Even though high performance is not so critical for some Linux Debian users. For instance, developers or system administrators are crucial for gamers, data scientists, and those performing video rendering. This step-by-step guide on how to install NVIDIA drivers on Linux Debian covers all the essentials-pre-requisites, installation procedures, and troubleshooting tips. This is a guide on simple installation and will explain how CyberPanel makes things straightforward for either a fresh Debian user or an experienced Linux administrator.
Linux Debian will most likely not install proprietary NVIDIA drivers; you will have to install NVIDIA drivers on Debian yourself if you require high graphics. Hence, in order to better support you in the exploitation of your NVIDIA hardware in Debian, we will see a few ways to install drivers, and then what will be done at each step.
Let’s learn together!
Prerequisites and Preparations
Before getting on how to install NVIDIA drivers on Linux Debian, ensure that the following prerequisites have been met:
System Upgrade: Updated your Debian to update all packages.


Compatibility Check: Your system should work well with NVIDIA drivers. Confirm the model of the GPU.
Get exclusive access to all things tech-savvy, and be the first to receive
the latest updates directly in your inbox.
Blacklist Nouveau Driver: Debian applies by default driver Nouveau, which in turn conflicts with the NVIDIA drivers. The driver should be blacklisted.
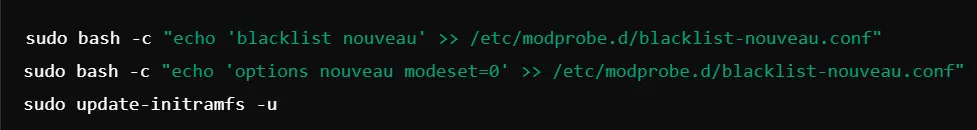
Step 1: Blacklist Nouveau Driver
Blacklists prevent Debian from loading the open-source Nouveau driver as it may cause problems with proprietary NVIDIA drivers. The following commands use to create a blacklist configuration file:

Step 2: Reboot Your System
Reboot your system, so all changes are enforced ensuring Nouveau is not active anymore.

Step 3: Installing the NVIDIA Driver on Linux Debian
We will mention two significant methods to how to install NVIDIA drivers on Linux Debian:
- Installation through Debian Repositories
- Installation from NVIDIA’s Official Website
How To Install NVIDIA Driver on Linux Debian
Installation Method 1: Install NVIDIA Drivers from Debian Repositories
The Linux Debian repos contain the pre-compiled versions of the NVIDIA drivers, hence installation is straightforward. To enable the “non-free” repository and how to install NVIDIA drivers on Linux Debian follow these steps:

Now, add the following line:

Update the Package List:


Install NVIDIA Driver:


Reboot To Apply Changes:
Reboot your system to apply changes and complete the process of how to install NVIDIA drivers on Linux Debian:

Method 2: Manual Installation Using NVIDIA’s Official Website
Here is how to install NVIDIA drivers on Linux Debian manually:
1. Download the Driver: Visit NVIDIA’s official website and download the latest Linux driver for your GPU model.
2. Make the Installer Executable:

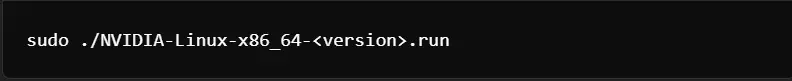
3. Run the installer:
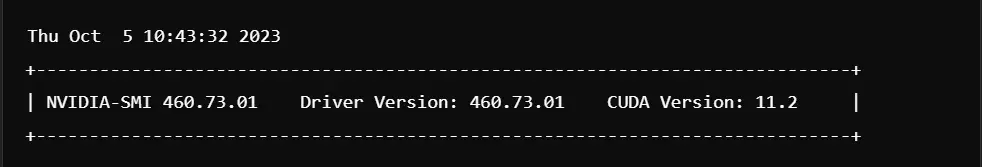
Verification of the NVIDIA Driver Installation
After completing the installation, verify the installation with the following command:

How To Install NVIDIA Drivers On Debian
Install NVIDIA Drivers in Debian 12
Installing the NVIDIA drivers on Debian 12 requires that you ensure the non-free and contrib repositories are enabled. Those repositories contain the packages required for NVIDIA drivers. Here is how to install NVIDIA drivers on Linux Debian:
Enable Non-Free Repositories: Open your sources list:

Add the following lines (if they aren’t already there):
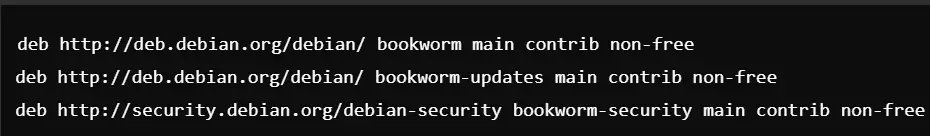
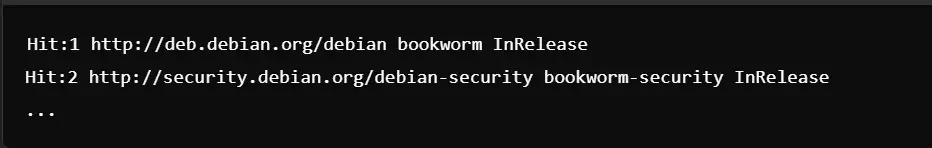
Now, update the package list:

