Businesses are redefining IT management standards in 2024.
Consider a large company that has reduced the footprint of its data centers by seventy percent through Server Virtualization. This technology is undoubtedly revolutionizing how businesses manage resources, boost efficiency, and adapt in an increasingly digital world to stay competitive. It is a cost-effective way to provide web hosting services and effectively utilize existing resources in IT infrastructure.
It sounds easy right? Well to know if it is that simple you’ll have to read through the whole Article.
Before jumping into further details on our topic, Here’s a quick background for you on what Servers are.
Servers are the backbone of technology. They are software or hardware devices that handle, store, and process data as well as provide services to other computers connected to a network a single operating system and a certain set of programs are installed on each physical server, which results in insufficient use of resources and increased expenses.
Here’s an example to make it simple: A user can set up a server, for instance, to handle print jobs, send and receive email, host a website, and restrict network access.
Get exclusive access to all things tech-savvy, and be the first to receive
the latest updates directly in your inbox.
Understanding Server Virtualization?
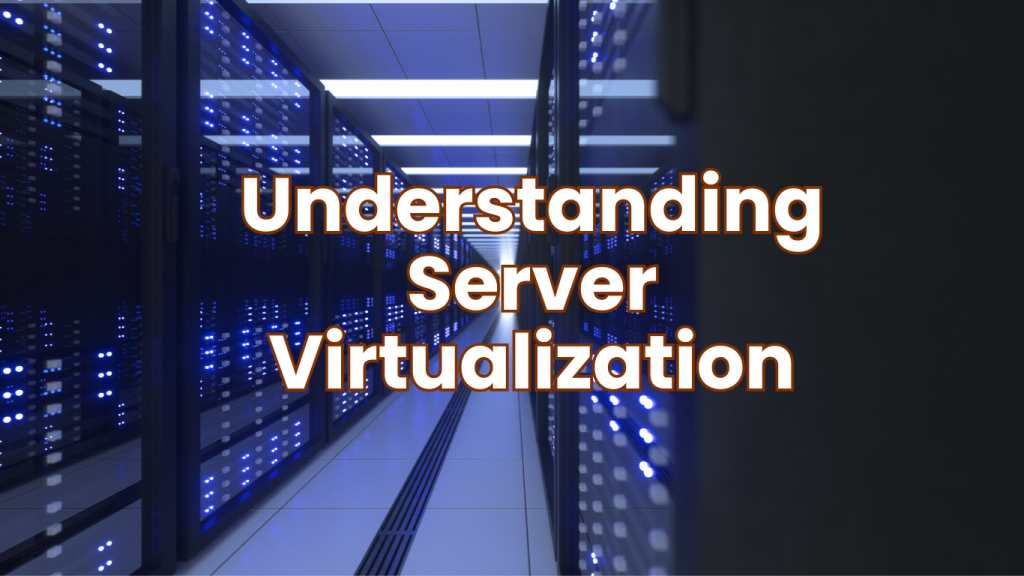
Now, the main focus of our discussion today is server virtualization and its key concepts.
Everything changed with the introduction of server virtualization.
In the past, computer hardware and software worked as a resource-conscious processing power designed to support only one application at a time, leading to inefficiencies and increased demands on resources as businesses expanded their use of applications and services.
The process of separating a physical server using software into several distinct and isolated virtual servers is known as server virtualization where each virtual Server can operate independently from its operating system.
Server virtualization is the underlying basis for cloud computing and enables various hybrid cloud models. A company can maximize its complete infrastructure’s processing, storage, and networking resources while using or offering web hosting services at a reasonable cost.
Types Of Server Virtualization
Here are 4 Server Virtualization types you should know about.
The hypervisor
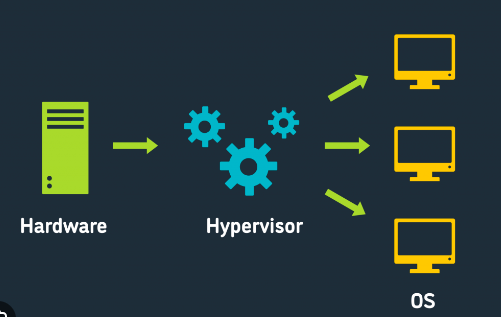
Between the operating system and the hardware, there is a layer known as a hypervisor or VMM (virtual machine monitor). It offers the features and services required to efficiently operate several operating systems. The hypervisor treats resources like CPU, memory, and storage as a pool that can be easily reallocated between existing guests or to new virtual machines.
