A command-line interface is powerful, but managing containers, volumes, networks, and logs manually can slow down even experienced sysadmins. LazyDocker eliminates that friction.
Docker is now an important tool for developers, DevOps engineers, and sysadmins who are distributing their applications at scale. The more advanced a container infrastructure is, the more work it is to be able to look at a log, debug a service, or monitor running containers. This intricacy results in excessive configuration, overlapping directives, and downtime.
LazyDocker is a terminal UI for Docker, also providing a clean and distraction-free environment to run containers, volumes, images, and Compose services. Rather than remembering a long series of commands, you can inspect and control everything from one interface.
In this article, you will learn both how to install LazyDocker on macOS, Linux (Ubuntu in particular), how it can make your life easier while working, and what the alternatives are. You’ll also discover where CyberPanel fits in a modern container-based world and when it can pair with LazyDocker.
What Is LazyDocker?
LazyDocker is a simple terminal UI for both Docker and Docker Compose. It’s built on top of Docker and Docker Compose, but doesn’t abstract any features away (it provides its own handy defaults)‚ just makes the world easier to operate in.
Key Features
- Live container logs
- Real-time CPU & memory stats
- Container lifecycle control (restart, stop, kill)
- Service management for Docker Compose
- Perfect to see all your volumes, networks, and images of the swarm
- Keyboard-first navigation
- Zero configuration required
For those developing in microservices or a multi-container development setup, this is time savings over toggling back and forth between commands.
Get exclusive access to all things tech-savvy, and be the first to receive
the latest updates directly in your inbox.
How LazyDocker Works
LazyDocker interacts with your local Docker daemon via the regular Docker API. It provides grouped sections for:
- Containers
- Volumes
- Images
- Docker Compose services
- Networks
At the bottom of each section, you can see resources, logs, actions, and metrics.
You will still need Docker and Docker Compose installed; LazyDocker just enables an easier way to interact with them.
Install LazyDocker on macOS
The easiest method is Homebrew. If you already have Homebrew installed, the process takes a few seconds.
Command
brew install lazydocker
After installation:
lazydocker
The interface will open instantly. macOS users benefit from fast navigation and a cleaner development workflow because LazyDocker integrates smoothly with local Docker Desktop installations.
How to Install LazyDocker on Linux
LazyDocker runs on all major Linux distributions. The universal installation approach uses the official script provided by the developer.
Universal Linux Installation
curl https://raw.githubusercontent.com/jesseduffield/lazydocker/master/scripts/install_update_linux.sh | bash
Once the script finishes:
lazydocker
This works on Arch, Debian-based distros, Fedora, Pop!_OS, and more.
How to Install LazyDocker Ubuntu
Ubuntu users often prefer apt-based or script-based installation. LazyDocker doesn’t exist in the Ubuntu repositories, so the script remains the recommended method.

Command for Ubuntu
curl https://raw.githubusercontent.com/jesseduffield/lazydocker/master/scripts/install_update_linux.sh | bash
Alternatively, build from source using Go (for developers who want full control):
git clone https://github.com/jesseduffield/lazydocker.git
cd lazydocker
go install
LazyDocker then becomes available globally on your shell.
Why LazyDocker Matters for DevOps
LazyDocker is ideal for:
- Local development
- Docker-based servers
- Monitoring Docker Compose stacks
- Debugging APIs and microservices
- Inspecting multi-container applications
It is also a pain that, on the crash of misbehaving containers, you must go read logs and metrics in separate terminal windows. LazyDocker consolidates everything in one place, leading to quicker reaction time.
LazyDocker Alternatives
As lightweight and efficient as LazyDocker is, it’s not the only game in town. On your environment/preferences of choice, these are maybe alternatives:
Portainer
Complete browser-based management of Docker.
Best for: teammates, remote servers, Mac users with a GUI.
Dockly
A Docker manager from the terminal that just works. (port of LazyDocker)
Ideal for: Developers who are TUI-style workflow fans.
Rancher Desktop
A large GUI tool for Kubernetes and container development.
Best for: K8s-centric workflows.
Docker Desktop Dashboard
Now bundled with Docker Desktop for Windows and macOS.
Best for: Beginners, local development.
And each of those alternatives has more features than LazyDocker, but not as simple and elegant as LazyDocker is.
