especially useful with Ubuntu server editions where you will be doing a lot of network management.
3. Run command ifconfig on Windows
The Windows version of the command is ipconfig, which achieves the same goal. Displays network information about Windows systems. It can be quickly used to show IP addresses, subnet masks, and default gateways for an interface.
Windows Example

4. ifconfig Command Not Found
If you are getting the ïfconfig command not found” error, it means that net-tools is not installed on your Linux system. You can resolve this by installing net-tools:

5. ifconfig Command on Linux for IP Address
To display the IP address of a specific interface, you can filter ifconfig results. For example:


Use cases of the ifconfig Command: 20 Examples
Show All Active Interfaces
It displays all active interfaces in the system along with the IP address, MAC address, netmask, and broadcast address.

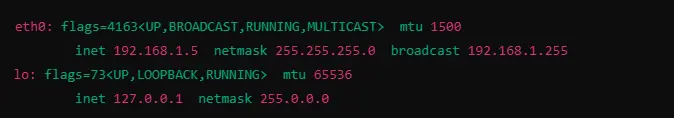
Information for Specific Interface eth0
It only shows information for a specific interface that is mentioned (e.g. eth0), and which is useful to check if a particular interface is alive or not.

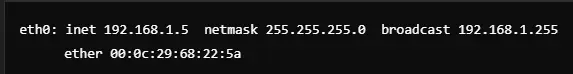
Static IP Setting
It is used for setting a static IP along with the netmask to an interface, mostly at servers or for special kinds of network setup.

Turn ON the Interface
Enable the network interface online, and enable the device to start communication on a network.


Disable Interface
This is used to disable an interface but does not remove its configurations; this command can be useful for diagnostic purposes or when testing.


Set MTU
It assigns the maximum transmission unit of packet size; this is usually implemented if there are specific requirements that require a minimum packet size or fine-tuning for better network performance.


Change MAC Address
This changes the MAC address for testing or to bypass certain restrictions based on MAC address restrictions set up in the network.


Add Alias (eth0:1)
Attach an alias IP for adding multiple IP addresses across a single physical interface such as virtual hosting or subnetting.


Disassociate an Alias
This method detaches an alias IP address from the interface with use cases being during some changes in network configurations.


Setup Broadcast Address
this kind of setup sets the broadcast addresses on the interface it’s a type of set that enables sending packets out to all network devices across it.


Show Network Counters
It displays detailed, but basic transmission and receives packet counters and error information to address a problem within the networks in terms of transmission and drops of packets.


Set Interface Metric
It associates a numeric metric with an interface, the routing decision when there are several interfaces available.


Set Subnet Mask
It makes further subnet precision possible by setting the subnet mask within IP addresses.
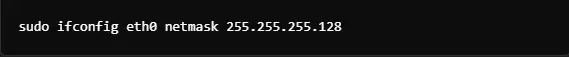

Show MTU Setting Only
extracts the MTU value of an interface, for a quick view of packet size limits on a network connection.


Show IPv4 Addresses
It shows all IPv4 addresses that are connected to active interfaces: handy for network inventory.

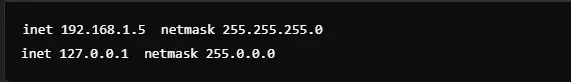
Enable Promiscuous Mode
It enables the interface to capture all packets irrespective of whether they are not destined for it. Often used in packet analysis and troubleshooting.


Disable Promiscuous Mode
Toggles off promiscuous mode to put the interface back into normal operation, restricting it to only the intended traffic.


Check MAC Address Only
It quickly shows the MAC address of the specified interface, which can be helpful for network configuration or troubleshooting.


Enable Multicast Mode
Enable an interface to perform processing on multicast packets – it is typically applied to the goal of video conferencing or streaming.


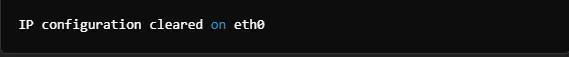
Clear IP Configuration
It reinitializes IP address configuration on a specific interface. This is typically set before associating another new IP.

Integration of ifconfig Command with CyberPanel for Advanced Network Management
CyberPanel is a very powerful web hosting control panel. It provides a simple interface for the management of the network. Administrators can configure the network settings with the help of CyberPanel without knowing the deep details about the command lines, especially the ifconfig command. For example, when you host multiple websites on a server, you need to assign different IPs to each site. This may be facilitated by CyberPanel by its integration with the ifconfig command to simplify IP management and server configurations.
FAQs on the ifconfig Command
1. What is the difference between ifconfig and ip command?
Both are associated with the management of network interfaces; however, ifconfig is part of the older package, net-tools while ip is part of the newer iproute2. Most of the new distributions prefer to use ip instead of ifconfig.
2. Do I use ifconfig for setting DNS addresses?
No, ifconfig can’t manage DNS configuration. You keep DNS in /etc/resolv.conf.
3. How can I get my public IP using ifconfig?
ifconfig only returns private IPs. If you want your public IP use curl ifconfig.me or curl ipinfo.io
4. Can I ever use ifconfig for debug purposes?
Yes, you can debug using ifconfig. For example, if you see that some packets are dropped or if you see any error in the ifconfig, then you know something is wrong somewhere.
5. How do I rename an interface using ifconfig?
You can’t make ifconfig natively change the names of interfaces. You can though using ip link set.
6. What does ‘MTU’ in ifconfig output represent?
MTU is the abbreviation for Maximum Transmission Unit, an interface parameter that defines the maximum size of packets transferred over the interface. The change in MTU might help if the network performance is poor under certain conditions.
Conclusion: Fine-Tune Your Linux Networking with the ifconfig Command
The ifconfig command remains a very important tool for network administrators and has made the management of network interfaces on Linux systems much easier. From setting static IPs to enabling or disabling interfaces, ifconfig is pretty flexible and in control over networking configurations. If one uses CyberPanel, the tasks can be easily done with user-friendly management tools that integrate with ifconfig to make server administration even simpler. From all that has been described above with the examples on the same, you will now know how to install and troubleshoot your network under Linux.
Use all this today and master control over your network with ifconfig commands under Linux!