In addition to handling the queuing, dispatching, and returning of the hardware requests, it recognizes traps and responds to privileged CPU instructions. The hypervisor is topped by a host operating system that controls and manages the virtual devices.
Hypervisor has Further 2 Types:
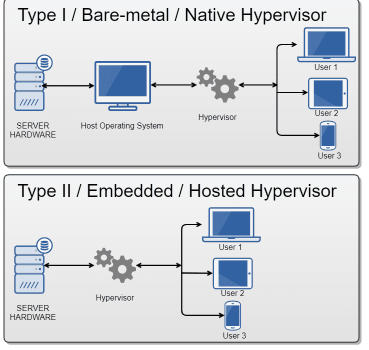
Type 1 Hypervisors (Bare-Metal): Operates without the need for a major operating system, directly on the host computer’s physical hardware. It controls guest operating systems through direct hardware interaction. Due to its efficiency and performance, this type is frequently used in enterprise settings.
Examples: VMware vSphere/ESXi, Microsoft Hyper-V, and Xen (used by AWS for its EC2 service).

Type 2 Hypervisors (Hosted): It is an application or software layer on a traditional operating system, that separates the host and guest operating systems for scheduling virtual machine resources.
Example: VMware Workstation, Oracle VirtualBox, Parallels Desktop (for Mac).
Para-virtualization
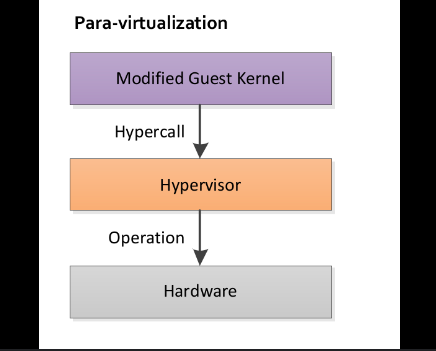
Para-virtualization is another Server Virtualization type, the servers in also utilize a hypervisor, but they do not perfectly replicate the hardware of the physical host. Instead, an API, typically integrated into modern servers, directly interacts with the operating systems of the host and virtual servers. As a result, the virtual servers recognize the resources of the host and other virtual servers as an extension of their own.
Involves the entire network working together as a cohesive unit. Since each operating system on the virtual servers is aware of one another in para-virtualization, the hypervisor requires less processing power to manage the entire system because the VMs handle it well.
The virtual machines (VMs) on the host server are not isolated from each other. They can interact over the network despite their relative independence.
Today, para-virtualization is less commonly used as servers are now being designed to more effectively support and work with bare-metal hypervisors.
Example: Amazon EC2 and Xen.
Kernel level Virtualization
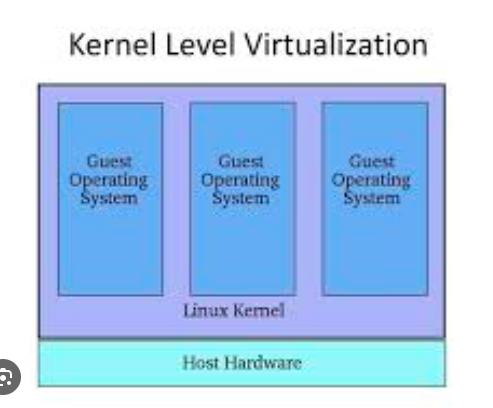
Kernel Level Virtualization is another type of Server Virtualization system that operates a different Linux kernel and perceives the linked virtual machine as a user-space process on the physical host, doing away with the need for a hypervisor.
Running several virtual machines on a single host is made simple by this. The virtual machine and the main Linux kernel communicate via a device driver.
Virtualization requires processor support (AMD – v or Intel VT).
The virtual machines’ execution and display containers are slightly modified QEMU processes. Kernel-level virtualization can be thought of as a more advanced version of server virtualization.
OS-Level Virtualization
This Server Virtualization type enables the use of multiple virtual environments without the need for a hypervisor. This type of virtualization, also known as “containerization,” utilizes the virtualization capabilities of the host operating system as the hypervisor. Processing takes place within each server’s “container” or virtual environment and is limited by the available resources.
For this virtualization method to function, it must be compatible with the same operating system as its host. It is widely used to improve today’s complex software environment’s security, manageability, and availability, with small runtime and resource overhead.
Example: Docker
Key Benefits Server Virtualization Can Bring Your Business
Here’s a list of advantages businesses can get after leveraging the right Server Virtualization OS.
Higher server Adaptability
Virtual machines (VMs) offer increased adaptability by allowing companies to install various operating systems on the same physical hardware, unlike traditional physical server installations that lack this flexibility.