Best Practices for Using LazyDocker
1. Keep Your Docker Environment Clean
Large images and unused volumes slow down LazyDocker. Use:
docker system prune
2. Avoid Running It as Root Unless Necessary
3. Keep Docker Compose Files Organized
Well-structured compose files help LazyDocker display services correctly.
4. Install Latest Docker Engine
LazyDocker relies on Docker APIs, outdated versions cause unexpected behavior.
Common Problems and Fixes
LazyDocker not launching
Check path:
which lazydocker
Docker daemon not running
Start Docker:
sudo systemctl start docker
Keyboard navigation not working
Terminal emulator must support ncurses.
Slow performance
Reduce number of containers or clean unused resources.
Where CyberPanel Fits In?
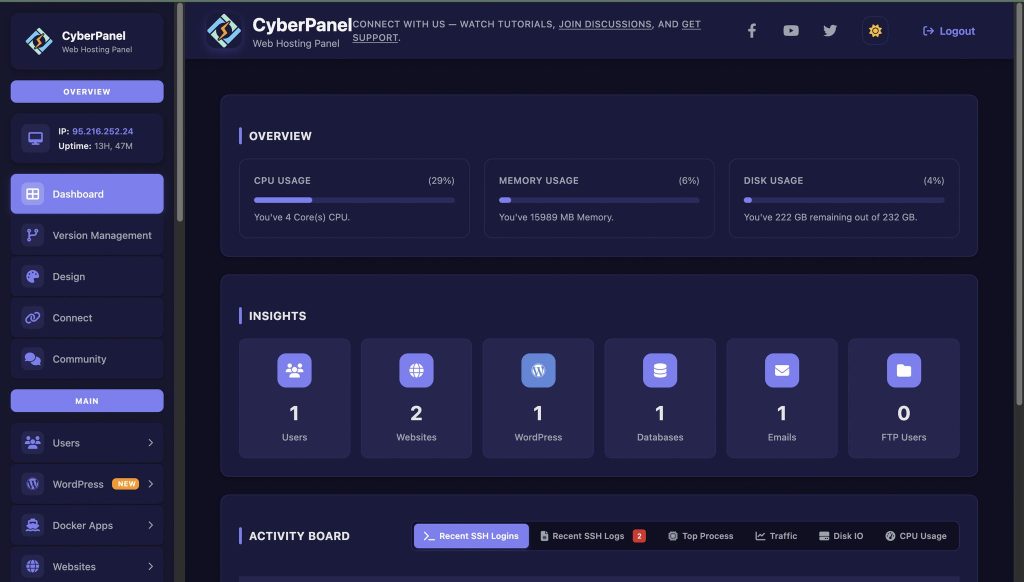
CyberPanel is responsible for hosting websites, DNS management, email configuration, SSL creation, and all about server resources. This web hosting control panel is not a container manager like LazyDocker, but it goes hand in hand with real-world infrastructure.
Here’s how:
App Hosting + Container Workflow
You could write and containerize your app with LazyDocker on your machine, and then deploy it at the end of the day to a VPS managed by CyberPanel.
LazyDocker provides immediate logs for containers.
CyberPanel provides logs for:
- Web server (OpenLiteSpeed)
- Databases
- DNS
This enables you to work with your containerized app and your hosted environment without switching tools.
Reverse Proxy / Deployment
Applications are typically running inside the containers on additional ports. CyberPanel easily allows you to create domains, SSL, as well as a reverse proxy pointing towards your containerised service.
Backup & Performance
LazyDocker is not for backups, yet CyberPanel manages full backups of websites, databases, and files.
Each of the above works together to create a full workflow:
Developed locally in Docker → test on a container → deploy to a server based on CyberPanel.
Final Thoughts!
LazyDocker is a simpler terminal UI for Docker, and it is lazy! Its dashboard in the terminal is fast and clean, which simplifies debugging of a container or a monitoring service a lot. Whether you are programming microservices, keeping oversight in complex networks, or even just testing your software locally, a Lazydocker enhances your workflow without interruption , the self-empowerment of Docker itself.
Try LazyDocker now and see how simple Docker management can become. Enhance your workflow and get full control today.
People Also Ask
Does LazyDocker support Docker Compose?
Yes. LazyDocker detects Docker Compose projects and shows their containers, logs, and statuses inside the interface.
Can LazyDocker run inside a remote server?
Yes. You can run LazyDocker on any remote Linux server through SSH as long as Docker is installed.
Will LazyDocker slow down my system?
No. It is lightweight and only uses minimal resources since it runs inside a terminal window.



