Are you still wondering about the best Linux distros? Don’t look further. CyberPanel got you covered and going to tell the top 10 Linux Distors.
Linux has emerged as a strong, flexible, and improved operating system that offers several distributions to suit the requirements of many users. It delivers various distros to its users, from beginners and developers to gamers and enterprise professionals. Each distro is bolstered by unique features, customization options, and performance improvements while catering to the preferences and workloads of different users. Hence, in this scenario, the right distro of Linux can decide on your productivity, security, and user experience.
We will be discussing the top 10 Linux distros, what makes each of these distros different, and look at some gaming-specific distros. We also talk about best practices for optimizing your Linux setup and how CyberPanel plays a very important role in managing servers across a variety of Linux environments. Whether stable, easy to use, or highly optimized for particular tasks, this in-depth overview will guide you on which the best distro is for your needs.
Linux Distros and Their Importance
A Linux distro refers to a version of the open-source Linux operating system. It involves a combination of kernel and a set of system utilities, together with various software tailored to specific user needs. Such Linux distros differ in package management, default applications, desktop environments, and additional features. Although coming from the same kernel, all Linux distros are bound to make provision for a variety of users-from casual users to developers, gamers, or IT professionals.
Importance of Linux Distros
Customization: Linux distros can be customized to a great extent. Users can choose their preferred distro which is relevant to their needs and further tailor their environment. While some distros, like Ubuntu and Linux Mint, are more usable, others like Arch Linux present a more technically developed version with a very lean setup suitable for technically able users.
Performance: All distros are optimized differently according to each performance requirement. Lightweight distros like Puppy Linux or Lubuntu are specifically built in the lightest way to run on an old machine, achieving efficiency in the allocation of system resources. Others like Fedora or Debian are designed in a more general manner to give the best possible performance with premium hardware and more high-end applications.
Get exclusive access to all things tech-savvy, and be the first to receive
the latest updates directly in your inbox.
Security: Linux distros have well-known solidity in security features. Because the Linux code is open source, it’s monitored by developers all around the world who scan its code for vulnerabilities and patch them immediately. In addition, distros like CentOS and Debian are mainly applied on servers since they have long-term stability and security.
Open-source philosophy: All Linux distributions tend to support the open-source philosophy. Most want to empower users and give them greater control over their software; they can see and change the source code of the distro they have selected for use. Thus, this builds a culture of transparency in software development and widely provides users with control over their software. This aspect is more critical in days when proprietary software tends to limit the powers of the users.
Diverse Use Cases: There are some diverse use cases with distros. For instance, some are built for cybersecurity professionals and ethical hackers, such as Kali Linux, while others, like Ubuntu Studio, are optimized for creative professionals and provide software that deals with audio and video production. As such, it is easy to find the most suitable distro for your work environment.
Cost-Effective Solutions: Since most of the Linux distros happen to be free to use, it is a cost-effective alternative for both individuals and organizations alike. For example, server distros like CentOS or Debian have no expensive license fee charges, which therefore saves on operational costs while at the same time having healthy, secure systems. However, do not confuse the cost-effectiveness of a free to use Linux distro with the need to combine it with a cheap Linux VPS. The cost of cheap often carries a higher price tag than the one you initially pay for it. So make sure to do adequate research beforehand including any ongoing website maintenance costs and hidden fees.
Top 10 Best Linux Distros
1. Ubuntu
Ubuntu is one of the top Linux distros mainly for usability and wide application. It is very suitable to begin using for novices since it provides a friendly interface, substantial community support, and versions that get long-term support for stability. Ubuntu also comes with a large software repository through apt, making it a very good package for developers, general users, and administrators.
Why choose it?
Very easy to use, always updated, and offers long-term support.
Suitable for: Beginners, developers, and system administrators.
Example of Code: Updating and Upgrading the Ubuntu System
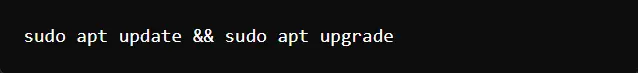
This command will fetch the latest package lists and install updates. It provides real-time progress on installed packages.

