Kali Linux tools can be used in lawful and helpful ways as a security practitioner, but they can also be used illegally, unlawfully, and unethically. Because in the field of digital security, penetration testing plays a vital role in safeguarding organizations’ data and sensitive information. As the demand for skilled professionals in cybersecurity continues to grow, ethical hacking has emerged as a highly sought-after and rewarding skill.
What is Kali Linux?
Kali Linux, previously called BackTrack Linux, is a free and open-source Linux distribution based on Debian.
Kali Linux was created by Mati Aharoni and Devon Kearns. It’s an operating system tailored for network analysts and penetration testers, or simply put, it’s for anyone involved in cybersecurity and analysis.
It enables users to conduct advanced penetration testing and security audits. It is compatible with various platforms and is available to both security professionals and enthusiasts.
This distribution includes numerous tools, configurations, and scripts tailored for specific industries. It has 600+ Penetration testing and network security tools pre-installed, allowing users to focus on tasks such as computer forensics, reverse engineering, and vulnerability detection without being distracted by unrelated activities. It is designed specifically for experienced penetration testers, so all documentation on this site assumes users have prior knowledge of and are familiar with the Linux operating system.
Why it’s the go-to choice for ethical hackers in 2026
- Always free: Kali Linux is entirely free and will remain so.
- Open source Git tree: The source code is accessible for anyone to modify or rebuild packages.
- FHS compliant: Linux users can easily find binaries, support files, libraries, and more.
- Extensive device support: Kali works with a wide range of hardware and wireless devices, including USB devices.
- Custom kernel with injection patches: The kernel has the latest injection patches for penetration testing.
- Secure environment: All modifications to the distribution are made using multiple secure protocols.
- GPG signed packages: Each package in Kali Linux is signed by the developer who created it.
- Multi-language support: Kali offers true multilingual support for users to work in their preferred language.
- Fully customizable: Kali Linux is made to be user-friendly for those who want to customize it.
- ARMEL and ARMHF support: Kali provides fully functional installations for both ARMEL and ARMHF systems, available on various ARM devices.
Kali Linux Tools Use Cases
Penetration Testing
Get exclusive access to all things tech-savvy, and be the first to receive
the latest updates directly in your inbox.
- Tools like Metasploit, Nmap, and Burp Suite in Kali Linux help find vulnerabilities and exploit weaknesses in systems, networks, servers, and web applications.
- This proactive method enhances defenses, stops breaches, and boosts overall system security.
Digital Forensics
- Tools such as Autopsy, Sleuth Kit, and Foremost in Kali Linux assist in investigating security incidents and recovering lost or compromised data.
- Experts can retrieve deleted files, analyze disk images, extract hidden data, and break down malware or suspicious files.
Security Research and Learning
- Kali Linux is perfect for system security research and education, enabling students to practice real-world attacks and test defense strategies.
- Its open-source nature promotes ongoing learning and experimentation.
Capture-the-flag (CTF) Competitions
- Kali Linux is favored for CTF competitions, offering all the necessary tools to tackle these challenges.
User Groups
- System security professionals, ethical hackers, students and educators, and CTF participants.
The Best Kali Linux Tools in 2026
Don’t look any further because we know the best Kali Linux tools list that are amazing in 2026:
1. Nmap: Network Mapping & Scanning
Network Mapper, commonly known as Nmap, has come a long way since it was first introduced as a port scanner back in 1997. It’s now a widely used tool that not only checks port statuses, guesses operating systems, and maps out network topologies, but also finds vulnerabilities and carries out brute-force password audits. Nmap is one of the Kali Linux tools for exploring networks that can do ping scans, port scans, version detection, and TCP/IP fingerprinting. It works on both Unix and Windows systems, plus it’s compatible with popular handheld devices such as the Sharp Zaurus and iPAQ.
Key features and capabilities of Nmap include:
- Detecting devices that are active on a network.
- Offering visual mapping through its Zenmap graphical user interface.
- Identifying services that are running on systems, along with their versions and types.
- Hosting helpful documentation and scripts on its website.
Here’s an example of how this tool is used:
<strong>root@kali:~</strong># nmap -v -A -sV 192.168.1.1 Starting Nmap 6.45 ( http://nmap.org ) at 2014-05-13 18:40 MDT NSE: Loaded 118 scripts for scanning. NSE: Script Pre-scanning. Initiating ARP Ping Scan at 18:40 Scanning 192.168.1.1 [1 port] Completed ARP Ping Scan at 18:40, 0.06s elapsed (1 total hosts) Initiating Parallel DNS resolution of 1 host. at 18:40 Completed Parallel DNS resolution of 1 host. at 18:40, 0.00s elapsed Initiating SYN Stealth Scan at 18:40 Scanning router.localdomain (192.168.1.1) [1000 ports] Discovered open port 53/tcp on 192.168.1.1 Discovered open port 22/tcp on 192.168.1.1 Discovered open port 80/tcp on 192.168.1.1 Discovered open port 3001/tcp on 192.168.1.1<strong><br></strong>
2. Snort