Cheaper Operating Costs
Server Virtualization Saves money by integrating Servers, minimizing the amount of hardware needed, and getting rid of unnecessary or idle resources. as businesses seek scalable and cost-effective IT infrastructures.
Deploy Workload Quicker
It helps quickly and easily duplicate and clone virtual machines (VMs) and move them to multiple host servers as needed to expedite the deployment of workloads such as Windows, Linux, or Apache.
Increased Application Performance
It provides greater application performance due to using virtual machines (VMs) for dedicated workloads.
Simplified Physical Infrastructure
By minimizing the number of servers, racks, and cables in the data center, the company improved its physical infrastructure and is now able to achieve the same computing objectives with less power, cooling, and space.
Efficiency and Productivity in Businesses
Enhanced IT efficiency and productivity through the reduction of server sprawl and the intricate upkeep and control of numerous physical servers.
Disaster Recovery
Server Virtualization enhances disaster recovery capabilities through features like live migration and automated backups.
Server Virtualization: Real-World Applications 2024
Let’s find out how Businesses and Organizations are making use of server virtualization in today’s competitive digital time and space as continuous advancements in server virtualization technologies, enhancements, and containerization are shaping the market landscape.
See the following real-world Server Virtualization Applications in various industries and Businesses that are game-changers.
Healthcare
- Electronic Health Records (EHRs): they provide secure, scalable solutions for storing and managing patient data.
- Telemedicine: Enhances the reliability and performance of telemedicine platforms, enabling remote consultations and healthcare delivery.
- Medical Research: Facilitates high-performance computing for data-intensive research projects, accelerating medical discoveries.
Education
- Virtual Classrooms: Supports robust online learning environments, offering scalable resources for virtual classrooms and e-learning platforms.
- Research Labs: Enables the creation of virtual labs where students can access software and tools without needing high-end hardware.
- Administration: Streamlines administrative tasks by consolidating multiple servers into a virtual environment, reducing costs and improving efficiency.
Finance
- Trading Platforms: Ensures high availability and low latency for trading applications, crucial for financial institutions.
- Data Analysis: Supports big data analytics and real-time processing for risk management, fraud detection, and customer insights.
- Regulatory Compliance: Provides secure, isolated environments for handling sensitive financial data, and meeting regulatory requirements.
Retail
- E-commerce: Enhances the scalability and performance of e-commerce platforms, ensuring smooth customer experiences during peak times.
- Inventory Management: Facilitates efficient inventory tracking and management by integrating various data sources into a virtualized environment.
- Customer Insights: Supports data analysis and personalized marketing strategies through scalable computing resources.
Manufacturing
- Production Management: Optimizes production processes by running multiple applications on a single physical server, improving operational efficiency.
- Supply Chain Management: Enhances the management of supply chains by providing real-time data processing and analytics.
- IoT Integration: Supports the integration of IoT devices and sensors in manufacturing processes, offering real-time monitoring and control.
Server Virtualization: Impact on Small and Large Enterprises
Let’s dig a little deeper into how or if it affects Businesses whether they’re Small Scale or Large Scale.
Small Enterprises
- Cost-effectiveness: By combining several virtual computers on fewer actual servers, this approach significantly lowers hardware and maintenance expenses.
- Scalability: Offers an adaptable and scalable IT infrastructure that can easily expand to meet the needs of the growing firm.
- Operational Flexibility: Promotes innovation and agility by enabling the rapid deployment and testing of new services and applications.
- Enhanced System Performance: Reduces downtime and optimizes resource utilization to improve overall system performance.
Big Enterprises
- Resource optimization: will reduce costs and improve operations by maximizing the use of resources throughout a sizable infrastructure.
- Enhanced Security: Provides strong security features, such as virtual environment isolation, which is essential for safeguarding private information.
- Global scalability: Facilitates worldwide operations by delivering dependable and uniform IT infrastructure across several sites.
- Disaster Recovery: By enabling quick recovery and little downtime during failures, disaster recovery strengthens business continuity and disaster recovery plans.
- High Availability: Guarantees high availability and uptime for vital applications, preventing disruptions to business processes.
Server Virtualization: 6 Top Emerging Trends 2025
These days, most people consider server virtualization to be a commodity. The technology businesses are using these days.
Tech professionals must adjust to the changing landscape and seize the opportunities presented by emerging trends to prosper in this fast-paced industry. Server Virtualization is one such trend that is influencing the direction of IT infrastructure. It is a powerful technology that aids in resource optimization, increases organizational agility, and lowers costs and its future is presently being shaped by some significant themes that show a dedication to increased productivity, adaptability, and creativity.
