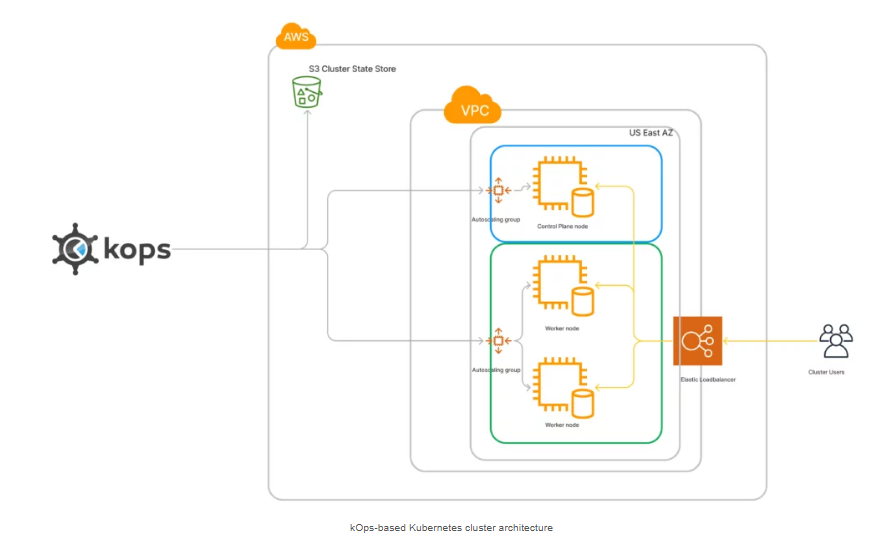
KOps (Kubernetes Operations) is an open-source tool that simplifies the deployment and management of Kubernetes clusters in cloud environments. It automates the provisioning of infrastructure, configuration of clusters, and ongoing maintenance for setups ready for production.
It’s primarily used for deploying Kubernetes clusters on AWS and GCE. However, the tool officially supports only AWS. It also supports additional cloud providers like DigitalOcean, GCP, and OpenStack is also available.
Kops Kubernetes handles the creation, upgrading, and scaling of Kubernetes clusters, focusing on functional efficiency. It operates smoothly across various cloud providers, offering a flexible solution for those hesitant about cloud use. With the assistance of Infrastructure as Code (IaC), Kops enables users to manage and version control cluster configurations alongside application code.
Kubernetes Kops Features & How It Works
- Can generate Terraform.
- Includes command line autocompletion.
- YAML Manifest-Based API Configuration.
- Automates the setup of Highly Available Kubernetes clusters.
- Utilizes a state-sync model for dry-runs and automatic idempotency.
- Offers zero-config managed Kubernetes add-ons.
- Provides templating and dry-run modes for creating Manifests.
- Select from the most popular CNI Networking providers right away.
- Ready for multi-architecture with ARM64 support.
- Allows adding containers, as hooks, and files to nodes through a cluster manifest.
Kubernetes Kops facilitates multi-zone, high availability (HA) deployments with complete SSH access, enabling infrastructure-as-code (IaC) style cluster definitions. It seamlessly integrates with custom networking and identity solutions, providing a do-it-yourself (DIY) Kubernetes experience.
Kops includes robust group lifecycle management, compatibility across multiple clouds, IaC practices, and support for high availability configurations. DevOps engineers, system administrators, and cloud architects gain advantages from Kops, allowing them to focus on application deployment rather than the complexities of infrastructure management.
Kops Kubernetes Installation (Step-by-Step)
This quick start guide showcases how to set up a Kubernetes cluster on AWS using kops, a user-friendly provisioning tool. It provides a fully automated installation process, ensures self-healing capabilities, and supports high availability, though with limited operating system options. Additionally, users have the option to create their cluster with kubeadm if they prefer a more hands-on approach.
Get exclusive access to all things tech-savvy, and be the first to receive
the latest updates directly in your inbox.
Prerequisites (kubectl, IAM, networking)
You must have kubectl installed in order for kops to work.