Snort is a free and open-source network intrusion prevention system that can analyze traffic in real-time and log packets on IP networks. It can analyze protocols, search and match content, and is effective in identifying various attacks and probes, including buffer overflows, stealth port scans, CGI attacks, SMB probes, OS fingerprinting attempts, and a lot more.
root@kali:~# snort --help
Snort has several options to get more help:
-? list command line options (same as --help)
--help this overview of help
--help-commands [<module prefix>] output matching commands
--help-config [<module prefix>] output matching config options
--help-counts [<module prefix>] output matching peg counts
--help-limits print the int upper bounds denoted by max*
--help-module <module> output description of given module
--help-modules list all available modules with brief help
--help-modules-json dump description of all available modules in JSON format
--help-plugins list all available plugins with brief help
--help-options [<option prefix>] output matching command line options
--help-signals dump available control signals
--list-buffers output available inspection buffers
--list-builtin [<module prefix>] output matching builtin rules
--list-gids [<module prefix>] output matching generators
--list-modules [<module type>] list all known modules
--list-plugins list all known modules
--show-plugins list module and plugin versions
--help* and --list* options preempt other processing so should be last on the
command line since any following options are ignored. To ensure options like
--markup and --plugin-path take effect, place them ahead of the help or list
options.
Options that filter output based on a matching prefix, such as --help-config
won't output anything if there is no match. If no prefix is given, everything
matches.
Report bugs to [email protected].
2. Metasploit Framework: Exploitation & Payload Delivery

The Metasploit Framework is a popular tool for penetration testing. It’s a full-fledged framework designed for gathering intel and executing exploits on targeted systems. It comes with ready-to-use exploit code and payloads to take advantage of known vulnerabilities.

Key features and capabilities of Metasploit:
- A collection of exploits and payloads, along with auxiliary tasks that don’t require payloads.
- It standardizes how users interact with exploit code, promoting payload reuse and a consistent approach to working with exploits.
- For beginners, there’s Metasploitable, a purposely vulnerable virtual machine that allows users to practice exploits and get familiar with Metasploit.
<strong>root@kali:~</strong># msfrpcd -h Usage: msfrpcd <options> OPTIONS: -P <opt> Specify the password to access msfrpcd -S Disable SSL on the RPC socket -U <opt> Specify the username to access msfrpcd -a <opt> Bind to this IP address -f Run the daemon in the foreground -h Help banner -n Disable database -p <opt> Bind to this port instead of 55553 -t <opt> Token Timeout (default 300 seconds -u <opt> URI for Web server3. Aircrack-ng: Wireless Network Penetration

Aircrack-ng is a collection of wireless security tools made up of various applications for monitoring, intercepting, and injecting data.
It features Airdecap-ng, which is a decryptor for Wired Equivalent Privacy, Wi-Fi Protected Access, and WPA capture files; Airodump-ng, a tool for gathering packets and WPA handshakes; Airtun-ng, which creates a virtual tunnel interface; and Besside-ng, a cracker for WEP and WPA.
- It focuses on 802.11 wireless LANs.
- It offers command-line tools that support extensive scripting.
- It can execute WEP dictionary attacks and fragmentation attacks.
Here’s a usage example:
root@kali:~# aircrack-ng -w password.lst wpa.cap
Aircrack-ng 1.5.2
[00:00:00] 232/233 keys tested (1992.58 k/s)
Time left: 0 seconds 99.57%
KEY FOUND! [ biscotte ]
Master Key : CD D7 9A 5A CF B0 70 C7 E9 D1 02 3B 87 02 85 D6
39 E4 30 B3 2F 31 AA 37 AC 82 5A 55 B5 55 24 EE
Transient Key : 33 55 0B FC 4F 24 84 F4 9A 38 B3 D0 89 83 D2 49
73 F9 DE 89 67 A6 6D 2B 8E 46 2C 07 47 6A CE 08
AD FB 65 D6 13 A9 9F 2C 65 E4 A6 08 F2 5A 67 97
D9 6F 76 5B 8C D3 DF 13 2F BC DA 6A 6E D9 62 CD
EAPOL HMAC : 28 A8 C8 95 B7 17 E5 72 27 B6 A7 EE E3 E5 34 454. Hydra: For Password Cracking