Here’s a list of 6 trends businesses should keep themselves updated with:
AI and Machine Learning Integration: Used for optimizing resource allocation and predictive maintenance and enhanced security procedures that use AI to quickly identify and address risks.
Serverless Computing: It streamlines the development process simplifying deployment and allowing Apps to scale flexibility when demand increases, freeing developers to concentrate only on the logic of the application rather than on infrastructure issues.
5G and Network Virtualization: By utilizing 5G technologies to enhance virtualized environment network connectivity and performance.
Containerization Revolution: Rise in containerization with tools like Kubernetes, enabling efficient management of microservices architectures, as they offer lightweight scalable solutions that make it easy for businesses to deploy and manage everything.
Software-Defined Infrastructure (SDI): Increased automation and more flexible IT infrastructures have benefited from the use of SDI, and software-based unified management has centralized control over virtualized resources.
Disaster Recovery and Business Continuity: Providing technologies for fault tolerance and continuous availability in virtualized environments and improved automated failover systems for business continuity during disruptions.
That’s all for the trends, We must remember that Server Virtualization will evolve with every new trend that emerges in the IT infrastructure, the process never stops. We as humans, specifically Businesses need to keep a close eye on what’s latest and how it can help meet their dynamic Business needs.
Server Virtualization: 5 Drawbacks and Solutions
Because server virtualization offers so many advantages, possibly one might overlook some of its drawbacks that businesses are forced to address at some point.
1) Running High-Demand Applications: Virtualization isn’t suitable for servers running high-demand applications because it splits the server’s processing power among multiple virtual machines. This division can lead to significant slowdowns when the server’s CPU can’t handle the load, causing tasks to take much longer and potentially leading to system crashes.
Solution: Network administrators should carefully evaluate CPU usage before implementing virtualization on such servers.
2)Backups: Creating backups can be challenging due to frequent software changes.
Solution: Using tools like Windows Server Backup can make the process more efficient, centralized, and convenient.
3)Licensing Compliance: If you exceed the number of licensed VMs allowed for the program, using licensed software in a virtual environment could lead to compliance issues.
Solution: Please ensure compliance with licensing when building virtual machines (VMs) and also monitor the usage of licensed software as the virtual environment expands to ensure compliance.
4)Software Compatibility: Not all software is designed for virtual environments, which can limit the number of compatible servers and applications. Although improving, software licensing is still challenging.
Solution: Conduct extensive compatibility testing before deploying new software in a virtualized environment.
5)Scalability Issues: Virtualization can complicate scaling operations. As virtualized networks grow, they may slow down because multiple network components share the same resources. This can be problematic for organizations looking to expand and utilize these shared resources effectively.
Solution: Evenly distributing workloads across virtual machines and physical servers, load balancers will ensure efficient resource utilization by preventing any single server become an obstacle.
How Do I Choose the Right Server Virtualization Platform?
We have selected the best Server Virtualization Platforms any Small-scale or Big Scale Business may use to meet their specific needs.
- V2 Cloud: V2 Cloud is a robust virtualization platform for remote desktop and application provisioning for small and midsized businesses (SMBs).
- Oracle VM Virtual Box: another renowned virtualization platform. DevOps teams leverage VirtualBox to achieve cost reductions and accelerate the secure deployment of applications.
- VMware vSphere: is a robust, scalable, and centralized virtualization platform that offers businesses comprehensive resources for managing virtual environments.
- Microsoft Azure Hyper-V: hypervisor integrated into Windows Server operating systems, enables seamless management of virtualized environments through its integration with Microsoft ecosystem tools like System Center.
- Citrix Workspace: With its centralized management, secure access, and streamlined application distribution across several platforms and devices, assures the safe delivery of desktops, apps, and data to end users.
Final Thoughts
Server Virtualization is the next big thing in IT, there is no doubt about that. The purpose of this article is to equip businesses with the current wave of virtualization. Which will fundamentally alter data centers, virtualization is not a new “holy grail of IT” and has always been a component of IT.
It’s crucial to understand the purpose of each technology and learn how to use it effectively rather than getting carried away by the recent excitement surrounding it.
We have discussed the types, benefits, the challenges you might face, and how they enable organizations to make the most of resources, reduce costs, and ensure that business transformation is consistent. With its many benefits and wide range of uses, server virtualization is an essential requirement for any organization hoping to stay competitive in the ever-evolving business landscape.