Install Kops
Download kops from the releases page (it is also easy to build from source):
On MacOS:
wget https://github.com/kubernetes/kops/releases/download/1.6.1/kops-darwin-amd64
chmod +x kops-darwin-amd64
mv kops-darwin-amd64 /usr/local/bin/kops
# you can also install using Homebrew
brew update && brew install kops
On Linux:
wget https://github.com/kubernetes/kops/releases/download/1.6.1/kops-linux-amd64
chmod +x kops-linux-amd64
mv kops-linux-amd64 /usr/local/bin/kops
Creating a Kubernetes Cluster with Kops
Run the “kops create cluster” command and set up your cluster configuration:
kops create cluster --zones=us-east-1c useast1.dev.example.comKops Kubernetes will generate the configuration for your cluster. Keep in mind that it only prepares the configuration and does not create the cloud resources yet; you will handle that in the next step using a kops update cluster. This allows you to check the configuration or modify it.
How To Verify KOps Kubernetes?
Run this command to verify if the Kubernetes Cluster was created:
<code>ubuntu@ip-161-32-38-140:~$ kOps kOps is Kubernetes ops. kOps is the easiest way to get a production grade Kubernetes cluster up and running. We like to think of it as kubectl for clusters. kOps helps you create, destroy, upgrade and maintain production-grade, highly available, Kubernetes clusters from the command line. AWS (Amazon Web Services) is currently officially supported, with GCE and VMware vSphere in alpha support. Usage: kOps [command] Available Commands: completion Output shell completion code for the given shell (bash or zsh). create Create a resource by command line, filename or stdin. delete Delete clusters,instancegroups, or secrets. describe Describe a resource. edit Edit clusters and other resources. export Export configuration. get Get one or many resources. import Import a cluster. replace Replace cluster resources. rolling-update Rolling update a cluster. toolbox Misc infrequently used commands. update Update a cluster. upgrade Upgrade a kubernetes cluster. validate Validate a kOps cluster. version Print the kOps version information. Flags: --alsologtostderr log to standard error as well as files --config string config file (default is $HOME/.kOps.yaml) -h, --help help for kOps --log_backtrace_at traceLocation when logging hits line file:N, emit a stack trace (default :0) --log_dir string If non-empty, write log files in this directory --logtostderr log to standard error instead of files (default false) --name string Name of cluster --state string Location of state storage --stderrthreshold severity logs at or above this threshold go to stderr (default 2) -v, --v Level log level for V logs --vmodule moduleSpec comma-separated list of pattern=N settings for file-filtered logging Use "kOps [command] --help" for more information about a command.</code>Create an S3 bucket for Kops state:
Create an S3 Bucket to store our Kubernetes cluster data with below command:
aws s3 mb s3://sadab The `aws s3 mb` command stands for “make bucket,” and specifying the bucket name as “sadab.”
Note: your S3 bucket name will be unique

Now, export the created bucket to the Kops by using the following command
export KOPS_STATE_STORE=s3://sadab<br>How to Delete a Cluster
Just like creating a Kubernetes cluster, deleting a Kubernetes cluster using kOps is very simple. This will remove all the cloud resources of the cluster and the cluster registry itself.