2. Fedora
Fedora is one of the ultra-sleek Linux distros, known for its latest innovation with open-source software. Maintained by Red Hat, it has been acting as a TestBench for the features that will eventually appear in the RHEL. It is often used by developers for developer tools and libraries.
Why choose it?
New software, strong developer features, and focus on security.
Suitable for Developers, sysadmins, and open-source enthusiasts.
Code Sample: Install dnf for package management

This command will install the specified package. It also displays the details about dependencies and installation status.
3. Debian

Debian is preferred for its stability along with its long release cycle, thus preferred by both servers and advanced users that require stability over cutting-edge new features. It is a base for other popular distros like Ubuntu and comes with an enormous repository of software.
Why prefer it?
Stability, huge software ecosystem, and long-term security.
Best suited for Server Administrators and Advanced Users
Code Example: Installing packages using apt.
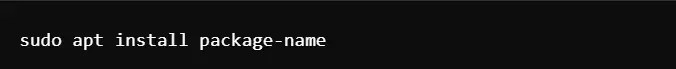
It installs the given package with dependency and configuration status.
4. Arch Linux
Arch Linux is simple, flexible, and minimalist, and it has a rolling release, thus providing users with full access to the latest features. This option is considered for experienced users who want to get complete control of system configuration.
Why use it?
Full customization and the latest version of the software via rolling release
Power users and other enthusiasts who enjoy self-configuration
Code Snippet: How pacman updates the system

This command upgrades the system to the latest available packages and displays updates as they are installed.
5. Linux Mint
Linux Mint is one of the very user-friendly Linux distros that is based on Ubuntu, though offering more of a traditional environment on a desktop. I feel it has real appeal in Windows-to-Linux conversions since its interface is very familiar, and multimedia support comes out of the box.
Why use it?
It is very easy to use. It’s stable. It has great media and software compatibility.
Suitable for: Beginners and Windows users.
Best Practices: Make use of the built-in update manager that scans for newer updates to your system.
6. CentOS Stream
CentOS Stream is a rolling release distro that is ahead of Red Hat Enterprise Linux. Thus, it’s the best choice for developers as well as enterprises that need a stable environment yet at the forefront. It’s also known for enterprise-level stability and long-term support.
Why use it?
Suitable for developers and organizations that need stable environments closely resembling Red Hat.
Suitable for: A server administrator or an enterprise setting.
Package management using yum Code example

This code updates all packages to the latest version.
7. Manjaro
Manjaro is based on Arch Linux and is a simplified version designed for easy installation and brings the best of the powerful features of Arch to the user’s table. With the rolling release model, you can bet to always have the latest available updates. Manjaro is perfect for power users who are looking for the convenience of Arch Linux with an easier setup.
Why use it?
User-friendly Arch experience, easy package management, and rolling updates.
Good for Intermediate to Advanced Users who want to tap into the power of Arch but don’t need its complexity.
Code Example: Install software with pacman

This command will display package installation progress, including dependencies.
8. openSUSE
openSUSE features a very powerful YaST configuration tool; system administration is a pleasure. It exists in two flavors: Leap, the stable release, and Tumbleweed, a rolling release. openSUSE presents a professional development environment also for the system administrator.
Why pick it?
Offers for each stability, Leap, and new software, Tumbleweed.
Ideal for: Developers, system administrators, and power users.
Best Practices: The use of YaST makes for a soft system configuration and update process.
9. Zorin OS
Zorin OS stands out as being much more suited for users looking to migrate either from Windows or from macOS. It provides a good-looking, quite familiar desktop experience and includes built-in support for multimedia and other applications. Performance Zorin OS has been optimized for performance on older hardware, too.
Why select it?
Has a Windows-like interface, optimized performance, and is very beginner-friendly.
Ideal for new Linux users and anyone else who is seeking a Windows-like environment.
Best practices: The desktop layout should be customized using the inbuilt Zorin Appearance tool.
10. Pop!_OS