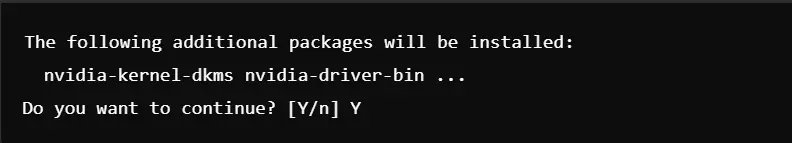
Install NVIDIA Driver by using the following command:

Now, reboot the system to activate the NVIDIA driver:

After rebooting, verify the installation:

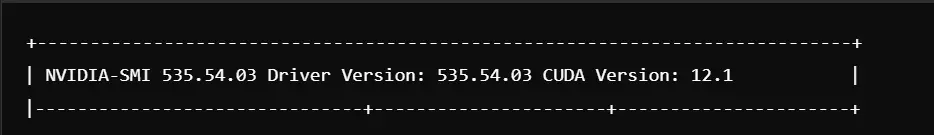
Install NVIDIA Drivers in Debian 11
For users of Debian 11 (Bullseye), the installation process is essentially the same but the sources list is a bit different. You can follow these steps for how to install NVIDIA drivers on Linux Debian 11:
Non-free Repositories: Insert the lines listed below into your /etc/apt/sources.list:
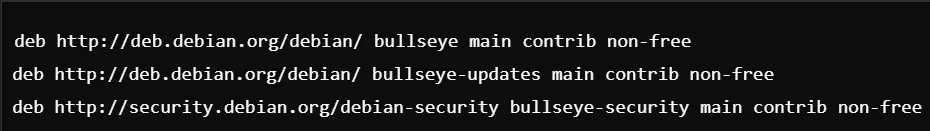
Install the NVIDIA Driver:

After rebooting, you have to confirm the installation:

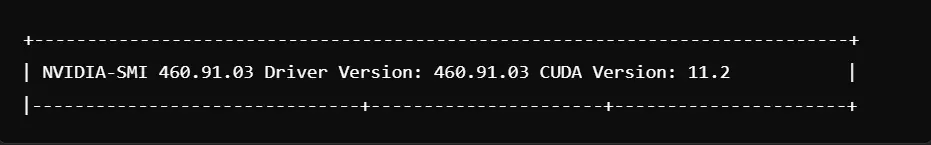
Debian Install nvidia-detect
The nvidia-detect utility is there to help identify which NVIDIA driver package is suitable for your GPU model. This can be particularly useful should you not know what driver you require. Follow these steps for how to install NVIDIA drivers on Linux Debian:
Install nvidia-detect:

Run nvidia-detect:

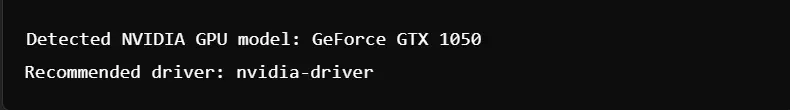
Package ‘nvidia-driver’ Has No Installation Candidate
If you receive “package ‘nvidia-driver’ has no installation candidate,” it usually means you do not have the non-free repository. This is how to correct that and how to install NVIDIA drivers on Linux Debian:
Verify and Update Sources List: Make sure your /etc/apt/sources.list includes the non-free repository:

Update the Package List:

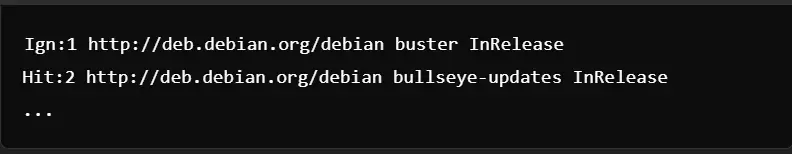
Reinstall the NVIDIA Driver:

Debian NVIDIA 535
For those needing the NVIDIA 535 driver version specifically, the Debian repository may not always have the latest version. Here’s how to manually install NVIDIA 535 and how to install NVIDIA drivers on Linux Debian:
Download NVIDIA 535: Go to NVIDIA’s official website and download the driver version 535.
Make the File Executable:

Run the Installer: Stop the graphical interface and run the installer in a virtual terminal (Ctrl+Alt+F3):

Verify the installation:

NVIDIA Linux Drivers
Installing NVIDIA drivers might be a bit different if you are using a different Linux distribution – like CentOS, Fedora, or Arch Linux. Here are the general steps on how to install NVIDIA drivers on Linux Debian:
Identify the GPU:

Install the drivers:

Verify installation:

Install NVIDIA Drivers Ubuntu
Automatic Installation: Run the following command


Verify with nvidia-smi

Important Legal and Compliance Information for NVIDIA Driver Installation on Debian
When exploring how to install NVIDIA drivers on Linux Debian and other Linux distributions, there are a few legal considerations and restrictions in its initial deployment. According to the kind of drivers installed or the intended and/or potential usage scenarios that fall into the categories of commercial, with specific licensing agreements, break them down as follows:
1. NVIDIA Driver Licensing
Proprietary License: Drivers are proprietary and have to accept the terms of an EULA to be legally able to use them
Non-Free Software: Debian classifies it under “non-free”; doing this will violate Debian because it is not open-source.
Best Practice: Read the EULA on NVIDIA’s website.
2. GPL Compliance for Kernel Modules
Kernel Compatibility: Closed-source binaries may cause conflicts under the GNU General Public License, creating an ethical dilemma with the kernel modules.
Tainted Kernel: Installing NVIDIA’s proprietary driver would taint the kernel while also potentially eliminating any ability for official Linux support.
Recommended alternative: If some level of open-source purism is needed, it is possible to use Nouveau. This should fully comply with all open source requirements but may result in a performance hit
3. Export Control Laws
EAR Compliance: Some drivers from NVIDIA – such as those that include the CUDA libraries for AI functionality support – are subject to U.S. EAR.
Restricted Countries: It is export-restricted in countries like North Korea and Iran.
Recommendation: Check with NVIDIA’s website or attorney for export control across the globe.
4. Commercial and Enterprise Use Cases
Commercial Licensing: Commercial license agreements with NVIDIA should be done if large-scale deployment is already in place.
Warranty Implications: Proprietary drivers will void warranties on hardware. Policies should be confirmed by the vendor.
Best Practice: Interface with NVIDIA’s enterprise support for compliance and warranty coverage.
5. Cyber Security Laws Compliance
Ensure updated NVIDIA drivers cover some security vulnerabilities, especially in regulated sectors like healthcare and finance.
Recommendation: Install CyberPanel or other applications to update without interfering with the services, which meet the requirements of cybersecurity laws.
Troubleshooting Common Problems
Installation of Driver Fails: The Nouveau driver must be blacklisted.
NVIDIA-SMI Not Detecting GPU: This could be due to incorrect installation of the driver. Try reinstalling the driver.
Resolution Problem with Display: Setting up the resolution settings for the display manually using xrandr.
Screen Flicker: The NVIDIA control panel is set for proper display settings.
Role of CyberPanel in Debian Optimization of NVIDIA Drivers
CyberPanel, an open-source web hosting control panel, is also essential to Debian system optimization on a machine installed with NVIDIA drivers. Automated maintenance work and the real-time monitoring it enables help make server management work a little easier. The interface offered by CyberPanel to its users ensures:
Automate Package Updates: CyberPanel always keeps up the packages by their essentials, like NVIDIA driver updates, so that you are always on top of your game.
Optimize Resources: Check out your GPU usage and system performance. This ensures that bottlenecks will never occur and proper resources get allocated.
Controlling Your Debian Remotely: CyberPanel allows you to control your Debian server from a distance by monitoring the health and driver status of your system.
This means that customers may get maximum graphical power by installing the CyberPanel in parallel with the drivers of NVIDIA while enjoying all the advantages of simpler management.
FAQs On How To Install NVIDIA Drivers On Linux Debian
1. Is there a way to install NVIDIA drivers in Debian without deactivating the Nouveau driver?
In fact, it is advisable to de-activate the Nouveau driver when proprietary NVIDIA drivers are used since the drivers usually conflict with each other.
2. If it won’t boot, what should I do?
Try booting into recovery mode deinstall the NVIDIA driver and try to see if it causes some conflict with the driver.
3. How often should I update NVIDIA drivers?
It is highly recommended to update every six months or whenever they come up with new features or even major updates.
4. Does cyberpanel support Debian?
Yes, cyberpanel supports Debian and therefore can be used for managing and optimizing server-side tasks.
5. How do I test if my NVIDIA driver installs successfully?
You can see the driver details of active GPUs by using the command nvidia-smi.
Conclusion: Unlock Full Graphics with NVIDIA on Debian
To sum up, this guide on how to install NVIDIA drivers on Linux Debian offers valuable insight into preparing, installing, and verifying the driver installation. The installation of NVIDIA drivers on Debian will maximize the peak performance and stability of your GPU. This guide is carefully followed to empower you with the knowledge of installing and configuring NVIDIA drivers confidently. Moreover, support from CyberPanel for Debian systems makes general management way easier and simplifies routine maintenance, ensuring smoothness from installation to daily use.
Are you ready? Start following these steps today to improve your Debian setting and enter a world of high-performance graphics computing!