ubuntu@ip-161-32-38-140:~$ kOps delete cluster --name kOpsdemo1.k8s.local --yes
TYPE NAME ID
autoscaling-config master-eu-central-1a.masters.kOpsdemo1.k8s.local lt-0cc11aec1943204e4
autoscaling-config nodes-eu-central-1a.kOpsdemo1.k8s.local lt-0da65d2eaf6de9f5c
autoscaling-group master-eu-central-1a.masters.kOpsdemo1.k8s.local master-eu-central-1a.masters.kOpsdemo1.k8s.local
autoscaling-group nodes-eu-central-1a.kOpsdemo1.k8s.local nodes-eu-central-1a.kOpsdemo1.k8s.local
dhcp-options kOpsdemo1.k8s.local dopt-0403a0cbbfbc0c72b
iam-instance-profile masters.kOpsdemo1.k8s.local masters.kOpsdemo1.k8s.local
iam-instance-profile nodes.kOpsdemo1.k8s.local nodes.kOpsdemo1.k8s.local
iam-role masters.kOpsdemo1.k8s.local masters.kOpsdemo1.k8s.local
iam-role nodes.kOpsdemo1.k8s.local nodes.kOpsdemo1.k8s.local
instance master-eu-central-1a.masters.kOpsdemo1.k8s.local i-069c73f2c23eb502a
instance nodes-eu-central-1a.kOpsdemo1.k8s.local i-0401d6b0d4fc11e77
iam-instance-profile:nodes.kOpsdemo1.k8s.local ok
load-balancer:api-kOpsdemo1-k8s-local-dason2 ok
iam-instance-profile:masters.kOpsdemo1.k8s.local ok
iam-role:masters.kOpsdemo1.k8s.local ok
instance:i-069c73f2c23eb502a ok
autoscaling-group:nodes-eu-central-1a.kOpsdemo1.k8s.local ok
iam-role:nodes.kOpsdemo1.k8s.local ok
instance:i-0401d6b0d4fc11e77 ok
autoscaling-config:lt-0cc11aec1943204e4 ok
autoscaling-config:lt-0da65d2eaf6de9f5c ok
autoscaling-group:master-eu-central-1a.masters.kOpsdemo1.k8s.local ok
keypair:key-0e93f855f382a68fb ok
Deleted kubectl config for kOpsdemo1.k8s.local
Deleted cluster: "kOpsdemo1.k8s.local"Kops Kubernetes vs. Other Kubernetes Deployment Tools
| Feature / Tool | Amazon EKS | kOps (Kubernetes Operations) | kubectl | Terraform |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Primary Purpose | Managed Kubernetes service by AWS | Kubernetes cluster creation & lifecycle management | CLI for interacting with Kubernetes clusters | General Infrastructure as Code (IaC) tool |
| Management | Fully managed by AWS | Self-managed | N/A (works with existing clusters) | User-managed via IaC |
| Ease of Use | Simplified setup & maintenance | Requires manual setup & admin effort | Simple once cluster exists | Requires setup & config knowledge |
| Customization | Limited customization options | Highly customizable | Limited to cluster resource operations | Highly customizable across providers |
| Scope | Runs & manages Kubernetes clusters | Full cluster lifecycle (setup, scaling, upgrade, delete) | Day-to-day resource management (pods, services, deployments) | Infrastructure provisioning across clouds |
| Integration | Seamless with AWS services | Works with AWS, GCP (limited) | Works with any Kubernetes cluster | Multi-cloud (AWS, GCP, Azure, etc.) |
Conclusion: Is Kops Still Relevant in 2026?
kOps is a powerful tool for deploying and managing Kubernetes clusters, giving you more control and customization than fully managed services like Amazon EKS. While kubectl is used for daily resource management and Terraform provides wider infrastructure automation, kOps is specifically designed for the Kubernetes lifecycle—creating clusters, scaling, and upgrading them.
If you want a cost-effective, customizable, and production-ready Kubernetes solution on AWS or other supported platforms, kOps is an excellent option. However, if you prefer simplicity with less administrative work, Amazon EKS or Terraform setups might be more suitable.
FAQs
1. What is kOps Kubernetes?
kOps (Kubernetes Operations) is a tool for creating, configuring, and managing Kubernetes clusters, primarily on AWS, but it also works with other environments. It acts as a “cluster manager” for Kubernetes.
2. Is kOps better than Amazon EKS?
kOps offers high customization and cost-effectiveness but needs more manual setup and upkeep. In contrast, EKS is fully managed by AWS, making it simpler but often pricier.
3. Can I use kOps with cloud providers other than AWS?
Yes. Although AWS is the main supported provider, kOps has limited support for GCP and other environments.
4. What’s the difference between kubectl and kOps?
kubectl is a command-line tool for managing resources in a Kubernetes cluster, such as pods and services. kOps, however, oversees the entire lifecycle of the cluster creation, upgrades, and scaling.
5. Should I use Terraform or kOps Kubernetes?
If your main focus is on managing Kubernetes clusters, kOps Kubernetes AWS is more specialized. Terraform is preferable if you want to manage a wider range of infrastructure across multiple providers, along with Kubernetes.