Hydra is an online password-cracking tool that employs brute-force and dictionary attacks to reveal weak passwords or inadequate password practices. It can target various protocols, including SSH, Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP), Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP), HTTP, HTML forms, virtual network computing, and more. Hydra offers both prebuilt and customizable word lists and is capable of running multiple threads in parallel to enhance efficiency and speed. It features a simple and intuitive interface.
root@kali:~# hydra -l root -P /usr/share/wordlists/metasploit/unix_passwords.txt -t 6 ssh://192.168.1.123
Hydra v7.6 (c)2013 by van Hauser/THC & David Maciejak - for legal purposes only
Hydra (http://www.thc.org/thc-hydra) starting at 2014-05-19 07:53:33
[DATA] 6 tasks, 1 server, 1003 login tries (l:1/p:1003), ~167 tries per task
[DATA] attacking service ssh on port 225. Wireshark: Packet Analysis & Monitoring

This network packet analyzer provides in-depth details about captured packet data.
This is one of the Kali Linux iconic tools used extensively in various industries and educational institutions. Wireshark reveals events and activities within the network. The tool can handle multiple types of captured file formats, including but not limited to Microsoft Network Monitor, Pcap NG, Siffer Pro, and more. Wireshark is effective in identifying security vulnerabilities and resolving networking issues. Additionally, it is popular among developers and QA engineers.
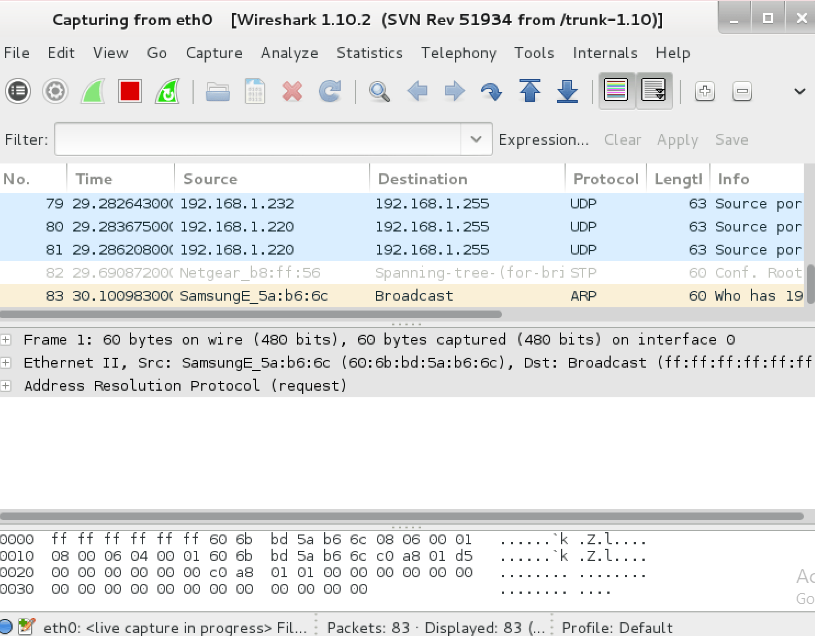
Wireshark is known as a network protocol analyzer, or packet analyzer, that captures network traffic and shows its components, such as logical and physical address details. It also reveals packet contents unless they are encrypted.
EndNote
Kali Linux tools are the top choice for penetration testers, ethical hackers, and cybersecurity experts in 2026. With its extensive tools, from network scanning with Nmap to exploitation using Metasploit, it prepares you for every phase of the security testing process.
Whether you like using classic tools such as Wireshark or trying out newer IP-focused utilities, Kali Linux makes sure you have everything you need.
The important part is not just knowing what tools are available, but mastering how and when to use them.
With responsible and ethical usage, Kali Linux can assist you in enhancing security, spotting vulnerabilities, and staying ahead of cyber threats.
FAQ’s
1. Which Kali Linux tools are most commonly used for penetration testing?
Some of the widely used Kali Linux tools are Nmap, Metasploit, Aircrack-ng, Wireshark, Burp Suite, and John the Ripper. These tools handle various tasks, from network scanning to wireless security and password cracking.
2. How can I install all tools in Kali Linux simultaneously?
You can install all Kali Linux tools with this command:
sudo apt install kali-linux-allHowever, installing every tool can take up a lot of disk space and may include tools that you don’t require. It’s advisable to install only the tools that are relevant to your testing needs.
3. What is the purpose of IP tools in Kali Linux?
IP tools in Kali Linux are utilized for network reconnaissance, scanning, and mapping. They assist in identifying active hosts, open ports, and services running on a target system, which is essential in the initial stages of penetration testing.
4. Is it legal to use Kali Linux tools?
Yes, Kali Linux tools are legal to use as long as they are employed for ethical reasons—such as testing your own systems or with the explicit consent of the system owner. Unauthorized use can result in serious legal repercussions.
5. How do iconic tools differ from newer Kali Linux tools?
Iconic tools like Nmap, Metasploit, and Wireshark have been trusted by professionals for many years due to their reliability and versatility. Newer tools may target emerging threats or specific penetration testing scenarios, providing new capabilities alongside the established classics.