Pop!_OS is a powerful developer distro-optimized version designed by System76 for developers, creative artists as well as gamers. This comes with great performance capabilities in addition to its support for Nvidia and AMD GPUs.
Why use it?
Designed with performance in mind, optimized for today’s hardware and gaming.
Suitable for: Gamers, developers, and creative professionals.
Best Practices: Ensure you do regular updates of graphics drivers for the best performance out of them.
Best Practices for Linux Distro
Upgrades: The systems and software should be frequently updated to ensure the installation of the latest security patches and features.
Use backup tools: Try to install tools like Timeshift or rsync to back up your system and other important data.
Installing core software: Install the installation of critical software, such as Docker, Git, and IDEs like Visual Studio Code, that will enhance your productivity.
Security Best Practices: Activate the firewall using ufw (Uncomplicated Firewall) and secure SSH keys if one is managing remote servers.
Which is Best for You Among Linux Distros?
For Newbies
- Ubuntu: It has a user-friendly interface, long-term support, and abundant community resources to help new users.
- Linux Mint: Ideal for those coming from Windows; stable, reliable, and comes with multimedia support out of the box.
- Zorin OS: Designed to provide a Windows-like or macOS-like experience, making the transition seamless for first-time Linux users.
For Advanced Users
- Arch Linux: Provides full control over every aspect of the system, ideal for users who want a minimalist and highly customizable environment.
- Manjaro: A more user-friendly derivative of Arch Linux, retaining its power and flexibility while simplifying setup and management.
For Developers
- Fedora: A cutting-edge distro with access to the latest open-source tools and features, tailored for software development.
Pop!_OS: It is designed out of the box, pre-optimized for code and development, with support for high-end hardware and various GPUs for smooth workflows. System Administrators will appreciate it due to its stability and security for server management on an extensively tested software package depository. - CentOS: It’sStream’s rolling release model is modeled similarly to Red Hat Enterprise Linux for enterprise-level dependability. Windows-to-Linux Migrators
- Linux Mint: Preserves a classic desktop theme and has the same applications that Windows users are familiar with, so they can easily adapt.
Zorin OS: It has many different desktop themes that resemble Windows or macOS and has amazing multimedia support.
For Gamers and Creative Professionals:
- Pop!_OS: Designed for gaming and creative activities with seamless integration for Nvidia and AMD GPUs.
For Enterprise Users:
- CentOS Stream: It is ideal for businesses that have a requirement for a secure, reliable server environment with support on an enterprise level.
How to Choose Linux Distros?
The choice of Linux distros depends on you:
Your level of expertise: The new user has to choose either Ubuntu or Linux Mint while the experts can always go for trying Arch or Manjaro.
Application: Developers or creative artists would require Fedora or Pop!_OS while business enterprises may require Debian or CentOS.
Transition Requirements: If you are coming from another OS, Linux Mint and Zorin OS will serve you well.
Go through its features, try a live version, and find a distro that matches your goals and skills!
Role of CyberPanel in Linux Distros
CyberPanel is a powerful tool for server management users since it integrates perfectly with almost all the available Linux distros. CyberPanel, which runs on OpenLiteSpeed, simplifies tasks in server management- hosting websites, creating databases, and installing SSL certificates. It comes in handy for server management using such Linux distros as Ubuntu, CentOS, or Debian.
Installation Instructions for CyberPanel on Ubuntu
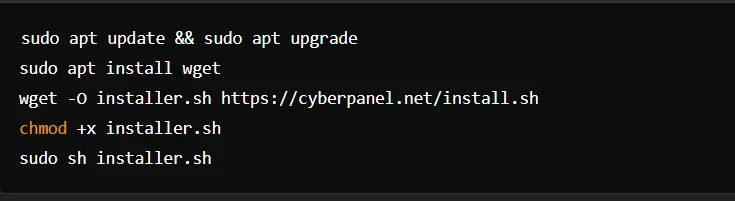
Output:
Starting CyberPanel installation...
Do you want to install CyberPanel with OpenLiteSpeed or LiteSpeed Enterprise? (Enter '1' for OpenLiteSpeed)
Updating the package repository...
Installing dependencies...
CyberPanel installation completed!After installation, our web hosting control panel offers a graphical user interface so that one can easily manage the activities related to web hosting management. This simplifies complex activities such as DNS management, configuration of backup, and email management.
Linux Distros: FAQs
1. Which are the best Linux distros for beginners?
The two best distros for beginners are Ubuntu and Linux Mint due to their usability, large communities, and documentation available.
2. Is Linux Good for gaming?
Yes, thanks to tools like Steam Proton and Lutris, many popular games are already available to play on Linux distros like, for instance, Ubuntu, Fedora, and Pop!_OS.
3. Which Linux distro is ideal for servers?
For servers, CentOS Stream, Debian, and Ubuntu Server are good choices because they provide stability and long-term support. Rolling release distro :
As a result, a rolling release distro such as Arch Linux or Manjaro will roll update packages permanently without necessarily requiring major version upgrades for your system to stay on top of the latest.
4. Can I run Linux on my computer having Windows?
You can use WSL to run Linux on Windows.
5. How do I choose the best Linux distro?
It depends on your usage. If you are a beginner, the best distros would be Ubuntu or Linux Mint. And if you are a developer, Fedora or Arch Linux would be the best choice.
Final Take: Choosing the Right Linux Distros to Suit Your Needs
To sum up, the decision of Linux distros will rely on one’s level of skill, particular needs, and preferences. Whether it is a beginner seeking an easy experience or an expert wanting all the control over his system, there’s bound to be a distro of your choice. Tools like CyberPanel can then further enhance the experience while managing servers even when choosing any Linux distro.
Ready to enter into the world of Linux? Investigate your match distros, and if you’re managing a server, then look at CyberPanel. Now it’s time to be in control of your operating system and take in the freedom that Linux can give you.



